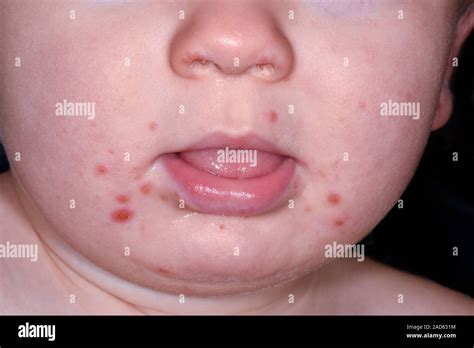
The relationship between hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) and oral health is a complex one, with the disease often presenting with mouth sores and other oral manifestations. HFMD is a common viral illness that primarily affects infants and children under the age of 5, but it can also occur in adults. The disease is characterized by a distinctive rash on the hands and feet, as well as sores in the mouth, which can be painful and uncomfortable.
Understanding HFMD and its Oral Symptoms
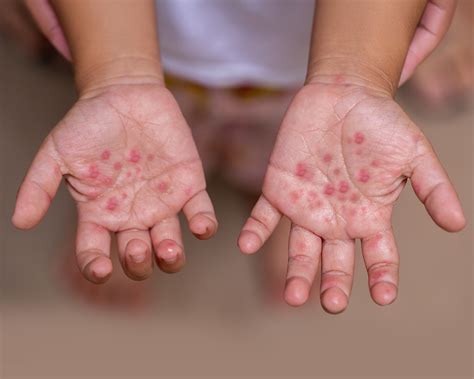
HFMD is caused by a group of viruses, including coxsackievirus A and enterovirus 71. The disease is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person, as well as through contaminated surfaces and objects. The oral symptoms of HFMD can include mouth sores, ulcers, and blisters, which can make eating, drinking, and swallowing painful. In some cases, the mouth sores can become infected, leading to more serious complications.
Oral Manifestations of HFMD
The oral manifestations of HFMD can vary in severity and presentation. In some cases, the mouth sores may be small and relatively painless, while in other cases, they can be large and extremely painful. The sores can appear on the tongue, the roof of the mouth, and the inside of the cheeks, and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, headache, and fatigue. In rare cases, HFMD can lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis, encephalitis, and paralysis.
| Oral Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Mouth Sores | Painful ulcers or blisters on the tongue, roof of the mouth, and inside of the cheeks |
| Ulcers | Open sores on the mucous membranes of the mouth |
| Blisters | Fluid-filled bumps on the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth |
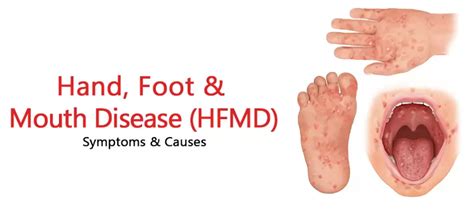
Key Points
- HFMD is a common viral illness that affects infants and children under the age of 5
- The disease is characterized by a distinctive rash on the hands and feet, as well as sores in the mouth
- The oral symptoms of HFMD can include mouth sores, ulcers, and blisters, which can be painful and uncomfortable
- HFMd can lead to more serious complications, such as meningitis, encephalitis, and paralysis, if left untreated
- Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to preventing long-term complications and promoting optimal oral health
In terms of prevention and treatment, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of HFMD and its oral symptoms. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are infected, can help prevent the spread of the disease. In terms of treatment, there is no specific cure for HFMD, but symptoms can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications and fluids. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to prevent dehydration and other complications.
Management and Prevention of HFMD
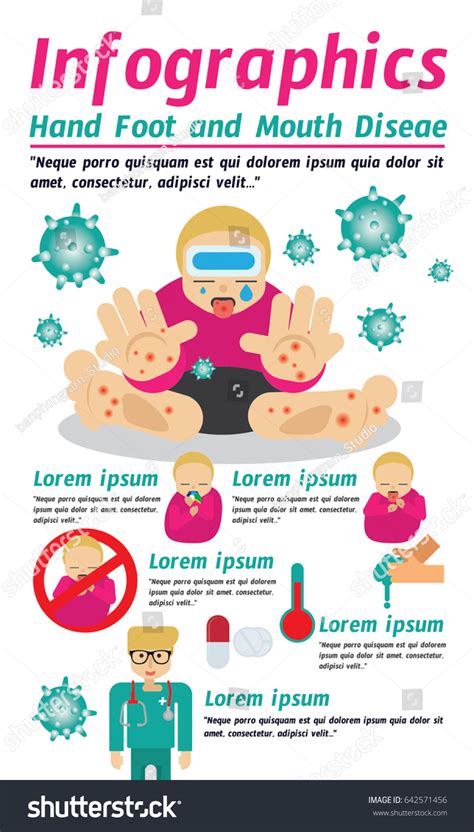
Managing and preventing HFMD requires a comprehensive approach that includes good hygiene practices, early diagnosis, and prompt treatment. Parents and caregivers can help prevent the spread of the disease by washing their hands frequently, especially after changing diapers or coming into contact with an infected person. They can also help manage symptoms by providing plenty of fluids and over-the-counter pain medications as needed.
Role of Vaccination in Preventing HFMD
While there is no specific vaccine for HFMD, there are several vaccines that can help prevent the spread of the disease. For example, the inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) has been shown to provide some protection against enterovirus 71, one of the viruses that causes HFMD. Additionally, good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are infected, can help prevent the spread of the disease.
What are the most common symptoms of HFMD?
+The most common symptoms of HFMD include a distinctive rash on the hands and feet, as well as sores in the mouth. Other symptoms can include fever, headache, and fatigue.
How is HFMD diagnosed?
+HFMd is typically diagnosed based on a physical examination and a review of the person's symptoms. In some cases, a viral culture or PCR test may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the potential complications of HFMD?
+The potential complications of HFMD can include meningitis, encephalitis, and paralysis. In rare cases, the disease can be fatal.
In conclusion, HFMD is a common viral illness that can have a significant impact on a person’s oral health and quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for the disease, individuals can take steps to prevent its spread and manage its symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to preventing long-term complications and promoting optimal oral health.