Calculating mass is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it is essential to understand the various methods and formulas used to determine the mass of an object. In this article, we will explore the different techniques for calculating mass, including the use of density, volume, and weight. We will also discuss the importance of unit conversions and the role of precision in mass calculations.
Key Points
- Understanding the concept of mass and its relationship to density and volume
- Using the formula mass = density × volume to calculate mass
- Converting between units of mass, such as kilograms and grams
- Applying the concept of weight and gravity to mass calculations
- Ensuring precision and accuracy in mass calculations
Understanding Mass and Density
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, and it is typically measured in units of kilograms (kg) or grams (g). Density, on the other hand, is a measure of the amount of mass per unit volume of an object. The formula for calculating mass is mass = density × volume. This formula can be used to calculate the mass of an object if its density and volume are known.
Density and Volume Calculations
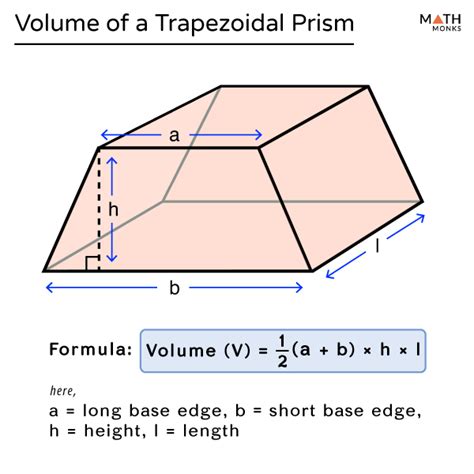
Density is typically measured in units of kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). Volume, on the other hand, is typically measured in units of cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³). To calculate mass, the density and volume of an object must be multiplied together. For example, if the density of an object is 500 kg/m³ and its volume is 2 m³, its mass can be calculated as follows: mass = 500 kg/m³ × 2 m³ = 1000 kg.
| Object | Density (kg/m³) | Volume (m³) | Mass (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1000 | 1 | 1000 |
| Air | 1.2 | 1 | 1.2 |
| Steel | 7800 | 1 | 7800 |
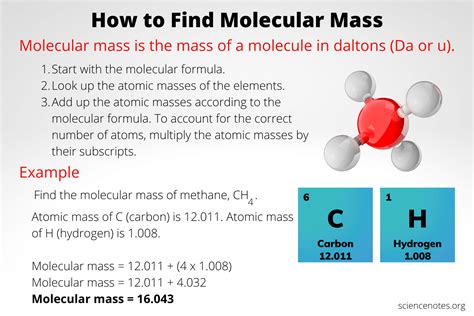
Converting Units of Mass
When calculating mass, it is often necessary to convert between different units of mass. For example, a mass of 1000 grams can be converted to kilograms by dividing by 1000, resulting in a mass of 1 kg. Similarly, a mass of 1 kg can be converted to grams by multiplying by 1000, resulting in a mass of 1000 g.
Weight and Gravity
Weight is a measure of the force exerted on an object by gravity, and it is typically measured in units of newtons (N). The weight of an object is equal to its mass multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity, which is approximately 9.8 m/s² on Earth. For example, if the mass of an object is 10 kg, its weight can be calculated as follows: weight = 10 kg × 9.8 m/s² = 98 N.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
+Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force exerted on an object by gravity. Mass is typically measured in units of kilograms or grams, while weight is typically measured in units of newtons.
How do I calculate the mass of an object if its density and volume are known?
+The mass of an object can be calculated using the formula mass = density × volume. For example, if the density of an object is 500 kg/m³ and its volume is 2 m³, its mass can be calculated as follows: mass = 500 kg/m³ × 2 m³ = 1000 kg.
What is the importance of precision in mass calculations?
+Precision is essential in mass calculations to ensure accurate results. Small errors in measurement or calculation can result in significant differences in the calculated mass, which can have important implications in fields such as engineering, physics, and chemistry.
In conclusion, calculating mass is a critical concept in physics and engineering, and it requires a thorough understanding of density, volume, and weight. By using the formula mass = density × volume and ensuring precision and accuracy in calculations, individuals can determine the mass of an object with confidence. Whether you are a student, engineer, or scientist, mastering the concept of mass calculation is essential for success in your field.



