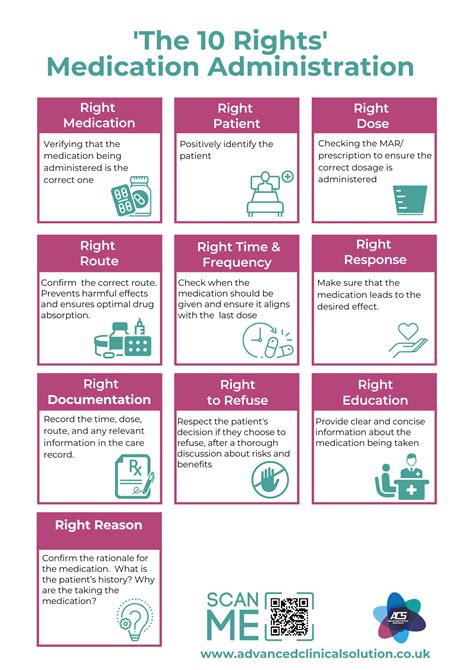
The five rights of medication administration are a fundamental concept in the field of nursing and healthcare, designed to ensure patient safety and prevent medication errors. These rights have been widely adopted as a standard of practice in healthcare settings worldwide, serving as a critical checklist for healthcare professionals to follow when administering medications to patients. The five rights of medication administration are the right patient, the right medication, the right dose, the right route, and the right time.
Historically, the concept of the five rights of medication administration emerged as a response to the growing concern over medication errors in the healthcare system. The Joint Commission, a non-profit organization that accredits and certifies healthcare organizations, has identified medication errors as a significant contributor to patient harm. In response, the five rights framework was developed to provide a structured approach to medication administration, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and attention to detail at each stage of the process.
Key Points
- The five rights of medication administration are a critical component of patient safety in healthcare settings.
- Each right must be verified before administering a medication to a patient.
- The right patient, medication, dose, route, and time are the core elements of the five rights framework.
- Barcoding technology and electronic health records have enhanced the safety of medication administration by reducing errors.
- Ongoing education and training for healthcare professionals are essential for maintaining competency in medication administration and adhering to the five rights.
Understanding the Five Rights

The first right, the right patient, involves verifying the identity of the patient to ensure that the medication is being administered to the correct individual. This step is crucial in preventing mix-ups and ensuring that each patient receives the medications prescribed for them. The use of two patient identifiers, such as the patient’s name and date of birth, is a recommended practice for verifying patient identity.
The second right, the right medication, requires that the healthcare professional verify the medication against the prescription or medication order to ensure accuracy. This involves checking the medication's name, strength, and formulation to prevent errors. The use of barcode scanning technology can aid in this process by automatically verifying the medication's identity.
Right Dose and Route
The third right, the right dose, involves administering the correct amount of medication as prescribed. This includes verifying the dose against the prescription or medication order and ensuring that the dose is appropriate for the patient’s age, weight, and medical condition. The fourth right, the right route, refers to the method by which the medication is administered, such as orally, intravenously, or topically. Ensuring the correct route of administration is critical for the medication’s efficacy and safety.
The fifth right, the right time, involves administering the medication at the prescribed time to ensure its effectiveness and to minimize potential side effects. This may involve synchronizing medication administration with other healthcare activities, such as meals or other treatments, to optimize the medication's benefits and reduce risks.
| Right | Description | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| Right Patient | Verify patient identity | Two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth) |
| Right Medication | Verify medication against prescription | Barcode scanning, visual inspection |
| Right Dose | Administer correct dose | Verify dose against prescription, consider patient factors (age, weight, condition) |
| Right Route | Administer via correct route | Verify route against prescription, use appropriate administration technique |
| Right Time | Administer at prescribed time | Verify time against prescription, consider synchronization with other healthcare activities |

Implementation and Challenges
Implementing the five rights of medication administration requires a multifaceted approach that includes education, technology, and policy development. Healthcare organizations must invest in ongoing education and training for their staff to ensure competency in medication administration and adherence to the five rights. The adoption of technology, such as barcode scanning and electronic health records, can significantly reduce medication errors by automating the verification process and providing real-time access to patient information.
Despite the benefits of the five rights framework, challenges persist in its implementation. These challenges include resource constraints, lack of standardization in medication labeling and packaging, and the need for continuous monitoring and evaluation to ensure that the five rights are consistently applied in practice. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of medication regimens and the rise of polypharmacy (the use of multiple medications by a patient) pose additional challenges for healthcare professionals in adhering to the five rights.
Future Directions
Looking to the future, the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, into medication administration systems holds promise for further enhancing patient safety. These technologies can analyze large datasets to identify potential medication errors before they occur and provide real-time alerts to healthcare professionals. Additionally, the development of more user-friendly and standardized medication packaging and labeling will aid in the accurate identification and administration of medications.
In conclusion, the five rights of medication administration are a cornerstone of patient safety in healthcare, providing a structured approach to ensuring that medications are administered correctly and safely. By understanding and adhering to these rights, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risk of medication errors and improve patient outcomes. Ongoing education, technological innovation, and policy development will continue to play critical roles in supporting the effective implementation of the five rights in clinical practice.
What are the five rights of medication administration?
+The five rights are the right patient, the right medication, the right dose, the right route, and the right time. These rights are designed to ensure that medications are administered safely and effectively to patients.
Why are the five rights important?
+The five rights are important because they help prevent medication errors, which can be harmful or even fatal to patients. By following the five rights, healthcare professionals can ensure that medications are administered correctly and safely.
How can technology support the five rights of medication administration?
+Technology, such as barcode scanning and electronic health records, can support the five rights by automating the verification process, providing real-time access to patient information, and reducing the risk of human error.
What challenges exist in implementing the five rights of medication administration?
+Challenges include resource constraints, lack of standardization in medication labeling and packaging, and the need for continuous monitoring and evaluation to ensure that the five rights are consistently applied in practice.
How can healthcare professionals ensure they are following the five rights correctly?
+Healthcare professionals can ensure they are following the five rights correctly by staying up-to-date with the latest guidelines and best practices, using technology to support the verification process, and continuously monitoring and evaluating their practice to identify areas for improvement.



