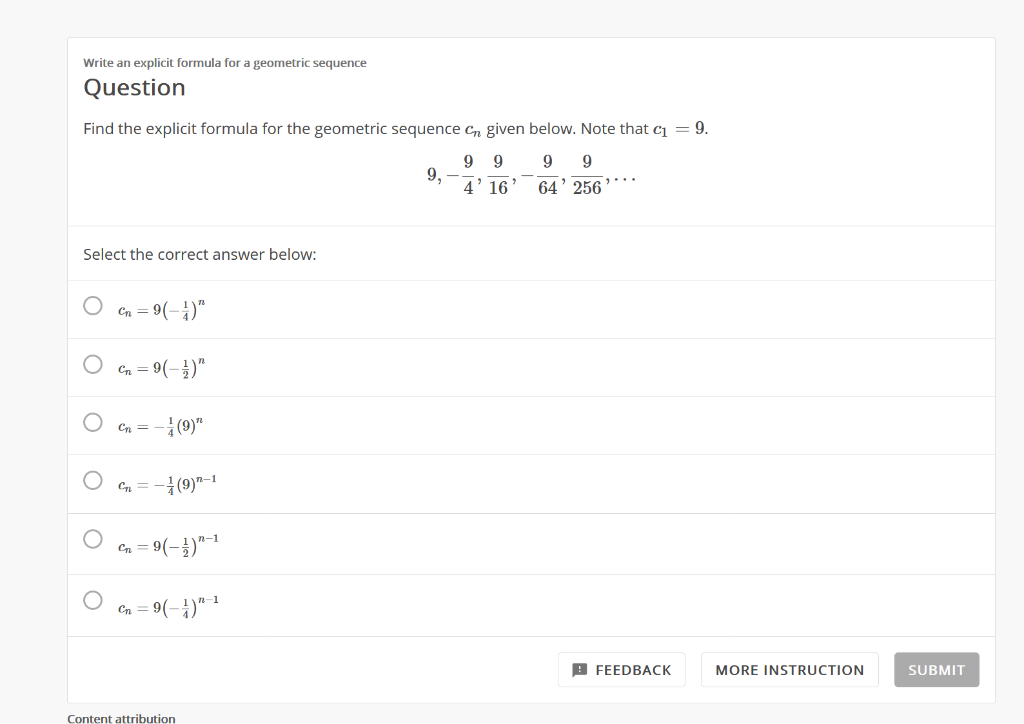
Geometric sequences and series are fundamental concepts in mathematics, crucial for understanding various phenomena in nature, finance, and other fields. A geometric sequence is a type of sequence where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. The explicit formula for the nth term of a geometric sequence is given by a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}, where a_n is the nth term, a_1 is the first term, and r is the common ratio. This formula allows for the direct calculation of any term in the sequence without needing to calculate all preceding terms.
Key Points
- The geometric sequence is defined by the formula a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}, where a_n is the nth term, a_1 is the first term, and r is the common ratio.
- The sum of the first n terms of a geometric sequence can be calculated using the formula S_n = a_1 \cdot \frac{1 - r^n}{1 - r} when r \neq 1.
- For an infinite geometric series where |r| < 1, the sum can be found using the formula S = \frac{a_1}{1 - r}.
- Geometric sequences and series have numerous applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and computer science.
- Understanding geometric sequences and series is essential for solving problems involving population growth, financial calculations, and signal processing.
Understanding Geometric Sequences

A geometric sequence is characterized by its first term (a_1) and the common ratio (r). For example, if the first term (a_1 = 2) and the common ratio (r = 3), the sequence would be 2, 6, 18, 54,…. Each term is obtained by multiplying the preceding term by 3. The explicit formula (a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)}) provides a straightforward method to find any term in the sequence. This is particularly useful in scenarios where the sequence is very long or when the terms are very large, making manual calculation impractical.
Calculating the Sum of a Geometric Series
Geometric series, which are the sums of the terms of geometric sequences, can be calculated using specific formulas depending on whether the series is finite or infinite. For a finite geometric series, the sum (S_n) of the first n terms is given by (S_n = a_1 \cdot \frac{1 - r^n}{1 - r}) when (r \neq 1). This formula is essential for applications such as calculating the total amount of money accumulated in a savings account with compound interest over a specific period. If (r = 1), the series becomes an arithmetic sequence, and the sum is simply (S_n = a_1 \cdot n), but this is a degenerate case of a geometric sequence.
| Formula Type | Formula | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| nth Term of Geometric Sequence | a_n = a_1 \cdot r^{(n-1)} | None |
| Sum of First n Terms of Geometric Series | S_n = a_1 \cdot \frac{1 - r^n}{1 - r} | r \neq 1 |
| Sum of Infinite Geometric Series | S = \frac{a_1}{1 - r} | |r| < 1 |
Applications of Geometric Sequences and Series

Geometric sequences and series have a wide range of applications across various disciplines. In finance, they are used to calculate compound interest, depreciation, and the present or future value of investments. In biology, geometric sequences can model population growth, where each generation is larger than the previous by a constant factor. In computer science, geometric series are used in algorithms for solving problems related to signal processing and data analysis.
Population Growth Modeling
A classic example of the application of geometric sequences is in modeling population growth. If a population of bacteria doubles every hour, starting with 100 bacteria, the population after (n) hours can be modeled using the geometric sequence formula (P_n = 100 \cdot 2^n), where (P_n) is the population size after (n) hours. This model assumes ideal conditions with unlimited resources and no deaths, illustrating the exponential growth characteristic of geometric sequences.
The importance of understanding geometric sequences and series cannot be overstated. They provide a fundamental framework for analyzing and predicting phenomena that exhibit exponential growth or decay. Whether in natural sciences, economics, or engineering, the ability to model and calculate using these mathematical tools is essential for making informed decisions and predicting outcomes.
What is the primary difference between a geometric sequence and a geometric series?
+A geometric sequence is a list of numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous term by a fixed, non-zero number called the common ratio. A geometric series, on the other hand, is the sum of the terms of a geometric sequence.
How do you calculate the sum of an infinite geometric series?
+The sum S of an infinite geometric series can be calculated using the formula S = \frac{a_1}{1 - r}, where a_1 is the first term and r is the common ratio, provided that |r| < 1.
What are some real-world applications of geometric sequences and series?
+Geometric sequences and series have applications in finance (compound interest, depreciation), biology (population growth), physics (half-life of radioactive materials), and computer science (signal processing, algorithm design).
In conclusion, geometric sequences and series are powerful mathematical tools with a wide range of applications. Understanding their principles and formulas is essential for anyone looking to analyze and predict exponential growth or decay in various fields. The explicit formula for the nth term of a geometric sequence and the formulas for the sum of finite and infinite geometric series provide a solid foundation for tackling problems in mathematics, science, and engineering.