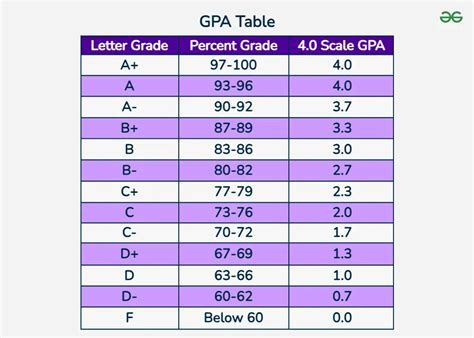
The GPA scale is a widely used metric for evaluating academic performance, particularly in the United States. It provides a standardized framework for assessing student achievement across different institutions and courses. Understanding the GPA scale is essential for students, educators, and administrators to navigate the complexities of academic assessment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the GPA scale, exploring its history, calculation methods, and implications for academic success.
Introduction to the GPA Scale
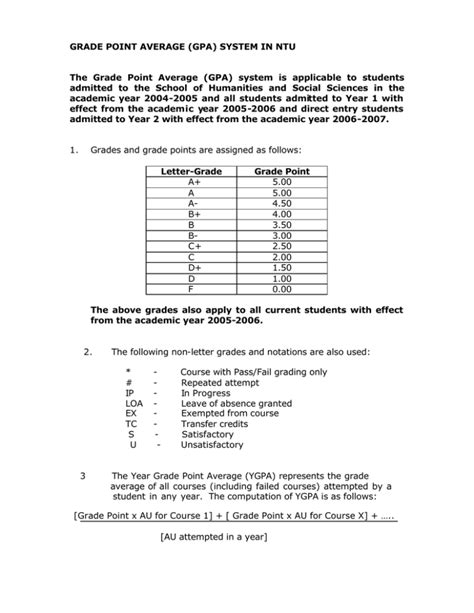
The GPA scale, or Grade Point Average scale, is a numerical system used to quantify student performance. It assigns a weighted value to each letter grade, allowing for the calculation of a cumulative average. The most common GPA scale ranges from 0.0 to 4.0, with higher values indicating better academic performance. This scale has become a ubiquitous tool in education, influencing college admissions, scholarship awards, and even employment opportunities.
Key Points
- The GPA scale is a numerical system used to evaluate academic performance.
- The most common GPA scale ranges from 0.0 to 4.0.
- Higher GPA values indicate better academic performance.
- The GPA scale influences college admissions, scholarship awards, and employment opportunities.
- Understanding the GPA scale is essential for students, educators, and administrators.
Calculation Methods
Calculating the GPA involves assigning a grade point value to each letter grade, then averaging these values over a specified period. The most common grade point values are:
| Letter Grade | Grade Point Value |
|---|---|
| A | 4.0 |
| B | 3.0 |
| C | 2.0 |
| D | 1.0 |
| F | 0.0 |
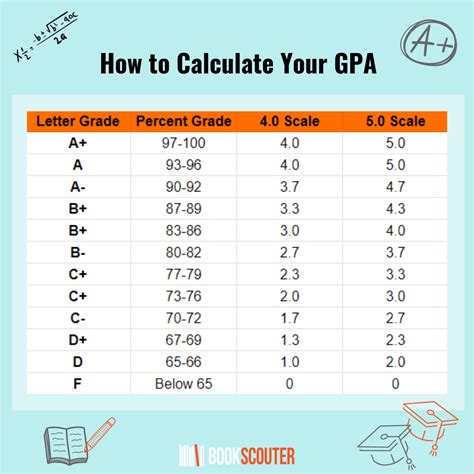
For example, a student earning an A in a 3-credit course would receive 12 grade points (4.0 x 3). The cumulative GPA is then calculated by dividing the total grade points earned by the total credits attempted.
Implications for Academic Success

A strong GPA can open doors to prestigious universities, lucrative scholarships, and competitive job opportunities. Conversely, a low GPA can limit these prospects, making it essential for students to understand the GPA scale and strive for academic excellence. Educators and administrators also rely on the GPA scale to evaluate student performance, identify areas for improvement, and develop targeted support initiatives.
Moreover, the GPA scale has been subject to criticism and controversy. Some argue that it oversimplifies the complexities of academic performance, neglecting important aspects like creativity, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence. Others contend that the GPA scale perpetuates inequality, as students from disadvantaged backgrounds may face barriers to achieving high grades.
Historical Context and Evolution
The GPA scale has its roots in the early 20th century, when educators sought to develop a standardized system for evaluating student performance. Over the years, the GPA scale has undergone significant changes, with various institutions adopting different scales and calculation methods. Today, the GPA scale remains a widely accepted metric, despite ongoing debates about its effectiveness and fairness.
Looking to the future, it's likely that the GPA scale will continue to evolve, incorporating new technologies and methodologies to provide a more comprehensive picture of academic performance. Some institutions are already exploring alternative assessment models, such as competency-based progression and personalized learning pathways.
Best Practices for GPA Scale Reporting
To ensure accurate and fair GPA scale reporting, educators and administrators should follow best practices, including:
- Clearly communicating GPA calculation methods and scales to students and parents.
- Providing regular progress updates and feedback to students.
- Offering targeted support initiatives for students struggling with low GPAs.
- Encouraging students to take ownership of their academic performance and set realistic goals.
What is the purpose of the GPA scale?
+The GPA scale provides a standardized framework for evaluating academic performance, allowing for comparisons across different institutions and courses.
How is the GPA calculated?
+The GPA is calculated by assigning a grade point value to each letter grade, then averaging these values over a specified period.
What are the implications of a low GPA?
+A low GPA can limit opportunities for college admissions, scholarships, and job opportunities, making it essential for students to understand the GPA scale and strive for academic excellence.
In conclusion, the GPA scale is a complex and multifaceted metric that plays a significant role in evaluating academic performance. By understanding the GPA scale, its calculation methods, and implications for academic success, students, educators, and administrators can work together to promote academic excellence and provide targeted support initiatives for students struggling with low GPAs. As the education landscape continues to evolve, it’s essential to recognize both the benefits and limitations of the GPA scale, striving for a more comprehensive and inclusive approach to academic assessment.