Fever, a common symptom of various illnesses, has been a subject of interest for medical professionals and researchers for centuries. The concept of fever has evolved over time, from being considered a disease in itself to being recognized as a symptom of an underlying condition. With the advancement of medical science, our understanding of fever has improved significantly, and we now know that it is a complex physiological response to infection or inflammation. In this article, we will explore 5 ways fever affects the body and discuss the latest research on this topic.
Key Points
- Fever is a natural response to infection or inflammation, and it plays a crucial role in the body's defense mechanism.
- The hypothalamus, the temperature regulation center in the brain, controls the body's temperature and responds to the presence of pyrogens.
- Fever can have both positive and negative effects on the body, depending on its severity and duration.
- Some studies suggest that fever can have beneficial effects on the immune system, such as enhancing the production of white blood cells.
- However, high and prolonged fever can be detrimental to the body, causing damage to the brain, kidneys, and other organs.
The Physiological Response to Fever
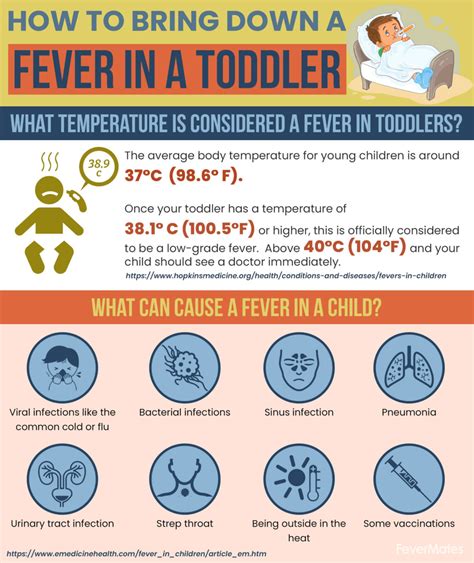
When the body detects the presence of an infectious agent, such as a bacterium or virus, it responds by producing pyrogens, which are substances that induce fever. The hypothalamus, the temperature regulation center in the brain, receives signals from the immune system and responds by increasing the body’s temperature. This increase in temperature is mediated by the release of prostaglandins, which are hormone-like substances that stimulate the hypothalamus to produce heat. As a result, the body’s temperature rises, and the individual experiences the characteristic symptoms of fever, such as chills, sweating, and fatigue.
The Role of the Hypothalamus in Fever Regulation
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s temperature and responding to the presence of pyrogens. It acts as a thermostat, constantly monitoring the body’s temperature and making adjustments as necessary to maintain a stable temperature. When the hypothalamus detects the presence of pyrogens, it responds by increasing the body’s temperature, which helps to create an environment that is unfavorable for the growth and reproduction of the infectious agent. The hypothalamus achieves this by stimulating the release of heat-producing substances, such as thyroxine, and by increasing the body’s metabolic rate.
| Body Temperature | Effects on the Body |
|---|---|
| Normal (98.6°F/37°C) | No significant effects |
| Mild fever (100.4°F/38°C) | Enhanced immune response, increased production of white blood cells |
| High fever (104°F/40°C) | Detrimental effects on the brain, kidneys, and other organs |
The Benefits and Risks of Fever

While fever is a natural response to infection or inflammation, it can have both positive and negative effects on the body. On the one hand, fever can enhance the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections. Additionally, fever can create an environment that is unfavorable for the growth and reproduction of the infectious agent, which can help to reduce the severity of the illness. On the other hand, high and prolonged fever can be detrimental to the body, causing damage to the brain, kidneys, and other organs. It is essential to recognize the signs of severe fever, such as seizures, confusion, and difficulty breathing, and to seek medical attention immediately if these symptoms occur.
The Importance of Monitoring Body Temperature
Monitoring body temperature is crucial in managing fever and preventing its potential complications. It is essential to use a reliable thermometer, such as a digital thermometer, to accurately measure the body’s temperature. Additionally, it is important to be aware of the signs of severe fever and to seek medical attention immediately if these symptoms occur. In some cases, medication, such as antipyretics, may be necessary to reduce the body’s temperature and alleviate the symptoms of fever.
What is the normal body temperature range?
+The normal body temperature range is between 97.7°F (36.5°C) and 99.5°F (37.5°C).
What are the signs of severe fever?
+The signs of severe fever include seizures, confusion, difficulty breathing, and chest pain.
How can I reduce my body temperature?
+You can reduce your body temperature by taking medication, such as antipyretics, staying hydrated, and using cool compresses or ice packs.
In conclusion, fever is a complex physiological response to infection or inflammation, and it plays a crucial role in the body’s defense mechanism. While fever can have both positive and negative effects on the body, it is essential to recognize the signs of severe fever and to seek medical attention immediately if these symptoms occur. By understanding the physiological response to fever and the importance of monitoring body temperature, we can better manage fever and prevent its potential complications.



