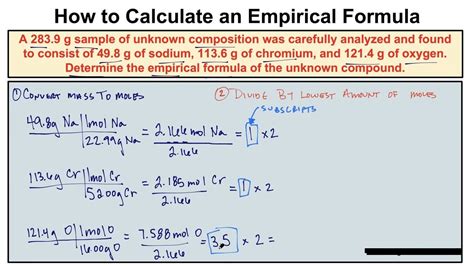
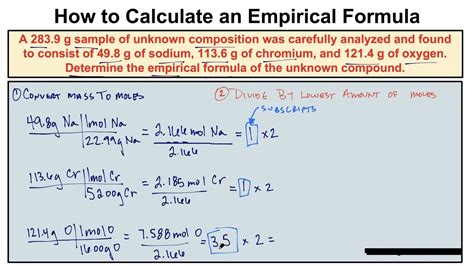
Calculating the empirical formula of a compound is a crucial step in understanding its composition and properties. The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound. To calculate it, one needs to know the percentage composition of the compound, which can be obtained through various analytical techniques such as combustion analysis or mass spectrometry. In this article, we will delve into the step-by-step process of calculating the empirical formula, exploring the underlying principles, and discussing the significance of empirical formulas in chemistry.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the calculation process, it’s essential to understand the basics. The empirical formula is different from the molecular formula, which represents the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule. The molecular formula is a multiple of the empirical formula. For instance, the empirical formula of benzene is CH, but its molecular formula is C6H6, indicating that the molecular formula is six times the empirical formula.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
The calculation of the empirical formula involves several steps. First, you need to convert the percentage composition into grams. Assume you have 100 grams of the compound to simplify calculations. Next, convert the mass of each element into moles using the formula: moles = mass/molar mass. Then, divide each mole value by the smallest number of moles to find the simplest ratio. If the ratios are not whole numbers, multiply them by a factor that will convert them into whole numbers. This factor is the same for all elements.
| Element | Percentage Composition | Molar Mass | Mass (in 100g) | Moles | Simplified Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 40% | 12.01 g/mol | 40g | 40/12.01 = 3.33 mol | 1 |
| Hydrogen (H) | 60% | 1.008 g/mol | 60g | 60/1.008 = 59.52 mol | 18 |

Key Considerations and Applications
The empirical formula is vital in various chemical applications, including the synthesis of compounds, understanding chemical reactions, and identifying unknown substances. It provides a foundation for calculating the molecular formula when the molar mass of the compound is known. The molecular formula can then be determined by multiplying the empirical formula by a factor that matches the molar mass of the compound.
Empirical Formula in Practice
In practice, chemists use empirical formulas to predict the properties of compounds, such as solubility, melting points, and reactivity. The empirical formula of a compound can also give clues about its structure. For instance, compounds with the same empirical formula but different molecular formulas can have different structures, a phenomenon known as isomerism.
Key Points
- The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
- Calculating the empirical formula involves converting percentage composition into grams, then into moles, and finally finding the simplest ratio.
- The empirical formula is crucial for understanding the composition and properties of compounds.
- It serves as a basis for determining the molecular formula when the molar mass is known.
- Empirical formulas have practical applications in synthesis, reaction understanding, and substance identification.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, calculating the empirical formula is a fundamental skill in chemistry that provides valuable insights into the composition and properties of compounds. As chemistry continues to evolve, understanding empirical formulas will remain essential for advancing our knowledge of chemical compounds and their applications. Whether in research, industry, or education, the empirical formula stands as a cornerstone of chemical analysis and synthesis.
What is the primary difference between an empirical formula and a molecular formula?
+The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound, while the molecular formula represents the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule, which can be a multiple of the empirical formula.
How do you calculate the empirical formula from the percentage composition of a compound?
+First, assume 100 grams of the compound and convert the percentage composition into grams. Then, convert the mass of each element into moles using the molar mass. Divide each mole value by the smallest number of moles to find the simplest ratio. If necessary, multiply the ratios by a factor to convert them into whole numbers.
What is the significance of the empirical formula in chemistry?
+The empirical formula is significant because it provides a basis for understanding the composition and properties of compounds. It is used in the synthesis of compounds, understanding chemical reactions, identifying unknown substances, and predicting properties such as solubility and reactivity.