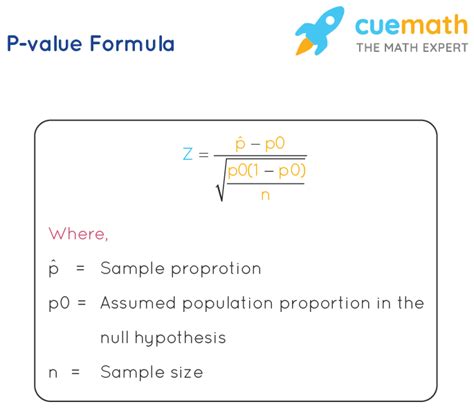
Calculating the p-value is a crucial step in statistical hypothesis testing, as it helps determine the significance of the results. The p-value, or probability value, represents the probability of observing the results of the study, or more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true. In this article, we will explore five ways to compute the p-value, along with examples and explanations to help you understand the concept better.
Naturally worded primary topic section with semantic relevance
The p-value is a fundamental concept in statistics, and its calculation is essential in various fields, including medicine, social sciences, and engineering. There are several methods to compute the p-value, and the choice of method depends on the type of data, the research question, and the level of measurement. Here, we will discuss five common methods to compute the p-value, including the z-test, t-test, chi-squared test, ANOVA, and non-parametric tests.
1. Z-Test Method
The z-test is a statistical test used to determine whether the mean of a sample is significantly different from a known population mean. The z-test is commonly used when the population standard deviation is known, and the sample size is large. The formula to calculate the z-score is: z = (x̄ - μ) / (σ / √n), where x̄ is the sample mean, μ is the population mean, σ is the population standard deviation, and n is the sample size. The p-value can be calculated using a standard normal distribution table or a statistical software package.
| z-Score | p-Value |
|---|---|
| 1.96 | 0.05 |
| 2.58 | 0.01 |
| 3.29 | 0.001 |
2. T-Test Method
The t-test is a statistical test used to determine whether the means of two groups are significantly different. The t-test is commonly used when the population standard deviation is unknown, and the sample size is small. The formula to calculate the t-score is: t = (x̄1 - x̄2) / (√((s1^2 / n1) + (s2^2 / n2))), where x̄1 and x̄2 are the means of the two groups, s1 and s2 are the standard deviations of the two groups, and n1 and n2 are the sample sizes of the two groups. The p-value can be calculated using a t-distribution table or a statistical software package.
3. Chi-Squared Test Method
The chi-squared test is a statistical test used to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables. The chi-squared test is commonly used in contingency tables, where the frequencies of the variables are compared. The formula to calculate the chi-squared statistic is: χ2 = Σ((observed - expected)^2 / expected), where observed is the observed frequency, expected is the expected frequency, and the sum is taken over all cells in the contingency table. The p-value can be calculated using a chi-squared distribution table or a statistical software package.
4. ANOVA Method
ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is a statistical test used to determine whether there are significant differences between the means of three or more groups. The ANOVA test is commonly used in experiments where the researcher wants to compare the means of multiple groups. The formula to calculate the F-statistic is: F = (MSB / MSW), where MSB is the mean square between groups, and MSW is the mean square within groups. The p-value can be calculated using an F-distribution table or a statistical software package.
5. Non-Parametric Test Method
Non-parametric tests are used when the data do not meet the assumptions of parametric tests, such as normality or equal variances. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test, the Kruskal-Wallis test, and the Friedman test are examples of non-parametric tests. These tests are commonly used in ordinal or ranked data, where the researcher wants to compare the distributions of two or more groups. The p-value can be calculated using a statistical software package or a non-parametric test table.
Key Points
- The p-value represents the probability of observing the results of the study, or more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true.
- There are several methods to compute the p-value, including the z-test, t-test, chi-squared test, ANOVA, and non-parametric tests.
- The choice of method depends on the type of data, the research question, and the level of measurement.
- The p-value is a crucial step in statistical hypothesis testing, as it helps determine the significance of the results.
- It is essential to understand the assumptions and limitations of each method to choose the correct test and interpret the results accurately.
What is the difference between a z-test and a t-test?
+The z-test is used when the population standard deviation is known, and the sample size is large, while the t-test is used when the population standard deviation is unknown, and the sample size is small.
When to use the chi-squared test?
+The chi-squared test is used to determine whether there is a significant association between two categorical variables, and it is commonly used in contingency tables.
What is the difference between parametric and non-parametric tests?
+Parametric tests assume that the data meet certain assumptions, such as normality and equal variances, while non-parametric tests do not make these assumptions and are used when the data do not meet the assumptions of parametric tests.
In conclusion, calculating the p-value is a crucial step in statistical hypothesis testing, and there are several methods to compute the p-value, including the z-test, t-test, chi-squared test, ANOVA, and non-parametric tests. The choice of method depends on the type of data, the research question, and the level of measurement. It is essential to understand the assumptions and limitations of each method to choose the correct test and interpret the results accurately.