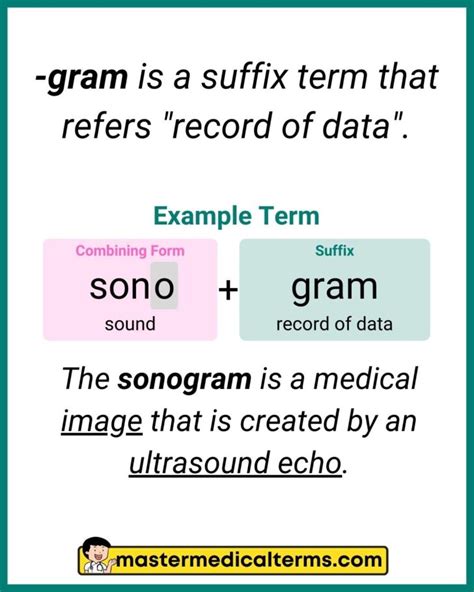
Understanding medical terminology is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to comprehend their health conditions. One of the key aspects of medical terminology involves the use of prefixes, roots, and suffixes to form complex words. Among these, the prefix "penta-" referring to five and the root "gram" meaning weight, lead to the formation of the term "pentagram," which, however, is more commonly associated with symbolism rather than medical terminology. In the medical field, terms related to weight or measurement often derive from the Greek word "gramma," meaning something written, but in the context of measurement, it refers to a unit of weight or mass. Let's explore five medical terms that relate to weight or measurement, each being relevant to different aspects of healthcare:
Medical Terms Related to Weight and Measurement
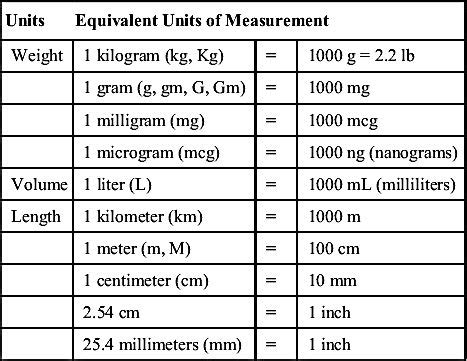
These terms are crucial for diagnosing, treating, and understanding various medical conditions. Each term has a specific application and is derived from Greek or Latin roots, which are foundational to medical terminology.
1. Hypoglycemia
This term refers to a condition characterized by an abnormally low level of blood glucose (sugar). The management of hypoglycemia involves measuring blood glucose levels, often in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or grams per liter, although the former is more commonly used. Understanding and managing blood glucose levels is critical for individuals with diabetes, as both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia can have serious health implications.
2. Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is a condition marked by an elevation of one or more of the various types of lipids (such as cholesterol, triglycerides) in the bloodstream. These lipids are measured in units of weight, such as milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), to assess the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Managing hyperlipidemia often involves dietary changes, exercise, and sometimes medication to reduce lipid levels and prevent complications like atherosclerosis.
3. Glycemia
Glycemia refers to the presence of glucose in the blood. Measuring glycemia, typically through blood glucose monitoring, provides crucial information for the management of diabetes mellitus. This measurement, often expressed in grams per liter or milligrams per deciliter, helps in assessing how well diabetes is being controlled and guides adjustments in treatment, including diet, exercise, and medication.
4. Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a condition that occurs when the body either cannot use glucose effectively or produces too much glucose. This condition can lead to various complications, including diabetes, if not properly managed. The measurement of blood glucose levels is fundamental in diagnosing and treating hyperglycemia, with values typically reported in grams per liter or, more commonly, milligrams per deciliter.
5. Normoglycemia
Normoglycemia refers to normal blood glucose levels. Maintaining normoglycemia is essential for overall health, as both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can have adverse effects on the body. The goal of managing diabetes and other glucose-related conditions is to achieve and maintain normoglycemia, which is typically defined by fasting blood glucose levels between 70 and 99 mg/dL, though these values can slightly vary based on the source and specific health guidelines.
Key Points
- Understanding medical terms related to weight and measurement is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals managing health conditions.
- Hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia, glycemia, hyperglycemia, and normoglycemia are key terms related to the measurement and management of glucose and lipid levels in the blood.
- These conditions are diagnosed and managed through measurements expressed in units of weight, such as milligrams per deciliter or grams per liter.
- Proper management of these conditions involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
- Education on these terms can empower individuals to better understand their health conditions and participate in their care.
In conclusion, while the prefix "penta-" and the root "gram" might not directly form a commonly used medical term, understanding the roots and prefixes of medical terminology can greatly aid in comprehending complex medical conditions and their management. The terms hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia, glycemia, hyperglycemia, and normoglycemia are fundamental to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of conditions related to glucose and lipid metabolism, emphasizing the importance of accurate measurement and interpretation of blood glucose and lipid levels in healthcare.
What is the primary method of measuring blood glucose levels?
+Blood glucose levels are primarily measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) using a glucometer, which provides immediate results and guides the management of diabetes and other glucose-related conditions.
Why is it important to manage hyperlipidemia?
+Managing hyperlipidemia is crucial because elevated levels of lipids in the blood can lead to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. Early detection and management through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication can significantly reduce these risks.
What is the significance of maintaining normoglycemia?
+Maintaining normoglycemia is essential for preventing the complications associated with both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Normoglycemia indicates that the body’s glucose metabolism is functioning properly, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.