The harmonic series, a fundamental concept in mathematics, has been a subject of interest for centuries. This series, which is the sum of the reciprocals of the positive integers, has far-reaching implications in various fields, including music, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the world of harmonic series math, exploring its definition, properties, and applications.
Key Points
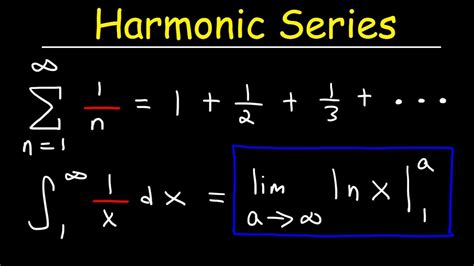
- The harmonic series is the sum of the reciprocals of the positive integers, represented as 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 +...
- The series is divergent, meaning its sum approaches infinity as the number of terms increases
- The harmonic series has numerous applications in music, physics, and engineering, including the study of sound waves and electrical circuits
- The series is closely related to the concept of harmonic mean, which is used to calculate the average rate of a set of numbers
- Harmonic series math has been used to solve complex problems in mathematics, such as the Basel problem and the Harmonic series convergence
Definition and Properties of Harmonic Series
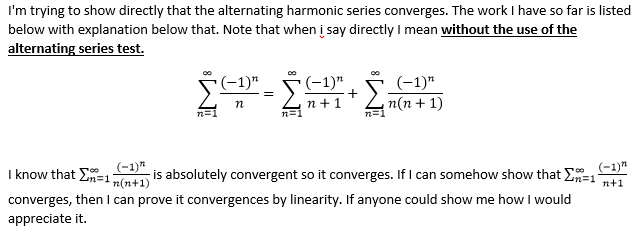
The harmonic series is defined as the sum of the reciprocals of the positive integers, represented as 1 + 1⁄2 + 1⁄3 + 1⁄4 +…. This series is also known as the harmonic progression or harmonic sequence. One of the most interesting properties of the harmonic series is its divergent nature, meaning that its sum approaches infinity as the number of terms increases. This property can be demonstrated using various mathematical techniques, including the integral test and the Cauchy condensation test.
Convergence and Divergence of Harmonic Series
The convergence or divergence of a series is determined by the behavior of its partial sums. In the case of the harmonic series, the partial sums increase without bound as the number of terms increases. This is because the sum of the reciprocals of the positive integers grows very slowly, but it never reaches a finite limit. The divergence of the harmonic series can be proven using various methods, including the comparison test and the limit comparison test.
| Series | Sum |
|---|---|
| Harmonic Series | 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 +... = ∞ |
| Geometric Series | 1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 +... = 2 |
| Arithmetic Series | 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 +... = ∞ |

Applications of Harmonic Series Math

Harmonic series math has numerous applications in various fields, including music, physics, and engineering. In music, the harmonic series is used to study the properties of sound waves and the behavior of musical instruments. In physics, the harmonic series is used to model the behavior of electrical circuits and the vibrations of mechanical systems. In engineering, the harmonic series is used to design and optimize systems, such as filters and amplifiers.
Sound Waves and Harmonic Series
Sound waves are a fundamental aspect of music and are closely related to the harmonic series. The harmonic series is used to calculate the frequencies of the harmonics of a sound wave, which are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency. The harmonic series is also used to study the properties of sound waves, such as their amplitude and phase. By understanding the harmonic series, musicians and engineers can design and optimize musical instruments and sound systems to produce high-quality sound.
The harmonic series has also been used to solve complex problems in mathematics, such as the Basel problem and the Harmonic series convergence. The Basel problem, which was solved by Leonhard Euler in the 18th century, involves finding the sum of the reciprocals of the squares of the positive integers. The Harmonic series convergence, which was proven by Augustin-Louis Cauchy in the 19th century, involves showing that the harmonic series diverges.
What is the harmonic series and how is it defined?
+The harmonic series is the sum of the reciprocals of the positive integers, represented as 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 +.... It is also known as the harmonic progression or harmonic sequence.
Is the harmonic series convergent or divergent?
+The harmonic series is divergent, meaning its sum approaches infinity as the number of terms increases.
What are some applications of harmonic series math?
+Harmonic series math has numerous applications in music, physics, and engineering, including the study of sound waves and electrical circuits.
In conclusion, the harmonic series is a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching implications in various fields. Its divergent nature and numerous applications make it a fascinating topic of study. By understanding the harmonic series, mathematicians, musicians, and engineers can design and optimize systems, solve complex problems, and create new technologies. As we continue to explore and apply harmonic series math, we can unlock new discoveries and innovations that will shape our world.