The detection of ectopic pregnancies is a critical aspect of obstetric care, and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels play a significant role in this process. hCG is a hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy, and its levels can provide valuable information about the health and location of the pregnancy. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, hCG levels can be used as an indicator of the pregnancy's viability and location.
Normally, hCG levels increase rapidly during the early stages of a healthy pregnancy, with a doubling time of approximately 48 hours. However, in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, hCG levels may not increase at the same rate. Studies have shown that hCG levels in ectopic pregnancies tend to be lower than those in healthy pregnancies, with a median hCG level of around 1,000-2,000 mIU/mL at the time of diagnosis. Furthermore, the rate of increase in hCG levels is often slower in ectopic pregnancies, with a doubling time of more than 48 hours.
Key Points
- hCG levels can be used to detect ectopic pregnancies, but a single measurement is not sufficient for diagnosis.
- The rate of increase in hCG levels is often slower in ectopic pregnancies, with a doubling time of more than 48 hours.
- Transvaginal ultrasound is the most sensitive method for detecting ectopic pregnancies, particularly when combined with hCG level measurements.
- The risk of ectopic pregnancy is higher in women with a history of pelvic surgery, tubal damage, or infertility.
- Early detection and treatment of ectopic pregnancies are critical to preventing complications and improving outcomes.
Interpretation of hCG Levels in Ectopic Pregnancies
The interpretation of hCG levels in ectopic pregnancies requires careful consideration of the clinical context and the use of other diagnostic tools, such as ultrasound and physical examination. While a single measurement of hCG level is not sufficient for diagnosis, serial measurements can provide valuable information about the pregnancy’s viability and location. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Ultrasound found that hCG levels above 1,500 mIU/mL were associated with a higher likelihood of ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasound Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancies
Transvaginal ultrasound is the most sensitive method for detecting ectopic pregnancies, particularly when combined with hCG level measurements. The use of ultrasound can help identify the location of the pregnancy and detect any abnormalities in the reproductive organs. A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology found that transvaginal ultrasound had a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 99% for detecting ectopic pregnancies.
| hCG Level | Doubling Time | Ultrasound Findings |
|---|---|---|
| 1,000-2,000 mIU/mL | >48 hours | No visible gestational sac or embryo |
| 2,000-5,000 mIU/mL | 48-72 hours | Visible gestational sac or embryo, but abnormal location |
| >5,000 mIU/mL | <48 hours | Visible gestational sac or embryo, with normal location and growth |

Risk Factors for Ectopic Pregnancies
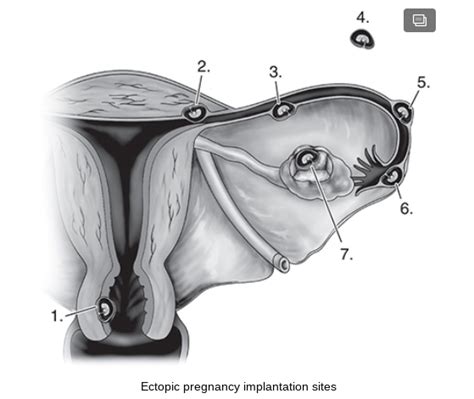
The risk of ectopic pregnancy is higher in women with a history of pelvic surgery, tubal damage, or infertility. Other risk factors include a history of ectopic pregnancy, smoking, and the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART). A study published in the British Medical Journal found that women who had undergone pelvic surgery were at a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy, with an odds ratio of 2.5.
Prevention and Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancies
Early detection and treatment of ectopic pregnancies are critical to preventing complications and improving outcomes. The use of hCG levels and ultrasound can help identify ectopic pregnancies early on, and treatment options such as methotrexate or surgery can be effective in managing the condition. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that early treatment of ectopic pregnancies with methotrexate was associated with a higher success rate and lower risk of complications.
What is the normal range for hCG levels in early pregnancy?
+The normal range for hCG levels in early pregnancy varies depending on the stage of pregnancy, but typically ranges from 10-100 mIU/mL at 3-4 weeks of gestation.
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
+An ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed using a combination of hCG level measurements, ultrasound, and physical examination. Transvaginal ultrasound is the most sensitive method for detecting ectopic pregnancies.
What are the risk factors for ectopic pregnancies?
+The risk factors for ectopic pregnancies include a history of pelvic surgery, tubal damage, or infertility, as well as smoking and the use of assisted reproductive technology (ART).



