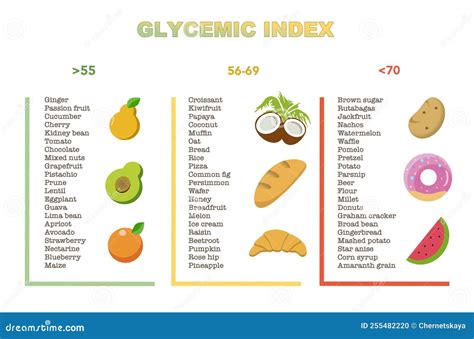
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100. The GI value of honey, a natural sweetener produced by bees from the nectar of flowers, has been a subject of interest due to its potential impact on blood sugar levels and health. Understanding the GI value of honey is crucial for individuals managing diabetes or those seeking to regulate their blood sugar levels.
Glycemic Index of Honey

Honey is composed of a mixture of sugars, primarily fructose and glucose, with trace amounts of other sugars. The exact GI value of honey can vary depending on the type of flowers the bees gather nectar from, the region, and the processing methods. Generally, the GI of honey ranges from 35 to 74, with an average value around 55. This places honey below table sugar (sucrose), which has a GI of approximately 65. The variation in honey’s GI is due to the differences in the fructose and glucose content, as fructose has a lower GI than glucose.
Factors Influencing the Glycemic Index of Honey
Several factors can influence the GI of honey, including the floral source, the climate and soil conditions of the region where the flowers are grown, and the degree of processing the honey undergoes. For instance, honey produced from nectar collected from flowers that are high in fructose will tend to have a lower GI compared to honey from flowers with higher glucose content. Additionally, raw, unfiltered honey may have a slightly different GI compared to filtered or pasteurized honey due to potential changes in sugar composition during processing.
| Honey Type | GI Value |
|---|---|
| Manuka Honey | 54.8 |
| Acacia Honey | 34.9 |
| Clover Honey | 69.2 |
| Wildflower Honey | 56.5 |

Key Points
- The glycemic index of honey varies but is generally lower than that of table sugar.
- The floral source of honey significantly influences its GI value, with fructose-rich honeys having lower GI values.
- Processing methods can affect the GI of honey, with raw honey potentially having a different GI compared to processed honey.
- Understanding the GI of honey is important for managing blood sugar levels and making informed dietary choices.
- The average GI value of honey is around 55, but it can range from 35 to 74 depending on the type.
When considering the health implications of consuming honey, it's essential to remember that while its GI value is relatively low, honey is still high in sugar and calories. Moderate consumption, therefore, is recommended. The nutritional benefits of honey, including its antioxidant properties and potential prebiotic effects, should also be taken into account. For those seeking natural sweeteners with lower GI values, certain types of honey, like acacia honey, might be preferable due to their lower GI compared to other varieties.
Health Implications and Consumption Guidelines
While honey’s GI value indicates how it may affect blood sugar levels, its overall impact on health is more complex. Honey contains various bioactive compounds that may offer health benefits, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and ascorbic acid. However, its high sugar content means that excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain, dental caries, and potentially exacerbate conditions like diabetes. As with any food, moderation is key. For individuals with diabetes or those trying to manage their blood sugar levels, choosing honey varieties with lower GI values and being mindful of portion sizes can help.
Future Research Directions
Further research into the glycemic index of different honey types and its health implications could provide valuable insights for consumers and healthcare professionals. Studies examining the effects of honey consumption on blood sugar control, weight management, and overall health outcomes would be particularly beneficial. Additionally, investigations into the potential benefits of honey as a prebiotic and its antioxidant properties could enhance our understanding of its nutritional value.
What is the average glycemic index value of honey?
+The average GI value of honey is approximately 55, but it can vary from 35 to 74 depending on the type of honey.
How does the type of flower affect the GI of honey?
+The type of flower (floral source) significantly influences the GI of honey. Flowers that are high in nectar rich in fructose will produce honey with a lower GI, while those with higher glucose content will produce honey with a higher GI.
Is honey a good choice for individuals with diabetes?
+Honey can be a part of a balanced diet for individuals with diabetes, but it should be consumed in moderation due to its sugar content. Choosing honey varieties with lower GI values may be beneficial, but it's essential to monitor blood sugar levels and consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary advice.
In conclusion, the glycemic index value of honey is an important consideration for those managing their blood sugar levels or seeking natural sweeteners. With its average GI value of 55 and the variation among different types of honey, understanding the specific characteristics of the honey being consumed is crucial. As research continues to uncover the nutritional benefits and potential health implications of honey consumption, making informed choices about honey and other sweeteners will become increasingly important for maintaining overall health and well-being.