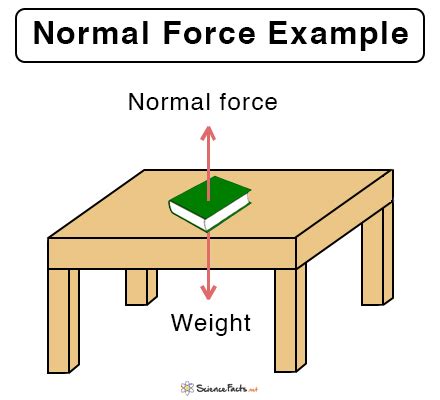
The normal force, also known as the perpendicular force, is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of objects in contact with surfaces. Calculating the normal force is essential in various fields, including engineering, mechanics, and physics. In this article, we will explore five ways to calculate the normal force, providing a comprehensive understanding of the concept and its applications.
Key Points
- The normal force is a vector quantity that acts perpendicular to the surface of contact.
- Calculating the normal force involves understanding the forces acting on an object, including gravity, friction, and external forces.
- The five methods for calculating the normal force include using the force balance equation, the acceleration equation, the force diagram, the energy principle, and the torque equation.
- Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the specific problem and the given information.
- Understanding the normal force is essential in designing and analyzing systems, such as bridges, buildings, and machines.
Method 1: Force Balance Equation
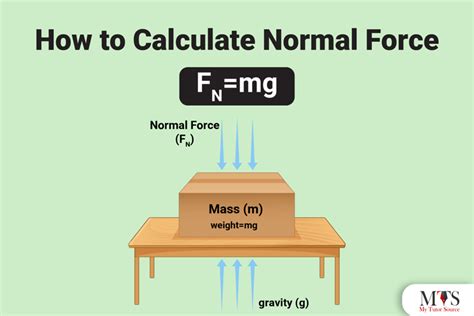
The force balance equation is a fundamental principle in physics that states that the net force acting on an object is equal to the sum of all the forces acting on it. To calculate the normal force using the force balance equation, we need to consider the forces acting on the object, including gravity, friction, and external forces. The equation can be written as:
FN + Fg + Ff + Fext = 0
where FN is the normal force, Fg is the force of gravity, Ff is the force of friction, and Fext is the external force.
Example: Calculating Normal Force using Force Balance Equation
Consider a block of mass 10 kg placed on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is 0.2. If a force of 50 N is applied to the block, calculate the normal force.
FN + Fg + Ff + Fext = 0
FN + (10 kg x 9.8 m/s2) + (0.2 x FN) + 50 N = 0
Solving for FN, we get:
FN = 98 N / (1 + 0.2) = 81.67 N
Method 2: Acceleration Equation
The acceleration equation is another fundamental principle in physics that relates the net force acting on an object to its acceleration. The equation can be written as:
Fnet = m x a
where Fnet is the net force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration.
To calculate the normal force using the acceleration equation, we need to know the acceleration of the object and the forces acting on it.
Example: Calculating Normal Force using Acceleration Equation
Consider a car of mass 1500 kg accelerating at a rate of 2 m/s2. If the coefficient of friction between the car and the road is 0.1, calculate the normal force.
Fnet = m x a
Fnet = 1500 kg x 2 m/s2 = 3000 N
The net force is the sum of the normal force and the force of friction:
Fnet = FN + Ff
Substituting the values, we get:
3000 N = FN + (0.1 x FN)
Solving for FN, we get:
FN = 3000 N / (1 + 0.1) = 2727.27 N
Method 3: Force Diagram
A force diagram is a graphical representation of the forces acting on an object. To calculate the normal force using a force diagram, we need to draw a diagram showing all the forces acting on the object, including gravity, friction, and external forces.
The normal force can be calculated by resolving the forces along the perpendicular direction.
Example: Calculating Normal Force using Force Diagram
Consider a ladder of length 5 m placed against a wall, making an angle of 60 degrees with the ground. If the mass of the ladder is 20 kg, calculate the normal force exerted by the wall on the ladder.
Draw a force diagram showing the forces acting on the ladder, including gravity and the normal force.
Resolve the forces along the perpendicular direction:
FN = Fg x sin(60 degrees)
FN = (20 kg x 9.8 m/s2) x sin(60 degrees)
FN = 169.82 N
Method 4: Energy Principle
The energy principle is a fundamental concept in physics that relates the energy of an object to its motion. To calculate the normal force using the energy principle, we need to consider the energy of the object and the forces acting on it.
The energy principle can be written as:
ΔE = W
where ΔE is the change in energy and W is the work done.
The work done can be calculated as:
W = F x d
where F is the force and d is the distance.
Example: Calculating Normal Force using Energy Principle
Consider a block of mass 10 kg moving at a velocity of 5 m/s. If the block is brought to rest by a force, calculate the normal force exerted by the force.
Calculate the initial kinetic energy of the block:
Ei = (1⁄2) x m x v2
Ei = (1⁄2) x 10 kg x (5 m/s)2 = 125 J
Calculate the final kinetic energy of the block:
Ef = 0 J
Calculate the change in energy:
ΔE = Ef - Ei = -125 J
Calculate the work done:
W = ΔE = -125 J
Calculate the force:
F = W / d
Assuming the distance is 1 m, we get:
F = -125 J / 1 m = -125 N
The normal force is the negative of the force:
FN = -F = 125 N
Method 5: Torque Equation
The torque equation is a fundamental principle in physics that relates the torque acting on an object to its rotational motion. To calculate the normal force using the torque equation, we need to consider the torque acting on the object and the forces acting on it.
The torque equation can be written as:
τ = r x F
where τ is the torque, r is the distance from the axis of rotation, and F is the force.
Example: Calculating Normal Force using Torque Equation
Consider a wheel of radius 0.5 m rotating at an angular velocity of 10 rad/s. If a force of 50 N is applied to the wheel, calculate the normal force exerted by the axle on the wheel.
Calculate the torque:
τ = r x F
τ = 0.5 m x 50 N = 25 Nm
Calculate the normal force:
FN = τ / r
FN = 25 Nm / 0.5 m = 50 N
What is the normal force, and why is it important?
+The normal force is a vector quantity that acts perpendicular to the surface of contact between two objects. It is essential in understanding the behavior of objects in contact with surfaces and is used in various fields, including engineering, mechanics, and physics.
How do I calculate the normal force using the force balance equation?
+To calculate the normal force using the force balance equation, you need to consider the forces acting on an object, including gravity, friction, and external forces. The equation can be written as: FN + Fg + Ff + Fext = 0.
What are the different methods for calculating the normal force?
+There are five methods for calculating the normal force: using the force balance equation, the acceleration equation, the force diagram, the energy principle, and the torque equation. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the specific problem and the given information.
In conclusion, calculating the normal force is a fundamental concept in physics that has various applications in engineering, mechanics, and physics. The five methods for calculating the normal force, including the force balance equation, the acceleration equation, the force diagram, the energy principle, and the torque equation, provide a comprehensive understanding of the concept and its applications. By understanding the normal force, we can design and analyze systems, such as bridges, buildings, and machines, and ensure their safety and efficiency.