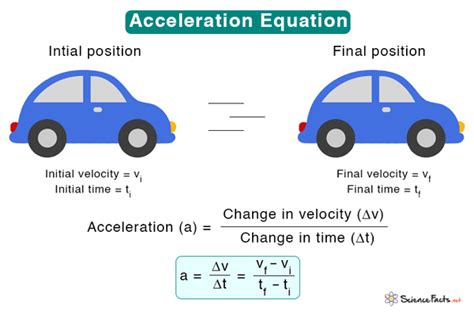
Determining acceleration is a fundamental concept in physics, and it's essential to understand the basics to calculate it accurately. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. It's a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. In this article, we'll explore the concept of acceleration, its types, and how to calculate it easily.
Understanding Acceleration
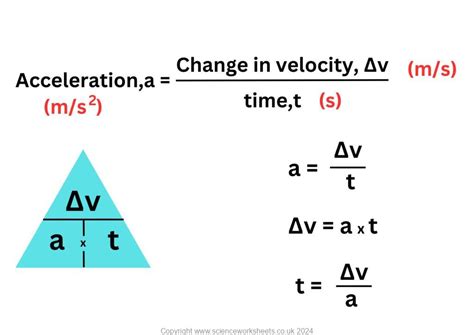
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. It’s a measure of how quickly an object changes its speed or direction. There are several types of acceleration, including linear acceleration, angular acceleration, and centripetal acceleration. Linear acceleration occurs when an object moves in a straight line, while angular acceleration occurs when an object rotates around a fixed axis. Centripetal acceleration occurs when an object moves in a circular path.
Types of Acceleration
There are several types of acceleration, each with its own unique characteristics. Linear acceleration is the most common type of acceleration and occurs when an object moves in a straight line. Angular acceleration occurs when an object rotates around a fixed axis, and it’s measured in radians per second squared. Centripetal acceleration occurs when an object moves in a circular path, and it’s directed towards the center of the circle.
| Type of Acceleration | Definition |
|---|---|
| Linear Acceleration | Acceleration that occurs when an object moves in a straight line |
| Angular Acceleration | Acceleration that occurs when an object rotates around a fixed axis |
| Centripetal Acceleration | Acceleration that occurs when an object moves in a circular path |
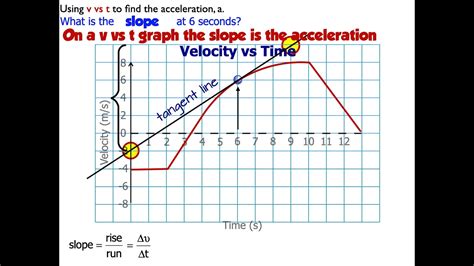
Key Points
- Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity
- There are several types of acceleration, including linear, angular, and centripetal acceleration
- Linear acceleration occurs when an object moves in a straight line
- Angular acceleration occurs when an object rotates around a fixed axis
- Centripetal acceleration occurs when an object moves in a circular path
Calculating Acceleration

Calculating acceleration is relatively easy, and it can be done using several different formulas. The most common formula for calculating acceleration is a = Δv / Δt, where a is the acceleration, Δv is the change in velocity, and Δt is the time over which the change occurs. This formula can be used to calculate linear acceleration, and it’s essential to understand the units of measurement for each variable.
Units of Measurement
The units of measurement for acceleration are meters per second squared (m/s²). This unit is a measure of the rate of change of velocity, and it’s essential to understand how to convert between different units of measurement. The formula for calculating acceleration can be used with any unit of measurement, as long as the units are consistent.
To calculate acceleration, you need to know the initial and final velocities of the object, as well as the time over which the change occurs. The formula for calculating acceleration is:
a = Δv / Δt
Where:
a = acceleration (m/s²)
Δv = change in velocity (m/s)
Δt = time (s)
For example, if an object accelerates from 0 m/s to 10 m/s in 2 seconds, the acceleration would be:
a = Δv / Δt = (10 m/s - 0 m/s) / 2 s = 5 m/s²
Real-World Applications
Acceleration has many real-world applications, and it’s essential to understand how it’s used in different fields. In physics, acceleration is used to describe the motion of objects, and it’s a fundamental concept in the study of mechanics. In engineering, acceleration is used to design and develop new technologies, such as vehicles and machines. In sports, acceleration is used to improve athletic performance, and it’s an essential component of many sports, such as football and basketball.
Practical Examples
There are many practical examples of acceleration in real-world applications. For example, a car accelerating from 0 to 60 mph in 10 seconds is an example of linear acceleration. A bicycle wheel rotating around its axis is an example of angular acceleration. A satellite orbiting the Earth is an example of centripetal acceleration.
What is acceleration?
+Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time.
What are the types of acceleration?
+There are several types of acceleration, including linear acceleration, angular acceleration, and centripetal acceleration.
How is acceleration calculated?
+Acceleration is calculated using the formula a = Δv / Δt, where a is the acceleration, Δv is the change in velocity, and Δt is the time over which the change occurs.
Meta Description: Learn how to determine acceleration easily with our comprehensive guide. Understand the concept of acceleration, its types, and how to calculate it using simple formulas.