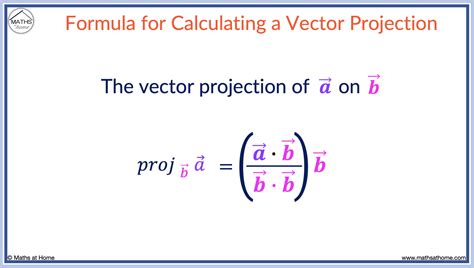
The projection formula is a fundamental concept in mathematics and statistics, used to predict the future value of a variable based on its past behavior. It is a powerful tool for forecasting and has numerous applications in various fields, including finance, economics, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the details of the projection formula, its components, and its applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential concept.
Key Points
- The projection formula is used to predict the future value of a variable based on its past behavior.
- It consists of three main components: the historical data, the trend component, and the seasonal component.
- The formula can be applied to various fields, including finance, economics, and engineering.
- It is essential to consider the limitations and potential biases of the projection formula when using it for forecasting.
- The formula can be modified and extended to accommodate different types of data and forecasting needs.
Understanding the Projection Formula
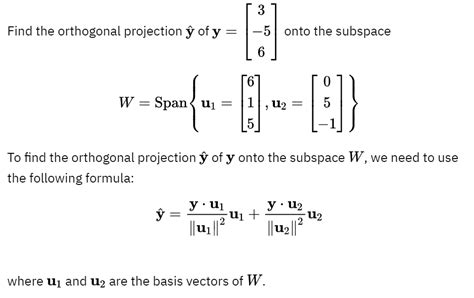
The projection formula is based on the idea that the future value of a variable can be predicted by analyzing its past behavior. The formula takes into account the historical data, trend, and seasonal components of the variable to make predictions. The general form of the projection formula is:
y(t) = β0 + β1 \* x(t) + ε(t)
where y(t) is the predicted value of the variable at time t, β0 is the intercept or constant term, β1 is the slope coefficient, x(t) is the historical data, and ε(t) is the error term.
Components of the Projection Formula
The projection formula consists of three main components: the historical data, the trend component, and the seasonal component.
Historical Data: The historical data is the foundation of the projection formula. It provides the basis for predicting the future value of the variable. The historical data can be in the form of time series data, which is a sequence of data points measured at regular time intervals.
Trend Component: The trend component represents the overall direction or pattern of the variable over time. It can be linear or non-linear, and it is typically estimated using regression analysis. The trend component is essential in capturing the long-term behavior of the variable.
Seasonal Component: The seasonal component represents the periodic fluctuations in the variable that occur at fixed intervals, such as daily, weekly, or yearly cycles. The seasonal component is essential in capturing the short-term behavior of the variable.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Historical Data | Foundation of the projection formula |
| Trend Component | Overall direction or pattern of the variable |
| Seasonal Component | Periodic fluctuations in the variable |
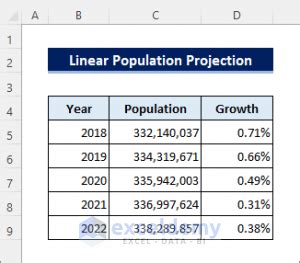
Applications of the Projection Formula
The projection formula has numerous applications in various fields, including finance, economics, and engineering. Some of the common applications of the formula include:
Financial Forecasting: The projection formula is widely used in finance to predict the future value of stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. It is also used to forecast revenue, expenses, and profits of companies.
Economic Forecasting: The formula is used in economics to predict the future value of economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment rates.
Engineering: The projection formula is used in engineering to predict the future value of variables, such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate, in complex systems.
Limitations and Potential Biases
The projection formula is not without limitations and potential biases. Some of the common limitations and biases include:
Assumes Linearity: The formula assumes that the relationship between the variables is linear, which may not always be the case.
Ignore Non-Linear Relationships: The formula ignores non-linear relationships between variables, which can lead to inaccurate predictions.
Sensitive to Outliers: The formula is sensitive to outliers, which can affect the accuracy of the predictions.
What is the projection formula used for?
+The projection formula is used to predict the future value of a variable based on its past behavior. It is a powerful tool for forecasting and has numerous applications in various fields, including finance, economics, and engineering.
What are the components of the projection formula?
+The projection formula consists of three main components: the historical data, the trend component, and the seasonal component. The historical data provides the basis for predicting the future value of the variable, while the trend and seasonal components capture the overall direction and periodic fluctuations of the variable.
What are the limitations and potential biases of the projection formula?
+The projection formula has several limitations and potential biases, including assuming linearity, ignoring non-linear relationships, and being sensitive to outliers. It is essential to consider these limitations and biases when using the formula for forecasting.
In conclusion, the projection formula is a powerful tool for forecasting that has numerous applications in various fields. However, it is essential to consider the limitations and potential biases of the formula when using it for forecasting. By understanding the components of the formula and its applications, users can make informed decisions and predictions about the future value of variables.