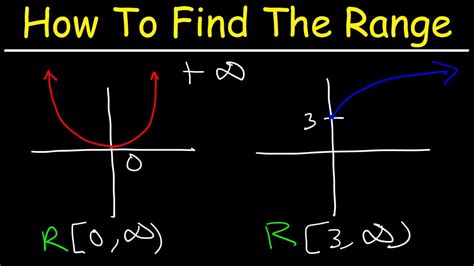
Understanding the range of a function is a crucial aspect of mathematical analysis, as it helps in determining the set of all possible output values a function can produce for the given input values. The range of a function is essentially the set of all possible y-values that the function can generate. Finding the range of a function can be straightforward for simple functions but may become complex for more intricate ones. In this article, we will explore how to find the range of a function easily, using various methods and techniques tailored to different types of functions.
Key Points
- Determining the domain of a function is crucial before finding its range.
- For linear functions, the range can be found by analyzing the slope and y-intercept.
- For quadratic functions, the vertex form helps in identifying the range.
- Understanding the behavior of the function as x approaches positive or negative infinity is vital for finding the range.
- Graphical representation can provide a visual insight into the range of a function.
Understanding the Basics: Domain and Range
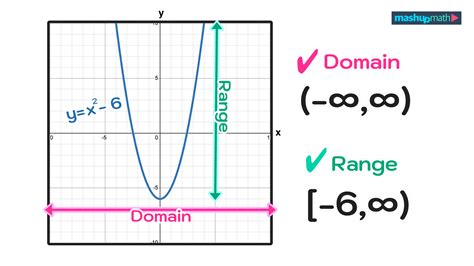
Before diving into finding the range of a function, it’s essential to understand the concept of the domain. The domain of a function is the set of all input values (x) for which the function is defined. The range, on the other hand, is the set of all output values (y) that the function can produce. For a function f(x), the domain is the set of x-values, and the range is the set of f(x) values.
Linear Functions
Linear functions, of the form f(x) = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept, have a range that can be easily determined. If the slope (m) is not zero, the function has a range of all real numbers, unless there are restrictions on the domain. For example, the function f(x) = 2x + 3 has a range of all real numbers because it can produce any real value of y. However, if the domain is restricted, the range will also be restricted accordingly.
| Function Type | Range Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Linear (m ≠ 0) | All real numbers, unless domain is restricted |
| Constant | Single value, equal to the constant |
| Quadratic | Depends on the vertex and direction of opening |
Quadratic Functions

Quadratic functions, of the form f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, have a range that depends on the vertex of the parabola and its direction of opening. If a > 0, the parabola opens upwards, and the range is all real numbers greater than or equal to the y-coordinate of the vertex. If a < 0, the parabola opens downwards, and the range is all real numbers less than or equal to the y-coordinate of the vertex. For instance, the function f(x) = x^2 has a range of [0, ∞) because it opens upwards and its vertex is at (0,0).
Other Types of Functions
For polynomial functions of degree greater than 2, rational functions, and trigonometric functions, finding the range can be more complex. It often involves analyzing the behavior of the function as x approaches positive or negative infinity, identifying any turning points or asymptotes, and considering the domain restrictions. Graphical representation can also provide valuable insights into the range of these functions.
Graphical Approach
A graphical approach can be particularly useful for visualizing the range of a function. By plotting the function on a coordinate plane, one can easily identify the set of y-values that the function achieves. This method is especially helpful for functions that are difficult to analyze algebraically. Moreover, graphing tools and software can facilitate the process, providing an accurate and quick way to determine the range.
Practical Applications
Understanding the range of a function has numerous practical applications across various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and computer science. For instance, in physics, the range of a function might represent the possible velocities of an object under certain conditions. In economics, the range of a function could indicate the possible prices of a commodity based on supply and demand. Being able to find and interpret the range of functions is thus a fundamental skill in these disciplines.
How do I find the range of a function that is defined by a formula?
+To find the range of a function defined by a formula, first identify the type of function (linear, quadratic, polynomial, etc.). Then, analyze its behavior, including any restrictions on the domain, and consider its graphical representation if necessary.
What is the difference between the domain and the range of a function?
+The domain of a function is the set of all input values (x) for which the function is defined, whereas the range is the set of all output values (y) that the function can produce.
Can the range of a function be restricted by its domain?
+Yes, restrictions on the domain of a function can directly affect its range. For example, if the domain is limited to positive numbers, the range will only include values that the function produces for positive inputs.
In conclusion, finding the range of a function is a critical aspect of function analysis, with applications across various disciplines. By understanding the type of function, its behavior, and any domain restrictions, one can determine its range. Whether through algebraic analysis, graphical representation, or a combination of both, identifying the range of a function provides valuable insights into its properties and potential applications.