The half angle identity is a fundamental concept in trigonometry, allowing individuals to simplify complex trigonometric expressions and solve equations with greater ease. To grasp this concept, it is essential to have a solid understanding of basic trigonometric functions, including sine, cosine, and tangent. The half angle identity can be applied to various trigonometric functions, but it is most commonly used with sine and cosine. In this article, we will delve into the world of half angle identities, exploring their applications, derivations, and practical uses.
Key Points
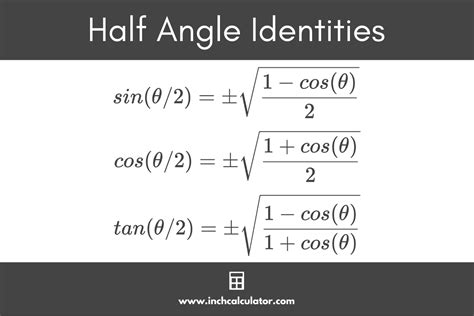
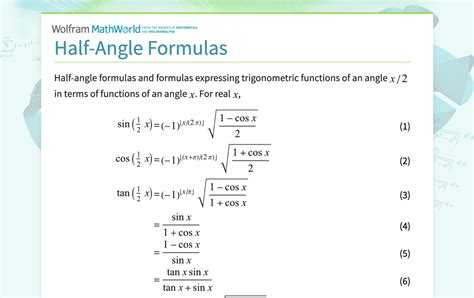
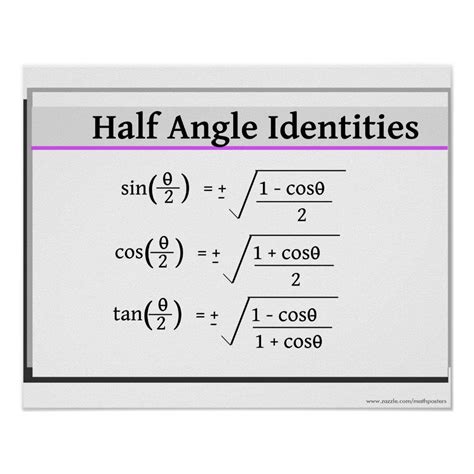
- The half angle identity for sine is given by the formula: $\sin\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos\theta}{2}}$
- The half angle identity for cosine is given by the formula: $\cos\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1+\cos\theta}{2}}$
- These identities are crucial in simplifying complex trigonometric expressions and solving equations
- Understanding the half angle identity requires a solid foundation in basic trigonometric functions
- Practical applications of the half angle identity can be found in fields such as physics, engineering, and mathematics
Derivation of Half Angle Identities
To derive the half angle identities, we can start with the double angle formula for cosine: \cos(2\theta) = 1 - 2\sin^2\theta. By rearranging this formula, we can express \sin^2\theta in terms of \cos(2\theta): \sin^2\theta = \frac{1-\cos(2\theta)}{2}. Taking the square root of both sides, we obtain: \sin\theta = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos(2\theta)}{2}}. Substituting \theta = \frac{\alpha}{2}, we arrive at the half angle identity for sine: \sin\left(\frac{\alpha}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos\alpha}{2}}.
Applications of Half Angle Identities
The half angle identities have numerous practical applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics. For instance, in physics, the half angle identity can be used to solve problems involving simple harmonic motion. In engineering, it can be applied to design and analyze systems involving rotational motion. In mathematics, the half angle identity is essential in simplifying complex trigonometric expressions and solving equations.
| Trigonometric Function | Half Angle Identity |
|---|---|
| Sine | $\sin\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos\theta}{2}}$ |
| Cosine | $\cos\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1+\cos\theta}{2}}$ |
Practical Examples and Solutions
To illustrate the practical applications of the half angle identity, let us consider a few examples. Suppose we want to find the value of \sin(15^\circ) using the half angle identity. We can start by expressing 15^\circ as \frac{30^\circ}{2}. Then, applying the half angle identity for sine, we obtain: \sin(15^\circ) = \sin\left(\frac{30^\circ}{2}\right) = \pm\sqrt{\frac{1-\cos(30^\circ)}{2}}. Since 15^\circ lies in the first quadrant, we choose the positive sign: \sin(15^\circ) = \sqrt{\frac{1-\cos(30^\circ)}{2}}.
Solving Trigonometric Equations
The half angle identity is also useful in solving trigonometric equations. For instance, consider the equation: 2\sin^2\theta + 3\cos\theta - 3 = 0. We can simplify this equation using the half angle identity for sine: \sin^2\theta = \frac{1-\cos(2\theta)}{2}. Substituting this expression into the original equation, we obtain a quadratic equation in terms of \cos\theta, which can be solved using standard algebraic techniques.
What is the half angle identity for tangent?
+The half angle identity for tangent is given by the formula: $\tan\left(\frac{\theta}{2}\right) = \frac{1-\cos\theta}{\sin\theta}$. This identity is useful in simplifying complex trigonometric expressions involving tangent.
How do I choose the correct sign for the half angle identity?
+The choice of sign depends on the quadrant in which the angle lies. If the angle lies in the first or second quadrant, the sign is positive. If the angle lies in the third or fourth quadrant, the sign is negative.
What are some common applications of the half angle identity?
+The half angle identity has numerous practical applications in fields such as physics, engineering, and mathematics. It is used to simplify complex trigonometric expressions, solve equations, and design systems involving rotational motion.
In conclusion, the half angle identity is a powerful tool in trigonometry, allowing individuals to simplify complex expressions and solve equations with greater ease. By understanding the derivation, applications, and practical uses of the half angle identity, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation for the subject and improve their problem-solving skills. Whether you are a student, engineer, or mathematician, the half angle identity is an essential concept to master, and its applications will continue to inspire and challenge you in the world of trigonometry.