The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly the carbohydrates in a particular food raise blood sugar levels. It is an essential concept in nutrition, especially for individuals managing diabetes or trying to regulate their blood sugar levels. One of the most commonly consumed fruits worldwide is the banana, known for its rich taste, convenience, and nutritional benefits. Understanding the glycemic index of a banana can help individuals make informed dietary choices.
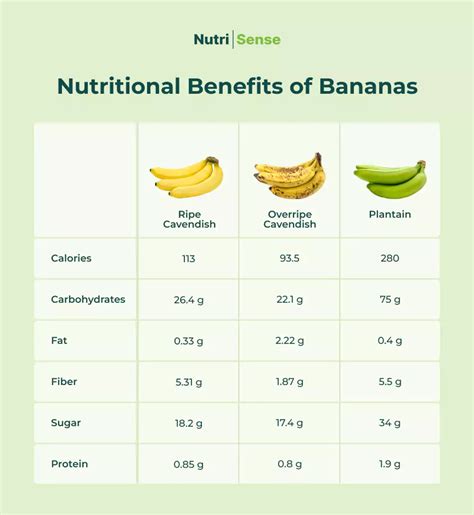
Bananas are a good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and several essential vitamins and minerals. The ripeness of a banana can significantly affect its glycemic index. Generally, the riper the banana, the higher its GI value, as the starches convert to more easily digestible sugars during the ripening process. A green, unripe banana will have a lower GI compared to a fully ripe one.
Key Points
- The glycemic index of a banana varies depending on its ripeness, with riper bananas having a higher GI.
- The average GI of a ripe banana is around 51, which is considered medium on the glycemic index scale.
- Bananas are also a good source of dietary fiber, which can help slow down the digestion and absorption of their natural sugars, potentially mitigating the impact on blood sugar levels.
- Portion control is essential when consuming bananas, especially for individuals with diabetes or those trying to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Cooking or processing bananas can alter their GI, with cooked bananas potentially having a higher GI than raw ones due to the breakdown of starches into more easily digestible carbohydrates.
Glycemic Index Values for Bananas
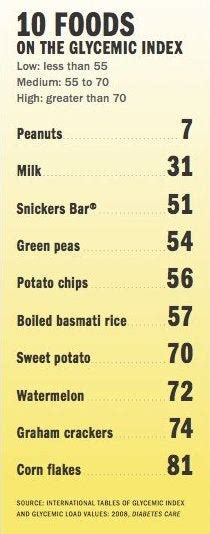
The glycemic index values for bananas can range from about 42 for a green, unripe banana to 51 for a ripe banana, with some studies suggesting that very ripe bananas might have a GI slightly above 60. However, the average GI value considered for a ripe banana is around 51. This value is relatively moderate, indicating that bananas cause a gradual and moderate rise in blood sugar levels compared to pure glucose, which is used as the reference point with a GI of 100.
Factors Influencing the Glycemic Index of Bananas
Several factors can influence the glycemic index of bananas, including the banana’s ripeness, as mentioned earlier. The variety of the banana can also play a role, though the differences are generally not significant enough to alter dietary advice based on GI alone. Additionally, the method of consumption—whether eaten raw, cooked, or as part of a mixed meal—can affect how the body digests and absorbs the carbohydrates in bananas.
| Condition of Banana | Glycemic Index Value |
|---|---|
| Green (Unripe) | 42 |
| Ripe | 51 |
| Overripe | Up to 60 |
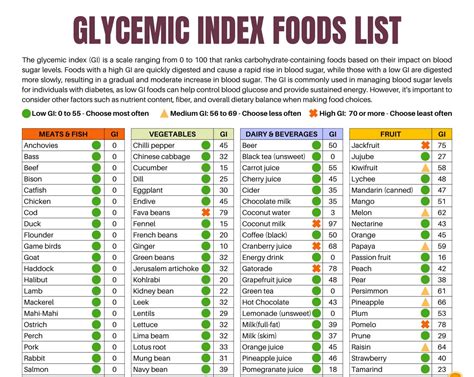
Practical Considerations for Consumption

For individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels, understanding the glycemic index of bananas and other foods is just the first step. Practical considerations, such as portion control and the timing of banana consumption in relation to meals and physical activity, can significantly impact how the body responds to the carbohydrates in bananas. Additionally, combining bananas with other foods that have a lower GI or that are high in protein and healthy fats can help moderate the glycemic response.
Nutritional Balance and Glycemic Management
Achieving nutritional balance is key to managing blood sugar levels effectively. This includes consuming a variety of foods from all food groups, being mindful of portion sizes, and selecting whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible. For bananas, this means enjoying them as part of a balanced diet, considering their GI, and being aware of how they fit into overall daily carbohydrate intake.
How does the ripeness of a banana affect its glycemic index?
+The ripeness of a banana significantly affects its glycemic index. As bananas ripen, their starches convert into more easily digestible sugars, which increases their GI. A riper banana will have a higher GI compared to an unripe one.
What is the average glycemic index of a ripe banana?
+The average glycemic index of a ripe banana is approximately 51, which is considered medium on the GI scale.
How can I incorporate bananas into my diet while managing blood sugar levels?
+To incorporate bananas into your diet while managing blood sugar levels, consider their GI, practice portion control, and balance your meals with other foods that have a lower GI or are high in protein and healthy fats. Combining bananas with nuts, seeds, or avocado, for example, can help moderate the glycemic response.
In conclusion, understanding the glycemic index of bananas and how it varies with ripeness can help individuals make more informed dietary choices, especially those managing blood sugar levels. By considering the GI of bananas and balancing their consumption with other nutrient-dense foods, individuals can enjoy the nutritional benefits of bananas while maintaining better control over their blood sugar levels.