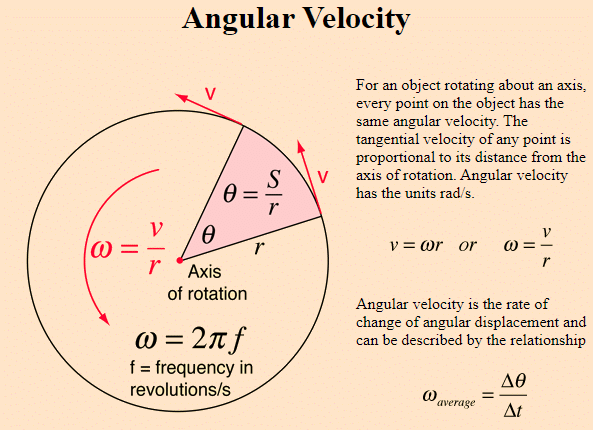
Angular velocity is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, describing the rate of change of an object's angular position with respect to time. It is a crucial parameter in understanding rotational motion and is widely used in various fields, including mechanics, robotics, and astronomy. Calculating angular velocity can be straightforward if you understand the underlying principles and formulas. In this article, we will delve into the world of angular velocity, exploring its definition, formulas, and practical applications, to provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to calculate it easily.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of angular velocity and its importance in rotational motion
- Learning the formula for calculating angular velocity: ω = Δθ / Δt
- Applying the formula to real-world scenarios, including uniform and non-uniform circular motion
- Utilizing the relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity: v = rω
- Exploring practical applications of angular velocity in mechanics, robotics, and astronomy
Definition and Formula of Angular Velocity
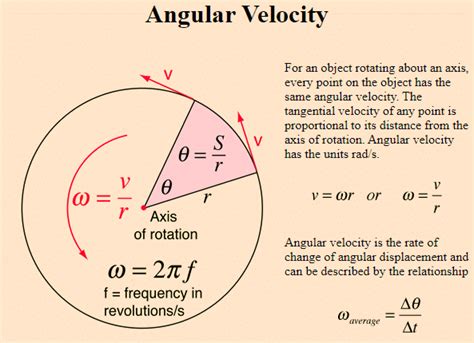
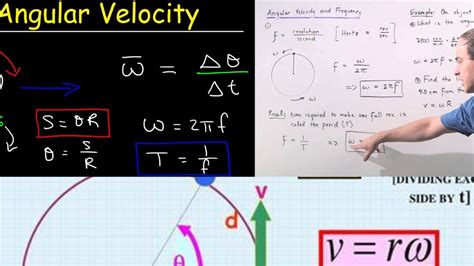
Angular velocity, denoted by the Greek letter omega (ω), is defined as the rate of change of an object’s angular position (θ) with respect to time (t). It is a measure of how fast an object rotates or revolves around a fixed axis. The formula for calculating angular velocity is given by: ω = Δθ / Δt, where Δθ is the change in angular position and Δt is the time over which this change occurs. This formula provides a direct and straightforward way to calculate angular velocity, making it a fundamental tool in understanding rotational motion.
Calculating Angular Velocity in Uniform Circular Motion
In uniform circular motion, the angular velocity is constant, and the object moves in a circular path with a constant speed. To calculate the angular velocity in this scenario, you can use the formula: ω = v / r, where v is the linear velocity and r is the radius of the circle. This formula highlights the relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity, demonstrating how they are interconnected in rotational motion. For example, if an object is moving in a circular path with a radius of 2 meters and a linear velocity of 4 meters per second, the angular velocity can be calculated as: ω = 4 m/s / 2 m = 2 rad/s.
| Scenario | Angular Velocity (ω) | Linear Velocity (v) | Radius (r) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uniform Circular Motion | 2 rad/s | 4 m/s | 2 m |
| Non-Uniform Circular Motion | Variable | Variable | Constant |
Practical Applications of Angular Velocity
Angular velocity has numerous practical applications in various fields, including mechanics, robotics, and astronomy. In mechanics, understanding angular velocity is crucial for designing and analyzing rotational systems, such as gears, motors, and turbines. In robotics, angular velocity is used to control the movement of robotic arms and wheels, enabling precise and efficient motion. In astronomy, angular velocity is used to study the rotation of celestial bodies, such as planets and stars, providing valuable insights into their composition and behavior.
Relationship Between Angular Velocity and Linear Velocity
The relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity is given by the formula: v = rω, where v is the linear velocity, r is the radius of the circular path, and ω is the angular velocity. This formula demonstrates how angular velocity and linear velocity are interconnected, highlighting the importance of understanding both concepts in rotational motion. For example, if an object is rotating with an angular velocity of 3 rad/s and has a radius of 1.5 meters, the linear velocity can be calculated as: v = 1.5 m * 3 rad/s = 4.5 m/s.
In conclusion, calculating angular velocity is a straightforward process that requires a basic understanding of the underlying principles and formulas. By applying the formula ω = Δθ / Δt and utilizing the relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity, you can easily calculate angular velocity in various scenarios, from uniform circular motion to non-uniform circular motion. Whether you are working in mechanics, robotics, or astronomy, understanding angular velocity is crucial for designing, analyzing, and optimizing rotational systems, making it a fundamental concept in modern science and engineering.
What is the formula for calculating angular velocity?
+The formula for calculating angular velocity is ω = Δθ / Δt, where Δθ is the change in angular position and Δt is the time over which this change occurs.
How is angular velocity related to linear velocity?
+The relationship between angular velocity and linear velocity is given by the formula: v = rω, where v is the linear velocity, r is the radius of the circular path, and ω is the angular velocity.
What are some practical applications of angular velocity?
+Angular velocity has numerous practical applications in various fields, including mechanics, robotics, and astronomy, such as designing and analyzing rotational systems, controlling robotic movement, and studying celestial body rotation.