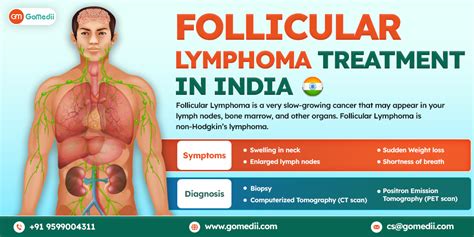
Follicular lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that affects the immune system, specifically the lymphatic system. It is characterized by the abnormal growth of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, in the lymph nodes. According to the American Cancer Society, follicular lymphoma accounts for approximately 20% of all NHL cases in the United States, with an estimated 14,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Understanding the complexities of follicular lymphoma is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Follicular Lymphoma
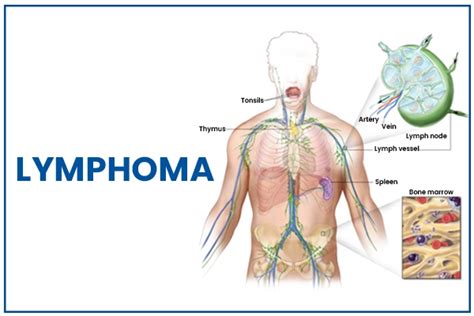
Follicular lymphoma is a slow-growing cancer that typically affects individuals over the age of 50. It is more common in women than men, and the exact cause is still unknown. However, research suggests that genetic mutations, environmental factors, and immune system dysfunction may contribute to the development of follicular lymphoma. The disease is usually diagnosed after a lymph node biopsy, which reveals the presence of cancerous cells. The symptoms of follicular lymphoma can vary, but common signs include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, weight loss, and fever.
Types of Follicular Lymphoma
There are two main subtypes of follicular lymphoma: grade 1-2 and grade 3. Grade 1-2 follicular lymphoma is the most common subtype, accounting for approximately 80% of all cases. It is characterized by a slow growth rate and a relatively good prognosis. Grade 3 follicular lymphoma, on the other hand, is more aggressive and has a poorer prognosis. The treatment approach for follicular lymphoma depends on the subtype, stage, and overall health of the patient.
| Subtype | Characteristics | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1-2 | Slow-growing, low-grade | Relatively good |
| Grade 3 | Aggressive, high-grade | Poorer |
Treatment Options for Follicular Lymphoma

The treatment of follicular lymphoma depends on the stage and subtype of the disease. In general, treatment options include watchful waiting, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy. Watchful waiting is often recommended for patients with early-stage, low-grade follicular lymphoma, as the disease may not require immediate treatment. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are commonly used to treat more advanced or aggressive cases. Immunotherapy, including rituximab and obinutuzumab, has emerged as a promising treatment option for follicular lymphoma, offering improved response rates and overall survival.
Emerging Therapies for Follicular Lymphoma
Recent advances in cancer research have led to the development of new therapies for follicular lymphoma. CAR-T cell therapy, for example, involves the use of genetically modified T cells to target and destroy cancer cells. This approach has shown significant promise in clinical trials, with high response rates and durable remissions. Other emerging therapies, including targeted therapies and checkpoint inhibitors, are also being investigated for their potential to improve treatment outcomes for follicular lymphoma patients.
Key Points
- Follicular lymphoma is a slow-growing cancer that affects the immune system
- There are two main subtypes: grade 1-2 and grade 3, with distinct characteristics and prognoses
- Treatment options include watchful waiting, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy
- Emerging therapies, such as CAR-T cell therapy and targeted therapies, offer new hope for improved treatment outcomes
- Personalized treatment planning and accurate diagnosis are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes
Living with Follicular Lymphoma
Receiving a diagnosis of follicular lymphoma can be a life-changing experience. Patients often face significant emotional and psychological challenges, including anxiety, depression, and fear of the unknown. However, with the right support and resources, individuals with follicular lymphoma can lead active and fulfilling lives. It is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Patients should also stay informed about their disease and treatment options, seeking guidance from healthcare providers and support groups as needed.
What are the common symptoms of follicular lymphoma?
+Common symptoms of follicular lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, weight loss, and fever. However, some patients may not experience any symptoms at all, especially in the early stages of the disease.
What is the prognosis for follicular lymphoma?
+The prognosis for follicular lymphoma depends on the subtype, stage, and overall health of the patient. Generally, patients with grade 1-2 follicular lymphoma have a relatively good prognosis, while those with grade 3 follicular lymphoma face a poorer outlook.
What are the treatment options for follicular lymphoma?
+Treatment options for follicular lymphoma include watchful waiting, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the stage and subtype of the disease, as well as the patient's overall health and preferences.
As research continues to advance our understanding of follicular lymphoma, patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop personalized treatment plans that improve outcomes and enhance quality of life. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with follicular lymphoma can navigate the challenges of their disease and find hope for a brighter future.