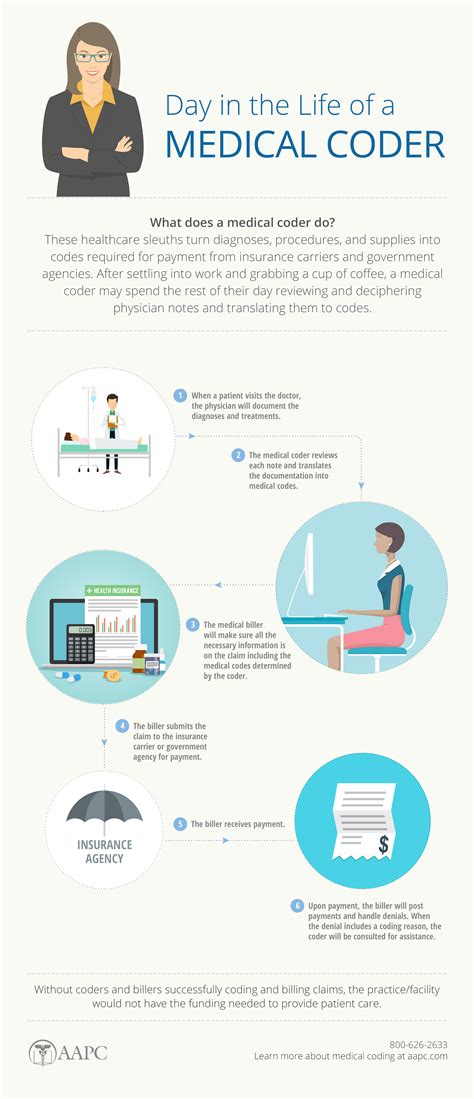
Becoming a medical coder is a rewarding career path that involves assigning codes to diagnoses and procedures in the healthcare industry. Medical coders play a crucial role in ensuring that healthcare providers receive accurate reimbursement for their services. The demand for skilled medical coders is on the rise, driven by the need for efficient and effective healthcare systems. In this article, we will explore the steps to become a medical coder, the skills required, and the career prospects in this field.
Key Points
- Earning a high school diploma or equivalent is the first step to becoming a medical coder
- Completing a medical coding program approved by the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) or the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) is essential
- Gaining practical experience through internships or volunteer work is vital for success in this field
- Obtaining certification as a Certified Professional Coder (CPC) or Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) can significantly enhance career prospects
- Staying up-to-date with industry developments and continuing education is crucial for medical coders
Education and Training
To become a medical coder, one needs to have a strong foundation in anatomy, physiology, and medical terminology. A high school diploma or equivalent is the minimum educational requirement. However, most employers prefer candidates with a post-secondary degree or certificate in medical coding. There are several options for medical coding programs, including associate’s degrees, diplomas, and certificates. These programs are usually offered by community colleges, vocational schools, and online institutions.
When choosing a medical coding program, it is essential to ensure that it is approved by a recognized accrediting agency, such as the Commission on Accreditation for Health Informatics and Information Management Education (CAHIIM) or the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC). These programs typically cover topics such as medical terminology, anatomy, coding systems, and healthcare laws and regulations.
Medical Coding Certification
Certification is a critical step in becoming a medical coder. The two main certification bodies for medical coders are the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC) and the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). The AAPC offers several certifications, including the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and the Certified Outpatient Coder (COC). AHIMA offers certifications such as the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS) and the Certified Coding Specialist - Physician-based (CCS-P).
To become certified, one needs to meet the eligibility requirements, which typically include completing a medical coding program and gaining a certain amount of work experience. The certification exams test the candidate's knowledge of coding systems, medical terminology, and healthcare regulations. Certification demonstrates expertise and commitment to the profession, and it can significantly enhance career prospects.
| Certification | Eligibility Requirements | Exam Format |
|---|---|---|
| CPC | Completion of a medical coding program and 2 years of work experience | 150 multiple-choice questions |
| CCS | Completion of a medical coding program and 1 year of work experience | 115 multiple-choice questions |
| COC | Completion of a medical coding program and 1 year of work experience | 100 multiple-choice questions |

Career Prospects and Salary

Medical coders are in high demand, and the job outlook is excellent. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment of medical records and health information technicians, including medical coders, is projected to grow 13% from 2020 to 2030, which is faster than the average for all occupations. Medical coders can work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and consulting firms.
The salary for medical coders varies depending on factors such as location, experience, and certification. According to the AAPC, the average annual salary for a CPC is around $54,000, while the average annual salary for a CCS is around $63,000. Experienced medical coders can earn salaries ranging from $70,000 to over $100,000 per year.
Skills Required
Medical coders need to have a range of skills, including:
- Analytical skills: Medical coders need to be able to analyze medical records and assign codes accurately.
- Attention to detail: Medical coders need to be detail-oriented and able to identify errors and inconsistencies in medical records.
- Communication skills: Medical coders need to be able to communicate effectively with healthcare providers and other stakeholders.
- Organizational skills: Medical coders need to be able to manage multiple tasks and prioritize assignments.
Conclusion
Becoming a medical coder requires a combination of education, training, and certification. Medical coders play a critical role in the healthcare industry, and the demand for skilled professionals is on the rise. By following the steps outlined in this article and staying up-to-date with industry developments, individuals can pursue a rewarding career in medical coding.
What is the average salary for a medical coder?
+The average annual salary for a medical coder varies depending on factors such as location, experience, and certification. According to the AAPC, the average annual salary for a CPC is around 54,000, while the average annual salary for a CCS is around 63,000.
How long does it take to become a medical coder?
+The time it takes to become a medical coder varies depending on the individual’s prior education and experience. Typically, it takes around 1-2 years to complete a medical coding program and gain certification.
What are the most common certifications for medical coders?
+The most common certifications for medical coders are the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) and the Certified Coding Specialist (CCS), which are offered by the AAPC and AHIMA, respectively.