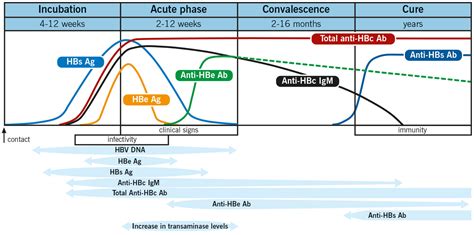
The hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb) is a protein that is produced by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus (HBV). It is one of the key markers used to diagnose and monitor the progression of hepatitis B infection, as well as to assess the effectiveness of vaccination against the disease. The presence of HBsAb in the blood indicates that the individual has either been vaccinated against hepatitis B or has recovered from an acute infection and is now immune to the virus.
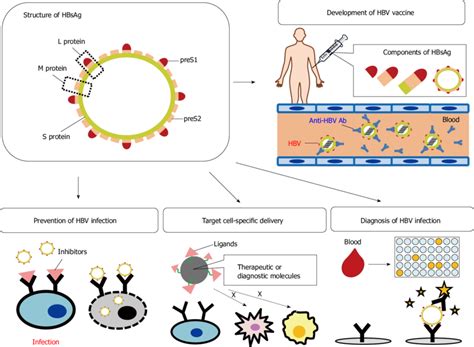
In the context of hepatitis B, the surface antigen (HBsAg) is a protein on the surface of the virus that stimulates the production of HBsAb. When an individual is first infected with HBV, the virus multiplies and releases HBsAg into the bloodstream, where it can be detected by laboratory tests. As the immune system responds to the infection, it produces HBsAb, which binds to the HBsAg and helps to neutralize the virus. The level of HBsAb in the blood can provide valuable information about the stage of infection and the effectiveness of treatment.
Key Points
- Hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb) is a key marker for diagnosing and monitoring hepatitis B infection.
- The presence of HBsAb in the blood indicates immunity to hepatitis B, either through vaccination or recovery from an acute infection.
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) stimulates the production of HBsAb and is used to diagnose acute infection.
- The level of HBsAb in the blood provides information about the stage of infection and the effectiveness of treatment.
- Vaccination against hepatitis B is the most effective way to prevent infection and induce long-term immunity.
HBsAb and Hepatitis B Infection
Understanding the role of HBsAb in hepatitis B infection is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. When an individual is infected with HBV, the virus undergoes a complex replication process that involves the production of HBsAg. The immune system recognizes HBsAg as foreign and mounts a response by producing HBsAb. The presence of HBsAb is a sign that the immune system is actively fighting the infection.
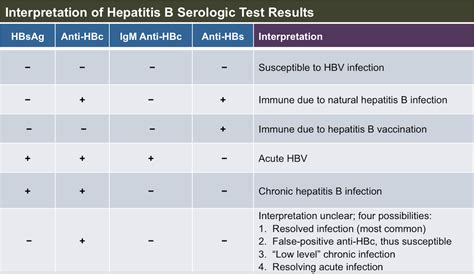
There are several interpretations of HBsAb test results, depending on the clinical context. A positive HBsAb result, indicating the presence of the antibody, can signify immunity to hepatitis B, either from vaccination or past infection. On the other hand, a negative result may indicate susceptibility to the virus or an early stage of infection before the immune system has had time to produce antibodies. In some cases, a negative HBsAb result in the presence of HBsAg indicates an active, replicating infection.
HBsAb in Vaccination
Vaccination against hepatitis B is a highly effective method for inducing long-term immunity against the virus. The hepatitis B vaccine contains a component that mimics HBsAg, which stimulates the immune system to produce HBsAb without causing the disease. After a complete series of vaccinations, the majority of individuals will develop a protective level of HBsAb, indicating immunity to hepatitis B. The level of HBsAb can wane over time, but immune memory cells remain, allowing for a rapid response to any future exposure to the virus.
| HBsAb Interpretation | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|
| Positive HBsAb | Immunity to hepatitis B, either from vaccination or past infection |
| Negative HBsAb with positive HBsAg | Active, replicating infection |
| Negative HBsAb without HBsAg | Susceptibility to hepatitis B or early stage of infection |
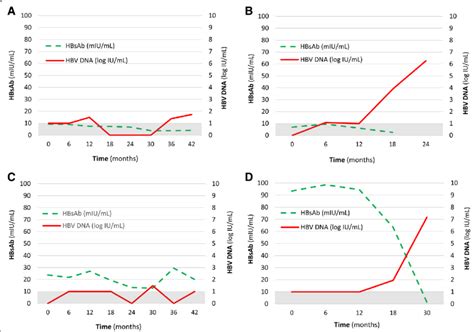
Challenges and Considerations
While HBsAb is a crucial marker for diagnosing and monitoring hepatitis B, there are challenges and considerations in its interpretation. One of the main challenges is the potential for false-negative results, which can occur if the test is performed too early in the infection before the immune system has had time to produce antibodies. Additionally, some individuals may not respond to vaccination and may remain susceptible to the virus, highlighting the importance of post-vaccination testing to confirm immunity.
Another consideration is the issue of HBsAb waning over time. As the level of HBsAb decreases, the individual may become susceptible to hepatitis B again. This is particularly concerning for individuals who were vaccinated at birth or in early childhood and may not have received booster doses. Regular monitoring of HBsAb levels and booster vaccinations as recommended can help maintain long-term immunity.
Future Directions
Research into hepatitis B and the role of HBsAb continues to evolve, with a focus on improving diagnostic tests, vaccines, and treatment options. One area of interest is the development of more sensitive and specific diagnostic tests that can detect HBsAb and other markers of hepatitis B infection earlier and more accurately. Additionally, there is ongoing research into new vaccine formulations and administration schedules that can provide longer-lasting immunity and better protection against the virus.
In conclusion, HBsAb plays a critical role in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B infection. Understanding the complexities of HBsAb and its interpretation is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals at risk of hepatitis B. By staying up-to-date with the latest research and recommendations, we can work towards better control and eventual elimination of this significant public health threat.
What does a positive HBsAb result mean?
+A positive HBsAb result indicates immunity to hepatitis B, either from vaccination or past infection.
Can HBsAb levels decrease over time?
+Yes, HBsAb levels can decrease over time, potentially leaving an individual susceptible to hepatitis B again. Regular monitoring and booster vaccinations can help maintain long-term immunity.
What is the significance of HBsAb in hepatitis B vaccination?
+Hepatitis B vaccination induces the production of HBsAb, which provides long-term immunity against the virus. The level of HBsAb after vaccination is a key indicator of the vaccine's effectiveness.
Meta description suggestion: “Learn about hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb), its role in diagnosing and monitoring hepatitis B infection, and its significance in vaccination against the disease.”