Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) being a major contributor to this burden. The diagnosis of AMI has undergone significant evolution over the years, with biomarkers playing a crucial role in this process. Among these biomarkers, troponin has emerged as the gold standard for diagnosing myocardial injury. The introduction of high sensitivity troponin (hs-Tn) assays has further refined the diagnostic accuracy, allowing for the detection of even minor myocardial damage. This article delves into the concept of high sensitivity troponin, its clinical significance, and the implications of its use in contemporary cardiology practice.
Introduction to High Sensitivity Troponin
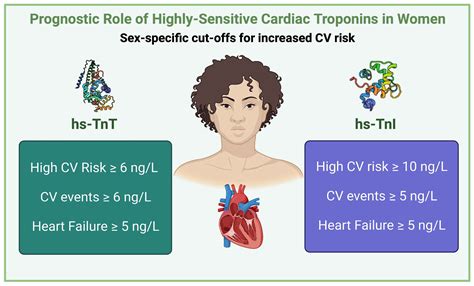
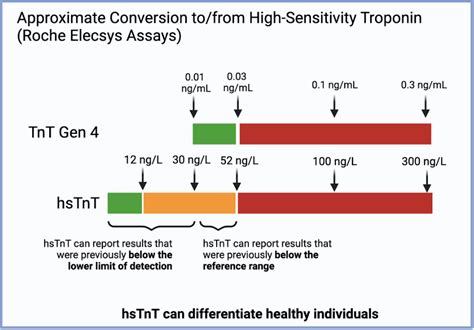
High sensitivity troponin assays are designed to detect troponin levels at much lower concentrations than their predecessors. This enhanced sensitivity enables the early detection of myocardial injury, even in patients with minor or minimal cardiac damage. The hs-Tn assays have a higher analytical sensitivity and can measure troponin levels as low as 1-3 ng/L, compared to the traditional assays which had a detection limit of around 10-20 ng/L. This advancement has significant implications for the diagnosis and management of patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Clinical Significance of High Sensitivity Troponin
The clinical significance of hs-Tn lies in its ability to identify patients at risk of adverse cardiac events early in the course of their disease. Elevated hs-Tn levels have been associated with increased mortality and morbidity in patients with ACS, as well as in those with chronic cardiovascular conditions. The use of hs-Tn has also been shown to improve the diagnostic accuracy of AMI, reducing the number of false negatives and allowing for more timely interventions. Furthermore, hs-Tn has been found to be a valuable tool in risk stratification, enabling clinicians to identify patients who may benefit from more aggressive management strategies.
| Characteristic | High Sensitivity Troponin | Traditional Troponin Assays |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Limit | 1-3 ng/L | 10-20 ng/L |
| Diagnostic Sensitivity | High | Lower |
| Clinical Application | Early detection of myocardial injury, risk stratification | Limited to detecting significant myocardial damage |
Clinical Applications of High Sensitivity Troponin

The clinical applications of hs-Tn are diverse and continue to evolve. In the context of ACS, hs-Tn is used for the early diagnosis of AMI, allowing for the timely initiation of evidence-based therapies such as antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, and coronary reperfusion strategies. Beyond ACS, hs-Tn has been explored as a biomarker for cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with chronic conditions such as heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and stable coronary artery disease. The use of hs-Tn in these settings may help identify patients at higher risk of adverse events, facilitating more targeted and aggressive management strategies.
Challenges and Limitations
While hs-Tn has revolutionized the field of cardiology, its implementation is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is the potential for increased false positives, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease or other conditions that may elevate troponin levels independently of myocardial injury. Additionally, the interpretation of hs-Tn results requires careful consideration of the clinical context, as minor elevations may not always be indicative of significant cardiac damage. Furthermore, the widespread adoption of hs-Tn has highlighted the need for standardized reporting and interpretation guidelines, to ensure consistency and accuracy in clinical practice.
Key Points
- High sensitivity troponin assays have improved the diagnostic accuracy of acute myocardial infarction and enabled the early detection of myocardial injury.
- The clinical significance of hs-Tn lies in its ability to identify patients at risk of adverse cardiac events and facilitate timely interventions.
- hs-Tn has applications beyond acute coronary syndrome, including cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with chronic conditions.
- The interpretation of hs-Tn results requires careful consideration of the clinical context to avoid false positives and ensure appropriate management.
- Standardized reporting and interpretation guidelines are essential for the consistent and accurate use of hs-Tn in clinical practice.
In conclusion, high sensitivity troponin has emerged as a powerful tool in contemporary cardiology, offering enhanced diagnostic accuracy and the potential for early intervention in patients with myocardial injury. As the field continues to evolve, it is crucial that clinicians are aware of the clinical significance, applications, and limitations of hs-Tn, to ensure its optimal use in improving patient outcomes.
What is the primary advantage of high sensitivity troponin assays over traditional troponin assays?
+The primary advantage of hs-Tn assays is their ability to detect troponin levels at much lower concentrations, enabling the early detection of myocardial injury and improving diagnostic accuracy.
How does high sensitivity troponin aid in the risk stratification of patients with acute coronary syndrome?
+hs-Tn aids in risk stratification by identifying patients with elevated troponin levels, who are at a higher risk of adverse cardiac events. This information can guide clinicians in making decisions regarding the intensity of treatment and the need for invasive strategies.
What are some of the challenges associated with the implementation of high sensitivity troponin in clinical practice?
+Challenges include the potential for increased false positives, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease, and the need for standardized reporting and interpretation guidelines to ensure consistency and accuracy in clinical practice.



