The concept of phase shift is fundamental in various fields, including physics, engineering, and signal processing. It refers to the lateral shift of a wave or a signal, which can be crucial in understanding and analyzing wave behavior, interference patterns, and signal characteristics. Finding the phase shift can be approached in several ways, depending on the context and the specific characteristics of the wave or signal in question. Here, we will explore five methods to determine phase shift, each with its own set of applications and requirements.
Understanding Phase Shift
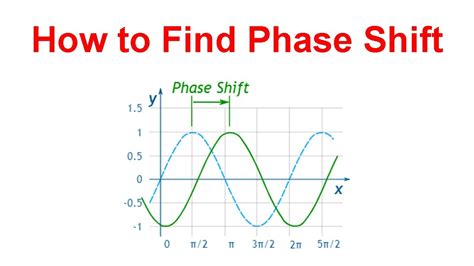
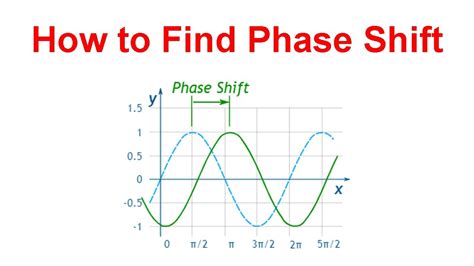
Before diving into the methods of finding phase shift, it’s essential to understand what phase shift represents. Phase shift is a measure of how much a wave’s phase has changed, typically measured in radians or degrees. This change can occur due to various factors, such as the wave passing through a different medium, reflection off a surface, or the presence of a phase-shifting device.
Method 1: Analytical Solution for Simple Harmonic Motion
In the context of simple harmonic motion (SHM), the phase shift can be found using the equation of motion. For a mass-spring system, the equation is (x(t) = A\sin(\omega t + \phi)), where (A) is the amplitude, (\omega) is the angular frequency, and (\phi) is the phase angle or phase shift. The phase shift (\phi) can be determined if the initial conditions are known. For example, if at (t = 0), (x(0) = x_0), then (\phi = \sin^{-1}\left(\frac{x_0}{A}\right)). This method requires a good understanding of the system’s dynamics and initial conditions.
Method 2: Graphical Method for Waveforms
A graphical method can be employed when dealing with waveforms, such as sinusoidal signals. By plotting the waveform and identifying the point where the wave crosses the time axis (or another reference point), one can measure the phase shift. This method involves comparing the phase-shifted waveform with a reference waveform. The horizontal distance between corresponding points on the two waveforms represents the phase shift. This approach is visual and intuitive but requires precise waveform measurements.
Method 3: Mathematical Modeling for Complex Systems
In more complex systems, where analytical solutions are not straightforward, mathematical modeling can be used to find phase shift. This involves setting up differential equations that describe the system’s behavior and solving them using numerical methods or approximation techniques. For instance, in electrical engineering, the phase shift in a circuit can be found by analyzing the circuit’s transfer function, which relates the output voltage to the input voltage in the frequency domain. The phase of the transfer function at a given frequency gives the phase shift of the circuit at that frequency.
Method 4: Experimental Measurement Techniques
Experimental methods involve directly measuring the phase shift using instruments such as oscilloscopes, phase meters, or lock-in amplifiers. For example, an oscilloscope can display two waveforms on the same screen, allowing for the direct measurement of phase shift by comparing the timing of features (like peaks or zeros) between the two signals. This approach is particularly useful in situations where theoretical modeling is complex or impractical. However, it requires access to appropriate measurement equipment and an understanding of experimental techniques.
Method 5: Computational Tools and Software
With the advent of powerful computational tools and software, finding phase shift can also be achieved through simulation and numerical analysis. Programs like MATLAB, Python libraries (e.g., NumPy, SciPy), or specialized software for signal processing can be used to generate waveforms, apply phase shifts, and measure the resulting phase difference. These tools are especially useful for analyzing complex waveforms or systems that are difficult to model analytically. They also offer the flexibility to simulate various scenarios and conditions, which can be invaluable in design and optimization tasks.
Key Points
- Phase shift is a critical parameter in understanding wave behavior and signal processing.
- Methods for finding phase shift include analytical solutions, graphical methods, mathematical modeling, experimental measurement, and computational simulations.
- The choice of method depends on the system's complexity, the nature of the wave or signal, and the availability of resources and equipment.
- Understanding phase shift is essential in fields like physics, engineering, and signal processing for applications ranging from filter design to interference analysis.
- Each method has its advantages and limitations, and selecting the appropriate method is crucial for accurate phase shift determination.
In conclusion, determining phase shift is a multifaceted problem that can be approached from various angles, each with its unique set of tools and techniques. Whether through analytical modeling, graphical analysis, mathematical simulation, experimental measurement, or computational tools, the ability to accurately find phase shift is essential for a deep understanding of wave phenomena and signal characteristics. By mastering these methods, professionals and researchers can better analyze, design, and optimize systems across a wide range of disciplines.
What is the significance of phase shift in signal processing?
+Phase shift is crucial in signal processing as it affects the timing and synchronization of signals, which is vital for applications like filter design, modulation analysis, and signal reconstruction.
How does phase shift relate to wave interference?
+Phase shift plays a key role in wave interference, as the relative phase between waves determines whether they interfere constructively or destructively. Understanding phase shift is essential for predicting and analyzing interference patterns.
What are some common challenges in measuring phase shift experimentally?
+Common challenges include ensuring the accuracy and synchronization of measurement instruments, minimizing noise and interference, and accounting for the effects of the measurement setup on the system being measured.