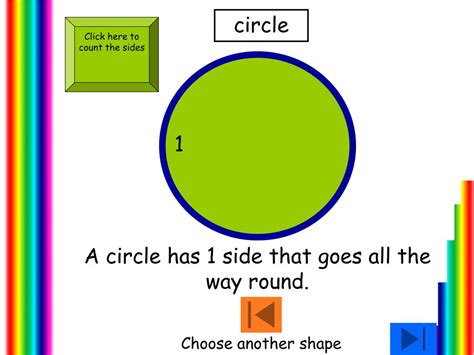
A circle, by definition, is a continuous curved shape that has no beginning or end. It is a two-dimensional figure that is perfectly round and has no corners or edges. One of the fundamental properties of a circle is that it has no sides. In fact, the concept of a side is more applicable to polygons, which are shapes with at least three sides. The number of sides of a polygon can vary greatly, from a triangle with three sides to a decagon with ten sides, and even to polygons with hundreds or thousands of sides. However, when it comes to a circle, the idea of sides does not apply in the same way.
Mathematically, a circle can be defined as the set of all points in a plane that are at a given distance (the radius) from a given point (the center). This definition does not involve the concept of sides but rather emphasizes the circular shape's symmetry and continuity. The absence of sides in a circle is what makes it such a unique and important geometric figure, with applications in various fields including architecture, engineering, and art.
Key Points
- A circle is a continuous curved shape with no beginning or end.
- The concept of sides does not apply to a circle in the same way it does to polygons.
- A circle is defined mathematically as the set of all points in a plane at a given distance from a given point.
- The absence of sides is a fundamental property that distinguishes a circle from other geometric shapes.
- Circles have numerous applications in various fields due to their unique properties.
Understanding Circles and Polygons
Circles and polygons are both important classes of geometric shapes, but they have distinct differences. Polygons are shapes with at least three sides, and the number of sides can vary greatly. Each side of a polygon is a straight line, and the angles where these sides meet can also vary. In contrast, a circle has no sides and no angles in the traditional sense used for polygons. Instead, a circle is characterized by its radius (the distance from the center to any point on the circle), its diameter (twice the radius), and its circumference (the distance around the circle).
Properties of Circles
Circles have several unique properties that make them interesting and useful in geometry and real-world applications. One key property is that all points on the circumference of a circle are equidistant from the center. This property is the basis for the definition of a circle. Another important property is the relationship between the radius, diameter, and circumference of a circle. The circumference of a circle is given by the formula C = 2πr, where C is the circumference, π (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159, and r is the radius of the circle.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Radius | The distance from the center to any point on the circle. |
| Diameter | Twice the radius, passing through the center of the circle. |
| Circumference | The distance around the circle, given by C = 2πr. |

Applications of Circles

Circles have numerous applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, art, and design. In architecture, circular shapes are used in the design of buildings, domes, and columns to provide strength and aesthetic appeal. In engineering, circles are crucial in the design of wheels, gears, and circular pipes, where the circular shape offers advantages in terms of stress distribution and material efficiency. In art and design, circles are used to create balanced and harmonious compositions, and they are a fundamental element in the creation of mandalas and other symbolic designs.
Mathematical and Scientific Applications
Mathematically, circles are used to model real-world phenomena, such as the orbits of planets and the trajectory of projectiles. The study of circles also leads to the development of important mathematical concepts, such as π (pi), which is the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. In science, the circular motion of objects is a key concept in understanding the laws of physics, including gravity and inertia. The application of circular motion can be seen in the rotation of the Earth, the orbits of satellites, and the movement of gears in machines.
What is the definition of a circle in geometry?
+A circle is defined as the set of all points in a plane that are at a given distance (the radius) from a given point (the center).
What are some common applications of circles in real-world scenarios?
+Circles have applications in architecture (design of buildings and domes), engineering (design of wheels and gears), art (creation of balanced compositions), and science (modeling of orbits and trajectories).
How does the property of a circle having no sides make it unique compared to other geometric shapes?
+The absence of sides in a circle distinguishes it from polygons, which have at least three sides. This property contributes to the circle’s symmetry, continuity, and unique applications in various fields.