Ladybugs, also known as lady beetles or ladybird beetles, are one of the most recognizable and beloved insects in the world. With their bright colors and distinctive spots, ladybugs have become a symbol of good luck and prosperity in many cultures. But beyond their charming appearance, ladybugs have a fascinating life cycle and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of ladybugs and explore seven interesting facts about their life cycle, behavior, and importance in our environment.
Ladybug Life Cycle and Development
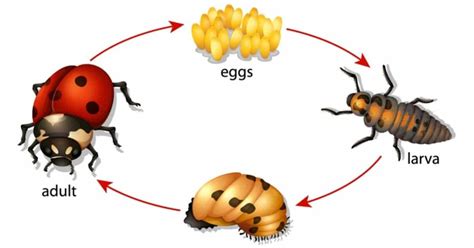
The life cycle of a ladybug consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Female ladybugs lay their eggs on the underside of leaves, usually near aphid colonies, which provide a food source for the developing larvae. The eggs hatch into larvae after about 3-5 days, and the larvae go through several instars, molting their skin as they grow. During this stage, the larvae are voracious eaters, consuming large quantities of aphids and other small insects. After about 10-14 days, the larvae enter the pupal stage, where they transform into adult ladybugs. The entire life cycle, from egg to adult, can take anywhere from 20 to 30 days, depending on factors such as food availability, temperature, and humidity.
Key Points
- Ladybugs have a four-stage life cycle: egg, larva, pupa, and adult
- Female ladybugs lay eggs near aphid colonies to provide food for larvae
- Larvae go through several instars, molting their skin as they grow
- The entire life cycle takes around 20-30 days to complete
- Ladybugs are important predators of aphids and other small insects
- They play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystem
Ladybug Diet and Foraging Behavior
Ladybugs are known for their voracious appetite for aphids, which are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on plant sap. A single ladybug can consume up to 60 aphids per hour, making them one of the most effective natural predators of these pests. In addition to aphids, ladybugs also feed on other small insects, such as scales, mealybugs, and spider mites. Ladybugs have a unique way of foraging for food, using their antennae to detect the presence of aphids and other prey. They can also secrete a foul-tasting fluid from their leg joints to deter predators, which helps to protect them from other insects and animals.
| Ladybug Species | Primary Food Source |
|---|---|
| Seven-spotted ladybug | Aphids, scales, mealybugs |
| Twice-stabbed ladybug | Aphids, spider mites, pollen |
| Convergent ladybug | Aphids, scales, mealybugs, nectar |
Ladybug Defense Mechanisms and Social Behavior

Ladybugs have several defense mechanisms to protect themselves from predators, including their bright colors, which serve as a warning signal to potential predators. They also have a unique way of releasing a foul-tasting fluid from their leg joints, which helps to deter predators. In addition to these defense mechanisms, ladybugs are also known for their social behavior, often gathering in large numbers on plants and other surfaces. This social behavior helps to increase their visibility to potential mates and also provides additional protection from predators.
Ladybug Migration and Overwintering Behavior
Some species of ladybugs are known to migrate to warmer climates during the winter months, while others overwinter in protected areas such as under bark, in leaf litter, or in other sheltered locations. During this time, ladybugs enter a state of dormancy, slowing down their metabolism and conserving energy. This allows them to survive the cold winter months and emerge in the spring when temperatures rise and food becomes more abundant.
What do ladybugs eat?
+Ladybugs are known for their voracious appetite for aphids, which are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on plant sap. They also feed on other small insects, such as scales, mealybugs, and spider mites.
How long does it take for a ladybug to complete its life cycle?
+The entire life cycle of a ladybug, from egg to adult, can take anywhere from 20 to 30 days, depending on factors such as food availability, temperature, and humidity.
What is the importance of ladybugs in our ecosystem?
+Ladybugs play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystem by controlling aphid populations and other pests, which helps to prevent damage to crops and other plants. They also contribute to pollination and are an important food source for other animals.
In conclusion, ladybugs are fascinating insects that play a vital role in our ecosystem. Their unique life cycle, behavior, and defense mechanisms make them one of the most interesting and important insects in the world. By understanding more about ladybugs and their role in our environment, we can appreciate the importance of these tiny creatures and take steps to protect and conserve them.
Meta description: “Discover the fascinating world of ladybugs and learn about their life cycle, behavior, and importance in our ecosystem. Get expert insights into these tiny creatures and their role in maintaining the balance of nature.” (147 characters)


