Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a common autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage to the gland's cells. While the primary symptoms of Hashimoto's are related to thyroid hormone imbalance, some patients may experience a range of skin manifestations, including a characteristic rash. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Hashimoto's thyroiditis rash, exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, as well as the broader implications of this condition on overall health.
Understanding Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
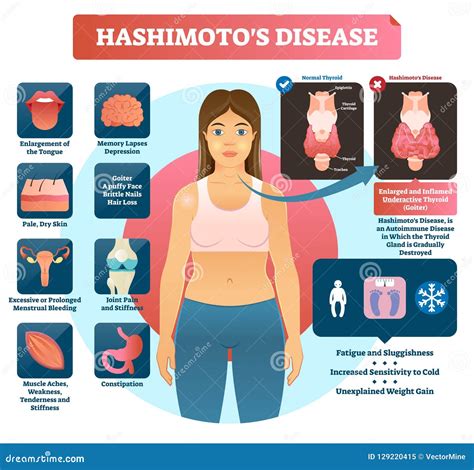
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to chronic inflammation and damage to the gland’s cells. This damage can disrupt the production of thyroid hormones, essential for regulating metabolism, growth, and development. The condition is more common in women than men, and it often runs in families. While the exact cause of Hashimoto’s is not fully understood, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Rash: Causes and Symptoms
The rash associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a relatively rare symptom, occurring in approximately 10-20% of patients. The rash is often described as a pink or reddish-brown, flat, or slightly raised patch, typically appearing on the face, neck, or upper torso. In some cases, the rash may be itchy or tender to the touch. The exact cause of the rash is not well understood, but it is thought to be related to the underlying autoimmune process and the resulting inflammation.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Pink or reddish-brown, flat, or slightly raised patch |
| Location | Face, neck, or upper torso |
| Symptoms | Itchy or tender to the touch |

Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosing Hashimoto’s thyroiditis involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The presence of a rash may be an indication of the condition, but it is not a definitive diagnostic criterion. Treatment for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis typically involves thyroid hormone replacement therapy to regulate thyroid hormone levels. In some cases, topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be prescribed to manage the rash and associated symptoms.
Treatment Options for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis Rash
Treatment for the rash associated with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is often focused on managing symptoms and reducing inflammation. Topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone cream, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching. Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine, may also be used to relieve itching and reduce the risk of scratching and further irritating the skin.
Key Points
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland
- The rash associated with Hashimoto's is a relatively rare symptom, occurring in approximately 10-20% of patients
- The rash is often described as a pink or reddish-brown, flat, or slightly raised patch, typically appearing on the face, neck, or upper torso
- Treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis typically involves thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Topical corticosteroids or antihistamines may be prescribed to manage the rash and associated symptoms
Complications and Comorbidities
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can increase the risk of developing other autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or type 1 diabetes. Patients with Hashimoto’s may also be at increased risk of developing thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer. The presence of a rash may be an indication of a more severe autoimmune response, and patients should be closely monitored for signs of complications or comorbidities.
Prevention and Management
While there is no cure for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, there are steps that can be taken to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. These include maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise. Patients should also work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor thyroid hormone levels and adjust treatment as needed.
What is the primary cause of Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
+The exact cause of Hashimoto's thyroiditis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
How common is the rash associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
+The rash associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis is a relatively rare symptom, occurring in approximately 10-20% of patients.
What is the typical treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
+Treatment for Hashimoto's thyroiditis typically involves thyroid hormone replacement therapy to regulate thyroid hormone levels.
Meta description: “Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid gland, and in some cases, a characteristic rash may appear. Learn more about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Hashimoto’s thyroiditis rash, and how to manage this condition to reduce the risk of complications.” (147 characters)