The General Linear Group, denoted as GL(n, F), is a fundamental concept in linear algebra and group theory. It plays a crucial role in various areas of mathematics, including geometry, representation theory, and number theory. In this article, we will delve into the definition, properties, and applications of the General Linear Group, providing a comprehensive overview of this essential mathematical structure.
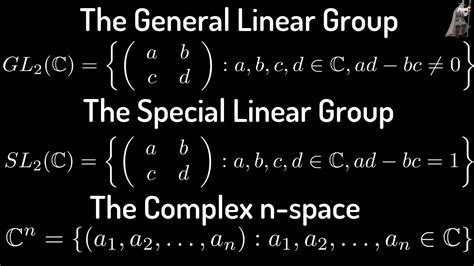
The General Linear Group is defined as the set of all invertible n x n matrices with entries in a field F, where n is a positive integer. The field F can be any mathematical structure that satisfies certain properties, such as the real numbers ®, complex numbers ©, or finite fields (e.g., F_p, where p is a prime number). The General Linear Group is equipped with the operation of matrix multiplication, which is associative, has an identity element (the identity matrix), and each element has an inverse.
Properties of the General Linear Group
The General Linear Group exhibits several important properties that make it a valuable tool in mathematics. Some of these properties include:
- Group structure: The General Linear Group forms a group under matrix multiplication, meaning that it satisfies the closure, associativity, identity, and invertibility properties.
- Dimension: The dimension of the General Linear Group is n^2, which can be seen by considering the n x n matrices as vectors in a vector space of dimension n^2.
- Topology: The General Linear Group can be equipped with a topology, known as the Zariski topology, which allows for the study of geometric properties, such as compactness and connectedness.
- Representation theory: The General Linear Group has a rich representation theory, which describes the ways in which the group can act on vector spaces.
Key Points
- The General Linear Group is a fundamental concept in linear algebra and group theory.
- It is defined as the set of all invertible n x n matrices with entries in a field F.
- The General Linear Group has a group structure, dimension, and topology.
- It plays a crucial role in representation theory, geometry, and number theory.
- The General Linear Group has numerous applications in physics, engineering, and computer science.
Applications of the General Linear Group
The General Linear Group has far-reaching implications in various areas of mathematics and science. Some of its notable applications include:
- Physics: The General Linear Group is used to describe the symmetries of physical systems, such as the Lorentz group in special relativity and the gauge group in particle physics.
- Computer science: The General Linear Group is employed in computer graphics, machine learning, and cryptography, where it is used to perform tasks such as linear transformations, matrix factorizations, and encryption.
- Engineering: The General Linear Group is applied in control theory, signal processing, and network analysis, where it is used to model and analyze complex systems.
- Number theory: The General Linear Group is used to study the properties of integers and modular forms, which are essential in number theory and algebraic geometry.
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Physics | Symmetries of physical systems |
| Computer science | Computer graphics, machine learning, cryptography |
| Engineering | Control theory, signal processing, network analysis |
| Number theory | Properties of integers and modular forms |
Subgroups and Quotients of the General Linear Group

The General Linear Group has several important subgroups and quotients that are used in various mathematical contexts. Some of these include:
- Special Linear Group: The Special Linear Group, denoted as SL(n, F), is the subgroup of the General Linear Group consisting of matrices with determinant 1.
- Orthogonal Group: The Orthogonal Group, denoted as O(n, F), is the subgroup of the General Linear Group consisting of matrices that preserve the dot product.
- Symplectic Group: The Symplectic Group, denoted as Sp(n, F), is the subgroup of the General Linear Group consisting of matrices that preserve the symplectic form.
These subgroups and quotients are used to study the properties of linear transformations and to classify the possible symmetries of mathematical objects.
Open Problems and Future Directions
Despite its importance and widespread applications, the General Linear Group remains an active area of research, with many open problems and future directions. Some of these include:
- Representation theory: The representation theory of the General Linear Group is still an active area of research, with many open questions about the structure and properties of its representations.
- Geometry: The geometry of the General Linear Group, including its topology and geometric invariants, is still not fully understood and is the subject of ongoing research.
- Applications: The applications of the General Linear Group continue to grow, with new areas such as machine learning and data science emerging as important areas of research.
What is the General Linear Group?
+The General Linear Group is the set of all invertible n x n matrices with entries in a field F, equipped with the operation of matrix multiplication.
What are the properties of the General Linear Group?
+The General Linear Group has a group structure, dimension, and topology, and plays a crucial role in representation theory, geometry, and number theory.
What are the applications of the General Linear Group?
+The General Linear Group has numerous applications in physics, engineering, computer science, and number theory, including symmetries of physical systems, computer graphics, and cryptography.
In conclusion, the General Linear Group is a fundamental concept in linear algebra and group theory, with far-reaching implications in various areas of mathematics and science. Its properties, applications, and subgroups make it a powerful tool for understanding the structure and properties of linear transformations, and its study continues to be an active area of research.