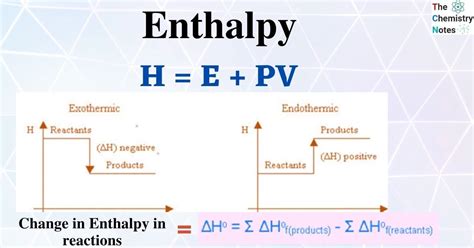
The concept of enthalpy is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics, representing the total energy of a system, including internal energy and the energy associated with the pressure and volume of a system. Calculating enthalpy easily and accurately is crucial for various applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering. To begin, it's essential to understand the formula for enthalpy, which is given by the equation H = U + pV, where H is the enthalpy, U is the internal energy, p is the pressure, and V is the volume of the system.
Understanding Enthalpy and Its Calculation
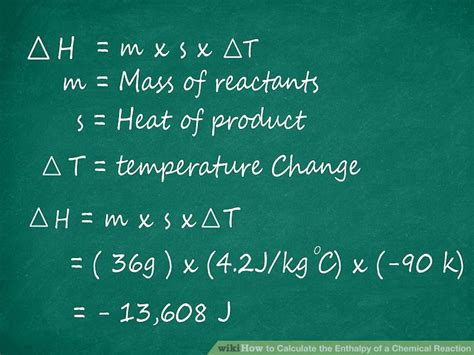
To calculate enthalpy easily, one must first determine the internal energy (U) of the system, which can be done by considering the temperature change and the specific heat capacity of the substances involved. The internal energy change (ΔU) can be calculated using the formula ΔU = mcΔT, where m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the temperature change. Once ΔU is known, the pressure (p) and volume (V) of the system must be determined to calculate the enthalpy change (ΔH) using the formula ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV).
Step-by-Step Guide to Easy Enthalpy Calculation
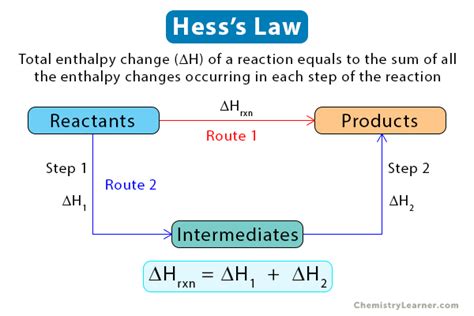
The process of calculating enthalpy can be simplified by following a step-by-step approach. First, identify the initial and final states of the system, including temperature, pressure, and volume. Next, calculate the internal energy change (ΔU) using the specific heat capacity and temperature change. Then, determine the change in the product of pressure and volume (Δ(pV)) and add it to ΔU to obtain the enthalpy change (ΔH). It’s also crucial to consider the conditions under which the process occurs, such as constant pressure or constant volume, as these conditions can significantly affect the calculation.
| Thermodynamic Property | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Energy Change (ΔU) | ΔU = mcΔT | Change in internal energy due to temperature change |
| Enthalpy Change (ΔH) | ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV) | Change in enthalpy, including internal energy and pV work |
| Specific Heat Capacity (c) | c = Q / (mΔT) | Amount of heat required to change the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree |
Applications of Enthalpy Calculation
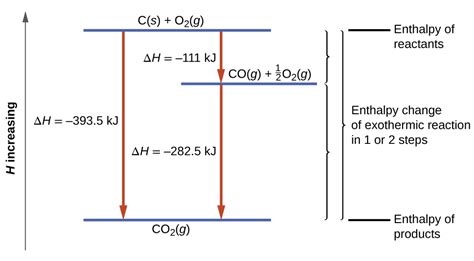
Calculating enthalpy easily and accurately has numerous applications across various fields. In chemistry, enthalpy changes are crucial for understanding chemical reactions, including combustion reactions, phase transitions, and the formation of solutions. In engineering, enthalpy calculations are used in the design of systems such as power plants, refrigeration units, and heating systems. Furthermore, in environmental science, understanding enthalpy changes can help in assessing the energy impacts of different processes and in developing more efficient and sustainable technologies.
Practical Considerations for Enthalpy Calculations
In practical scenarios, calculating enthalpy involves considering the specific conditions of the process. For reactions occurring at constant pressure, the enthalpy change (ΔH) can be directly related to the heat transferred (Q) between the system and its surroundings. However, for processes at constant volume, the internal energy change (ΔU) is equivalent to the heat transferred. Understanding these distinctions is vital for accurate enthalpy calculations and for applying the results effectively in real-world applications.
Key Points
- Enthalpy (H) is calculated using the formula H = U + pV, where U is the internal energy, p is the pressure, and V is the volume.
- The internal energy change (ΔU) can be calculated using the formula ΔU = mcΔT, where m is the mass, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the temperature change.
- Enthalpy change (ΔH) is given by ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV), incorporating both the internal energy change and the work done due to the change in pressure and volume.
- Consistent units are crucial for accurate calculations, with joules (J) for energy, pascals (Pa) for pressure, and cubic meters (m³) for volume.
- Enthalpy calculations have wide-ranging applications in chemistry, engineering, and environmental science, including the assessment of chemical reactions, system design, and environmental impact evaluations.
In conclusion, calculating enthalpy easily and accurately requires a thorough understanding of thermodynamic principles, attention to detail in calculations, and an appreciation for the practical applications of enthalpy in various fields. By following a systematic approach and considering the specific conditions of a process, individuals can master the calculation of enthalpy and apply this knowledge to solve complex problems and contribute to advancements in science and technology.
What is the primary difference between internal energy and enthalpy?
+Internal energy (U) refers to the total energy within a system, including kinetic energy, potential energy, and potential energy associated with the vibrations and rotations of atoms and molecules. Enthalpy (H), on the other hand, is a measure of the total energy of a system, including internal energy, plus the energy associated with the pressure and volume of a system, given by the equation H = U + pV.
How do I calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction at constant pressure?
+For a reaction at constant pressure, the enthalpy change (ΔH) can be calculated using the formula ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV). Since the pressure is constant, Δ(pV) simplifies to pΔV, where p is the constant pressure and ΔV is the change in volume. If the reaction involves gases, the ideal gas law (pV = nRT) can be used to relate the volume change to the number of moles of gas and the temperature change.
What are some common applications of enthalpy calculations?
+Enthalpy calculations have numerous applications in chemistry, engineering, and environmental science. These include understanding chemical reactions, designing power generation systems, assessing the energy efficiency of industrial processes, and evaluating the environmental impact of different technologies. By calculating enthalpy changes, scientists and engineers can predict the energy requirements and outputs of various processes, contributing to the development of more efficient and sustainable technologies.