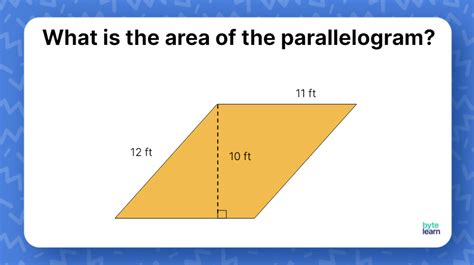
The area of a parallelogram is a fundamental concept in geometry, and it's essential to understand the formula and the underlying principles to calculate it accurately. In this article, we will delve into the world of parallelograms, exploring their properties, and providing a step-by-step guide on how to find their area.
Key Points
- The area of a parallelogram is calculated using the formula: Area = base × height
- The base and height of a parallelogram are perpendicular to each other
- The area of a parallelogram can also be calculated using the formula: Area = vector1 × vector2
- Understanding the properties of parallelograms, such as opposite sides being equal and parallel, is crucial for calculating their area
- Real-world applications of parallelograms, such as in architecture and engineering, require accurate calculations of their area
Understanding Parallelograms
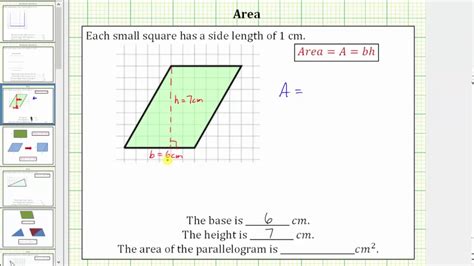
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are equal and parallel. This unique property makes it an essential shape in geometry, with numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. To calculate the area of a parallelogram, we need to understand its properties and the relationship between its base and height.
Properties of Parallelograms
Parallelograms have several distinct properties that set them apart from other quadrilaterals. These properties include:
- Opposite sides are equal and parallel
- Opposite angles are equal
- The diagonals bisect each other
Understanding these properties is crucial for calculating the area of a parallelogram, as they provide the foundation for the formulas and techniques used.
Calculating the Area of a Parallelogram
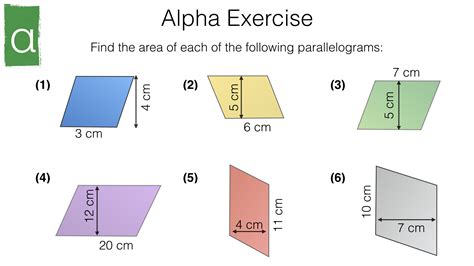
The area of a parallelogram can be calculated using two primary methods: the base × height method and the vector method. Both methods are effective, but the choice of method depends on the information available and the specific requirements of the problem.
Base × Height Method
The base × height method is the most common technique for calculating the area of a parallelogram. The formula is straightforward: Area = base × height. This method requires knowledge of the base and height of the parallelogram, which can be obtained using various techniques, such as measuring the sides or using trigonometry.
| Base (b) | Height (h) | Area |
|---|---|---|
| 5 cm | 3 cm | 15 cm² |
| 10 cm | 4 cm | 40 cm² |
| 7 cm | 2 cm | 14 cm² |

Vector Method
The vector method is an alternative technique for calculating the area of a parallelogram. This method involves using vectors to represent the sides of the parallelogram and then calculating the cross product of the vectors. The formula is: Area = |vector1 × vector2|.
Real-World Applications of Parallelograms
Parallelograms have numerous real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and design. Understanding the properties and area of parallelograms is crucial for these applications, as it enables professionals to create accurate designs and calculate structural loads.
Architecture
In architecture, parallelograms are used to design buildings and structures that require stability and balance. The area of a parallelogram is essential for calculating the floor space and structural loads of a building.
Engineering
In engineering, parallelograms are used to design bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure projects. The area of a parallelogram is critical for calculating the structural loads and stresses on these structures.
What is the formula for calculating the area of a parallelogram?
+The formula for calculating the area of a parallelogram is: Area = base × height or Area = |vector1 × vector2|.
What are the properties of a parallelogram?
+A parallelogram has several distinct properties, including opposite sides that are equal and parallel, opposite angles that are equal, and diagonals that bisect each other.
What are some real-world applications of parallelograms?
+Parallelograms have numerous real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and design. They are used to design buildings, bridges, tunnels, and other infrastructure projects that require stability and balance.
In conclusion, calculating the area of a parallelogram is a fundamental concept in geometry, and it’s essential to understand the formula and the underlying principles to calculate it accurately. By using the base × height method or the vector method, professionals can calculate the area of a parallelogram with precision and accuracy, enabling them to create accurate designs and calculate structural loads for various applications.