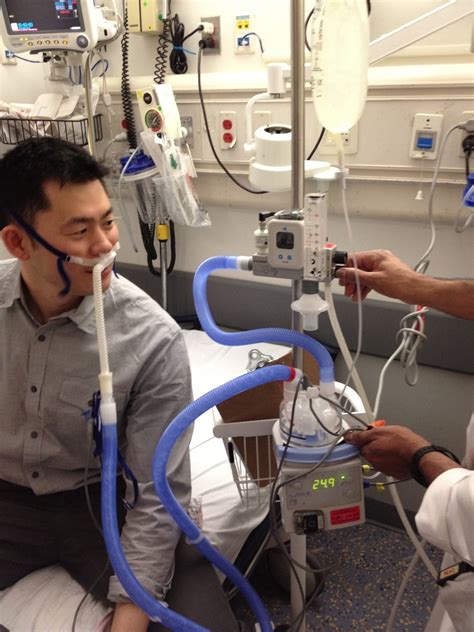
Heated high flow nasal cannula (HHFNC) therapy has emerged as a crucial modality in the management of respiratory distress, particularly in patients with acute respiratory failure. This therapy involves the delivery of heated, humidified gas at high flow rates through nasal cannulae, which helps to improve oxygenation and reduce the work of breathing. The use of HHFNC has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential benefits in reducing the need for intubation and improving patient outcomes. In this article, we will delve into the principles, benefits, and applications of HHFNC therapy, as well as its limitations and potential complications.
Key Points
- HHFNC therapy involves the delivery of heated, humidified gas at high flow rates through nasal cannulae to improve oxygenation and reduce the work of breathing.
- The use of HHFNC has been shown to reduce the need for intubation and improve patient outcomes in patients with acute respiratory failure.
- HHFNC therapy can be used in a variety of settings, including the intensive care unit, emergency department, and general ward.
- The therapy requires careful patient selection, monitoring, and adjustment of flow rates and oxygen concentrations to ensure optimal outcomes.
- Potential complications of HHFNC therapy include nasal mucosal dryness, epistaxis, and gastric distension.
Principles of Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy
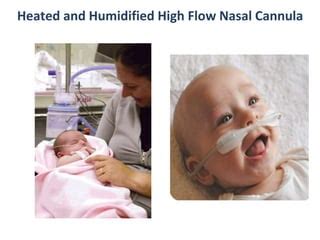
HHFNC therapy works by delivering heated, humidified gas at high flow rates through nasal cannulae, which helps to improve oxygenation and reduce the work of breathing. The heated gas is typically set at a temperature between 37°C and 40°C, and the flow rate can range from 30 to 60 liters per minute (L/min). The use of heated gas helps to reduce the viscosity of secretions, making it easier for patients to clear their airways. Additionally, the high flow rate helps to reduce the dead space in the upper airway, which can improve oxygenation and reduce the work of breathing.
Benefits of Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy
The benefits of HHFNC therapy have been well-documented in the literature. Studies have shown that HHFNC can reduce the need for intubation and improve patient outcomes in patients with acute respiratory failure. Additionally, HHFNC has been shown to reduce the length of stay in the intensive care unit (ICU) and improve patient comfort and satisfaction. The therapy can also be used in a variety of settings, including the ICU, emergency department, and general ward.
| Setting | Indications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| ICU | Acute respiratory failure, hypoxemic respiratory failure | Reduced need for intubation, improved patient outcomes |
| Emergency Department | Acute respiratory distress, asthma exacerbation | Improved oxygenation, reduced need for hospital admission |
| General Ward | Chronic respiratory disease, post-operative respiratory care | Improved patient comfort, reduced need for oxygen therapy |
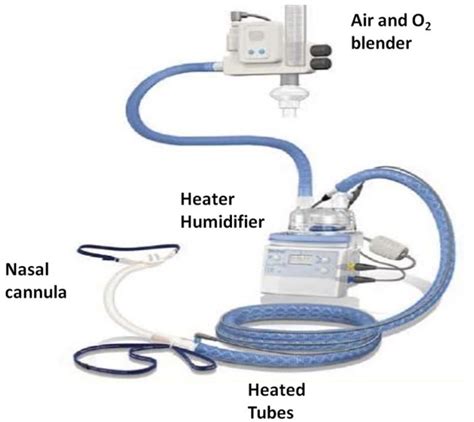
Applications of Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy
HHFNC therapy can be used in a variety of clinical settings, including the ICU, emergency department, and general ward. The therapy is typically indicated for patients with acute respiratory failure, hypoxemic respiratory failure, and chronic respiratory disease. Additionally, HHFNC can be used for post-operative respiratory care, particularly in patients who are at risk of respiratory complications.
Limitations and Potential Complications of Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy
While HHFNC therapy has been shown to be effective in improving patient outcomes, there are several limitations and potential complications that need to be considered. One of the main limitations of HHFNC is the need for careful patient selection and monitoring. Patients who are at risk of respiratory failure or have underlying respiratory disease may require closer monitoring and adjustment of flow rates and oxygen concentrations. Additionally, HHFNC can cause nasal mucosal dryness, epistaxis, and gastric distension, particularly if the flow rates are too high or the gas is not properly humidified.
What are the indications for HHFNC therapy?
+HHFNC therapy is typically indicated for patients with acute respiratory failure, hypoxemic respiratory failure, and chronic respiratory disease. Additionally, HHFNC can be used for post-operative respiratory care, particularly in patients who are at risk of respiratory complications.
What are the potential complications of HHFNC therapy?
+Potential complications of HHFNC therapy include nasal mucosal dryness, epistaxis, and gastric distension. Additionally, HHFNC can cause respiratory alkalosis, particularly if the flow rates are too high or the gas is not properly humidified.
How do I adjust the flow rates and oxygen concentrations for HHFNC therapy?
+The flow rates and oxygen concentrations for HHFNC therapy should be adjusted based on the patient's clinical response and oxygenation status. Typically, the flow rates are started at 30-40 L/min and adjusted as needed to achieve an SpO2 of 92-95%. The oxygen concentrations can be adjusted based on the patient's oxygenation status and underlying respiratory disease.
In conclusion, HHFNC therapy has emerged as a crucial modality in the management of respiratory distress, particularly in patients with acute respiratory failure. The therapy has been shown to reduce the need for intubation and improve patient outcomes, and can be used in a variety of clinical settings. However, careful patient selection, monitoring, and adjustment of flow rates and oxygen concentrations are crucial to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize potential complications. As a respiratory therapist, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest evidence and best practices in HHFNC therapy to provide high-quality care to patients with respiratory disease.