The world of tiny flying insects is often overlooked, yet it's teeming with fascinating creatures like gnats and flies. While both may seem similar at first glance, they belong to different families and exhibit distinct characteristics. Understanding the differences between gnats and flies can provide insights into their behaviors, habits, and the roles they play in our ecosystem. Let's delve into five key facts that differentiate gnats from flies, exploring their unique traits and importance in the natural world.
Biological Classification and Appearance
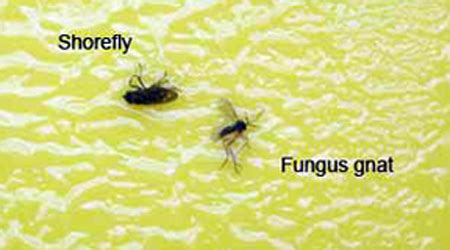
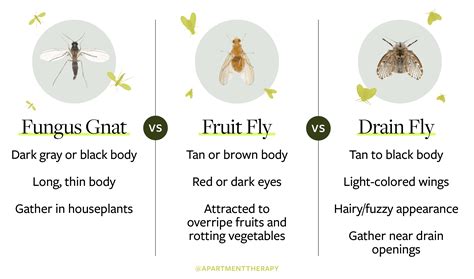
Gnats and flies are both insects, but they belong to different orders. Gnats are typically classified under the order Diptera, which also includes flies, but they are more specifically part of the suborder Nematocera. This suborder includes a wide range of species, many of which are small, delicate, and often mistaken for one another. Flies, on the other hand, are generally harder to confuse with gnats due to their larger size and more robust bodies. The size difference is one of the most noticeable distinctions between the two, with gnats usually being much smaller than flies. For example, fungus gnats, a common type of gnat, are typically around 1-5 millimeters in length, while houseflies, one of the most recognizable types of flies, can be 6-8 millimeters long.
Habitat and Diet
The habitats and diets of gnats and flies also vary significantly. Gnats often thrive in moist environments and are attracted to decaying organic matter, fungi, and even the moist soil of overwatered plants. They can be found near bodies of water, in damp basements, or around plants. Flies, while also found in various environments, tend to have a more diverse range of habitats and are attracted to a broader spectrum of food sources, including sweet substances, decaying matter, and even blood in the case of certain species like mosquitoes.
| Type of Insect | Typical Habitat | Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Gnats | Moist environments, near water or fungi | Decaying organic matter, fungi |
| Flies | Varying environments, including urban and natural settings | Sweet substances, decaying matter, blood (in some species) |
Behavior and Life Cycle

The behavior and life cycles of gnats and flies differ as well. Gnats are known for their swarming behavior, especially during mating. They can form large clouds of insects, which can be quite a nuisance to humans. Flies, on the other hand, do not swarm in the same way and tend to fly individually. The life cycle of gnats typically involves four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Flies undergo a similar transformation, but the specifics can vary depending on the species. For instance, the life cycle of a housefly can be as short as 10 days, while some gnats may take longer to mature.
Impact on Human Society
Both gnats and flies can have significant impacts on human society, albeit in different ways. Gnats are often considered pests due to their ability to damage plants and their presence in homes can be a nuisance. Certain species of gnats, like the eye gnat, can even cause discomfort to humans and animals by biting. Flies, especially those that bite like mosquitoes and horseflies, can transmit diseases and cause pain through their bites. However, flies also contribute to the ecosystem by serving as pollinators and decomposers, and some species are even used as a food source for humans and animals.
Key Points
- Gnats and flies belong to the same order (Diptera) but have distinct differences in appearance, habitat, and diet.
- Gnats are generally smaller, thrive in moist environments, and are attracted to decaying organic matter and fungi.
- Flies are larger, have a broader range of habitats, and are attracted to a variety of food sources including sweet substances and decaying matter.
- Both gnats and flies play important roles in the ecosystem as decomposers and, in some cases, pollinators.
- The life cycles of gnats and flies involve four stages (egg, larva, pupa, and adult), but the duration and specifics can vary significantly between species.
In conclusion, while gnats and flies may seem similar at first, they exhibit a range of differences in terms of their biology, behavior, and impact on human society. Understanding these distinctions not only enhances our appreciation for the diversity of life but also informs strategies for managing pest populations and appreciating the ecological roles these insects play.
What is the primary difference between gnats and flies in terms of their habitats?
+Gnats are typically found in moist environments and are attracted to decaying organic matter and fungi, while flies have a more diverse range of habitats and are attracted to a broader spectrum of food sources.
How do gnats and flies contribute to the ecosystem?
+Both gnats and flies play crucial roles in the ecosystem. They serve as decomposers, breaking down organic matter, and some species of flies are important pollinators. Additionally, they are a food source for various animals.
What is the average lifespan of a gnat versus a fly?
+The lifespan of gnats and flies can vary significantly depending on the species. However, gnats typically live for a few days to a week, while some species of flies can live for several weeks.