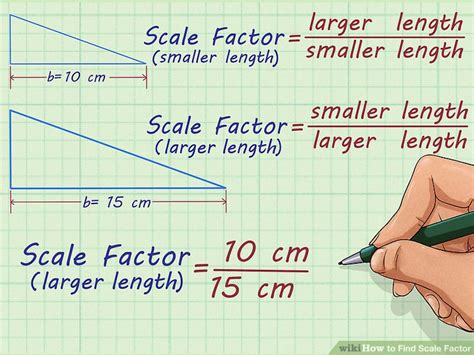
The concept of scale factor is a fundamental principle in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, and architecture. It refers to the ratio of the size of an object or a representation to its actual size. Understanding scale factor is crucial for accurate measurements, designs, and constructions. In this article, we will explore five ways scale factor is applied in different contexts, highlighting its importance and versatility.
Key Points
- Scale factor is used in geometry to describe the relationship between similar figures.
- In engineering, scale factor is crucial for designing and constructing models and prototypes.
- Architects rely on scale factor to create detailed drawings and models of buildings and structures.
- Scale factor is also used in computer graphics and video game development to create realistic models and environments.
- In data analysis, scale factor is used to normalize data and compare different sets of data.
Geometric Applications of Scale Factor
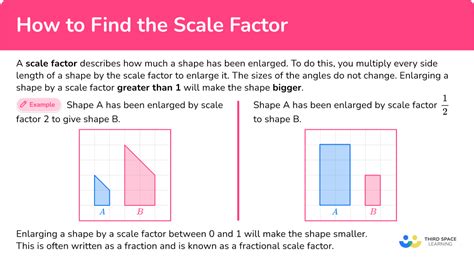
In geometry, scale factor is used to describe the relationship between similar figures. When two figures are similar, their corresponding sides are in proportion. The scale factor is the ratio of the lengths of the corresponding sides. For example, if two similar triangles have side lengths of 3 cm and 6 cm, the scale factor is 2:1 or 2. This means that the second triangle is twice as large as the first triangle. Understanding scale factor is essential for solving problems involving similar figures, such as finding the area or perimeter of a figure.
Calculating Scale Factor
To calculate the scale factor, you need to find the ratio of the corresponding sides of the two figures. For example, if you have two similar rectangles with side lengths of 4 cm and 6 cm, and 8 cm and 12 cm, you can calculate the scale factor as follows:
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Scale Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 4 cm | 8 cm | 2:1 |
| 6 cm | 12 cm | 2:1 |
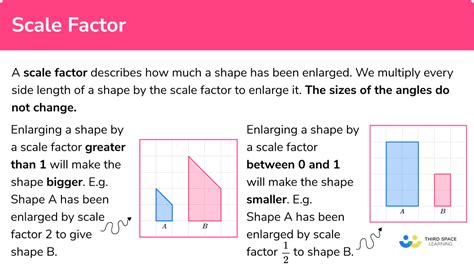
In this example, the scale factor is 2:1, which means that the second rectangle is twice as large as the first rectangle.
Engineering Applications of Scale Factor

In engineering, scale factor is crucial for designing and constructing models and prototypes. Engineers use scale factor to create detailed drawings and models of structures, such as bridges, buildings, and machines. The scale factor is used to ensure that the model is accurate and proportional to the actual structure. For example, if an engineer is designing a bridge, they may create a model with a scale factor of 1:100, which means that the model is 1/100th the size of the actual bridge.
Prototype Development
Scale factor is also used in prototype development to test and refine designs. By creating a prototype with a smaller scale factor, engineers can test the design and make adjustments before constructing the actual structure. This approach saves time, money, and resources, and ensures that the final product is accurate and functional.
Architectural Applications of Scale Factor
Architects rely on scale factor to create detailed drawings and models of buildings and structures. The scale factor is used to ensure that the drawings and models are accurate and proportional to the actual building. For example, an architect may create a drawing with a scale factor of 1:50, which means that the drawing is 1/50th the size of the actual building.
Building Design
Scale factor is also used in building design to create detailed models of buildings and structures. By creating a model with a smaller scale factor, architects can visualize the design and make adjustments before constructing the actual building. This approach ensures that the final product is accurate, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
Computer Graphics and Video Game Development
Scale factor is also used in computer graphics and video game development to create realistic models and environments. By using a scale factor, developers can create models that are proportional to the actual objects, ensuring that the game or simulation is realistic and engaging.
3D Modeling
In 3D modeling, scale factor is used to create detailed models of objects and environments. By using a scale factor, developers can ensure that the models are accurate and proportional to the actual objects, creating a realistic and immersive experience for the user.
Data Analysis Applications of Scale Factor
In data analysis, scale factor is used to normalize data and compare different sets of data. By using a scale factor, analysts can ensure that the data is proportional and comparable, allowing for accurate analysis and interpretation.
Data Normalization
Data normalization is the process of scaling data to a common range, usually between 0 and 1. This is done to prevent features with large ranges from dominating the model, and to improve the accuracy of the analysis. By using a scale factor, analysts can normalize the data and compare different sets of data, ensuring that the analysis is accurate and reliable.
What is the purpose of scale factor in geometry?
+The purpose of scale factor in geometry is to describe the relationship between similar figures, allowing for the calculation of area, perimeter, and other properties.
How is scale factor used in engineering?
+Scale factor is used in engineering to create detailed drawings and models of structures, ensuring that the model is accurate and proportional to the actual structure.
What is the importance of scale factor in data analysis?
+The importance of scale factor in data analysis is to normalize data and compare different sets of data, ensuring that the analysis is accurate and reliable.
In conclusion, scale factor is a fundamental principle with a wide range of applications in various fields, including geometry, engineering, architecture, computer graphics, and data analysis. Understanding scale factor is crucial for accurate measurements, designs, and constructions, and its importance cannot be overstated. By applying scale factor, professionals can create detailed models, normalize data, and compare different sets of data, ensuring that the final product is accurate, functional, and reliable.