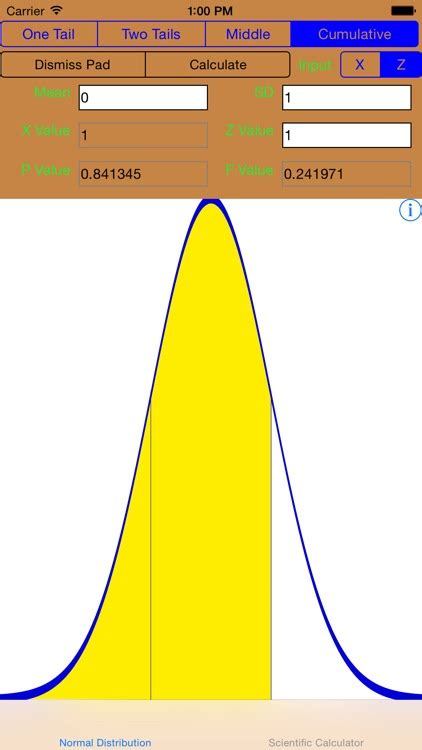
The Gaussian distribution, also known as the normal distribution, is a probability distribution that is widely used in statistics and data analysis. It is a continuous distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean. In this article, we will explore the concept of Gaussian distribution, its properties, and how to calculate it using a Gaussian distribution calculator.
What is Gaussian Distribution?
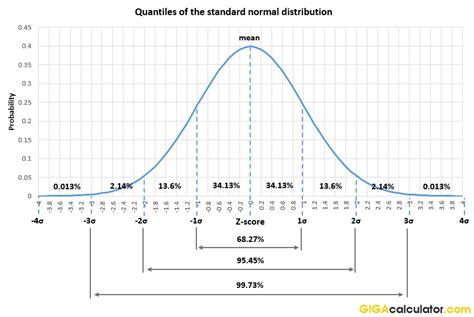
The Gaussian distribution is a probability distribution that is characterized by its mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ). It is a continuous distribution, meaning that it can take on any value within a given range, and it is symmetric about the mean. The Gaussian distribution is often used to model real-world phenomena, such as the distribution of heights, weights, and IQ scores, because it provides a good approximation of the underlying distribution of the data.
Properties of Gaussian Distribution
The Gaussian distribution has several important properties that make it useful for statistical analysis. These properties include:
- Mean (μ): The mean of the Gaussian distribution is the central tendency of the distribution, and it is the value around which the distribution is symmetric.
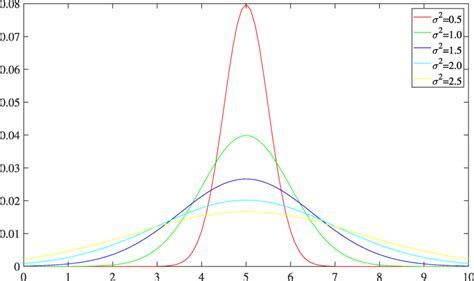
- Standard Deviation (σ): The standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution is a measure of the spread of the distribution, and it is the square root of the variance.
- Variance (σ^2): The variance of the Gaussian distribution is a measure of the spread of the distribution, and it is the average of the squared differences from the mean.
- Skewness: The Gaussian distribution is symmetric about the mean, meaning that it has zero skewness.
- Kurtosis: The Gaussian distribution has a kurtosis of 3, which means that it is mesokurtic, or “normal-shaped”.
Gaussian Distribution Calculator
A Gaussian distribution calculator is a tool that can be used to calculate the probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a Gaussian distribution. The calculator typically takes in the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) as input, and it outputs the PDF and CDF values for a given value of x.
How to Use a Gaussian Distribution Calculator
To use a Gaussian distribution calculator, follow these steps:
- Enter the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) of the Gaussian distribution.
- Enter the value of x for which you want to calculate the PDF and CDF.
- Click the “Calculate” button to calculate the PDF and CDF values.
- View the results, which will typically include the PDF and CDF values, as well as a graph of the Gaussian distribution.
| Mean (μ) | Standard Deviation (σ) | x | CDF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.24197 | 0.84134 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 0.05399 | 0.97725 |
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 0.00443 | 0.99865 |
Key Points
- The Gaussian distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean.
- The Gaussian distribution is characterized by its mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ).
- A Gaussian distribution calculator can be used to calculate the probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a Gaussian distribution.
- The calculator takes in the mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ) as input and outputs the PDF and CDF values for a given value of x.
- Understanding the properties of the Gaussian distribution and how to interpret the results is essential when using a Gaussian distribution calculator.
Applications of Gaussian Distribution
The Gaussian distribution has numerous applications in statistics, data analysis, and real-world phenomena. Some examples include:
- Statistics: The Gaussian distribution is used to model the distribution of sample means and to calculate confidence intervals.
- Data Analysis: The Gaussian distribution is used to model the distribution of data and to identify outliers.
- Engineering: The Gaussian distribution is used to model the distribution of measurement errors and to calculate reliability.
- Finance: The Gaussian distribution is used to model the distribution of stock prices and to calculate risk.
Real-World Examples
The Gaussian distribution is used to model real-world phenomena, such as:
- Heights: The distribution of heights in a population is often modeled using a Gaussian distribution.
- Weights: The distribution of weights in a population is often modeled using a Gaussian distribution.
- IQ Scores: The distribution of IQ scores in a population is often modeled using a Gaussian distribution.
What is the difference between a Gaussian distribution and a normal distribution?
+The terms "Gaussian distribution" and "normal distribution" are often used interchangeably, but they refer to the same probability distribution.
How do I calculate the mean and standard deviation of a Gaussian distribution?
+The mean and standard deviation of a Gaussian distribution can be calculated using the formulas μ = ∑x_i / n and σ = √(∑(x_i - μ)^2 / (n - 1)), respectively.
What are some common applications of the Gaussian distribution?
+The Gaussian distribution has numerous applications in statistics, data analysis, and real-world phenomena, including modeling the distribution of sample means, identifying outliers, and calculating reliability.
In conclusion, the Gaussian distribution is a powerful tool for statistical analysis and data modeling. Understanding its properties and how to calculate it using a Gaussian distribution calculator can provide valuable insights into real-world phenomena. By applying the concepts and formulas outlined in this article, users can gain a deeper understanding of the Gaussian distribution and its applications in various fields.