The realm of female hormone testing is a complex and multifaceted field, encompassing a wide array of assessments designed to evaluate the delicate balance of hormones that play a crucial role in the female body. Hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, among others, are pivotal in regulating menstrual cycles, fertility, and overall health. The following is a comprehensive list of female hormone tests, each serving a unique purpose in diagnosing and managing various conditions related to hormonal imbalances.
Introduction to Female Hormone Tests

Female hormone tests are medical assessments used to measure the levels of different hormones in the body. These tests can help diagnose hormonal imbalances, which can lead to a variety of symptoms and health issues, including irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and mood changes. The choice of test depends on the symptoms presented and the suspected underlying condition. Understanding the different types of female hormone tests and their applications is essential for both healthcare providers and patients seeking to address hormonal imbalances.
Key Points
- Female hormone tests measure the levels of various hormones in the body to diagnose and manage hormonal imbalances.
- Common female hormones tested include estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH).
- The choice of hormone test depends on the patient's symptoms and the suspected underlying condition.
- Tests can be performed through blood samples, urine samples, or saliva samples.
- Interpreting hormone test results requires consideration of the individual's menstrual cycle phase, age, and other health factors.
Types of Female Hormone Tests
Several types of tests are available to assess female hormone levels, each targeting specific hormones and serving different diagnostic purposes.
Estrogen Test
Estrogen tests measure the levels of estrogen in the blood or urine. Estrogen plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics and reproductive processes. Abnormal estrogen levels can lead to issues such as irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and certain types of cancer.
Progesterone Test
The progesterone test assesses the level of progesterone, a hormone essential for preparing the uterus to implant a fertilized egg. It also helps maintain pregnancy. Low levels of progesterone can lead to miscarriage or infertility.
Testosterone Test
Although often associated with males, females also produce small amounts of testosterone, which is important for overall health, including bone density and libido. High levels of testosterone in females can lead to conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), characterized by acne, excess hair growth, and cysts on the ovaries.
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Test
FSH is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries, which produce estrogen. An FSH test can help diagnose issues related to fertility and menopause. Elevated FSH levels can indicate diminished ovarian reserve or menopause.
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Test
LH, another hormone produced by the pituitary gland, triggers the release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation) and the production of progesterone by the empty follicle in the ovary. The LH test can help evaluate fertility issues and diagnose conditions like PCOS.
| Hormone | Normal Range | Test Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Estrogen | Varies by age and menstrual cycle phase | Evaluate menstrual irregularities, fertility issues |
| Progesterone | 2-25 ng/mL in the mid-luteal phase | Assess ovulation, pregnancy maintenance |
| Testosterone | 15-70 ng/dL | Diagnose hyperandrogenism, PCOS |
| FSH | 1.4-9.6 IU/L in premenopausal women | Evaluate fertility, menopause status |
| LH | 1.9-12.5 IU/L in the follicular phase | Assess ovulation, fertility issues |
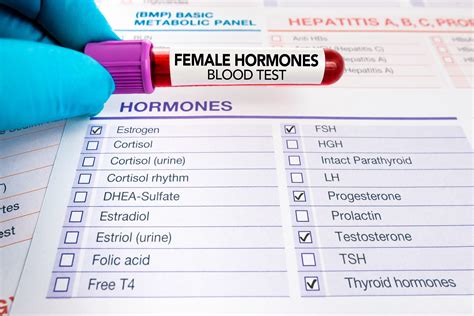
Implications and Applications of Female Hormone Tests
The results of female hormone tests have significant implications for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of various conditions. For instance, hormonal imbalances can be treated with hormone replacement therapy (HRT), birth control pills, or other medications targeting specific hormonal deficiencies or excesses. Lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and stress management, can also play a crucial role in restoring hormonal balance.
Limitations and Considerations
While female hormone tests are valuable diagnostic tools, their interpretation requires careful consideration of several factors, including the patient’s age, menstrual cycle phase, and overall health status. Additionally, the timing of the test and the methodology used can affect the results. It’s also important to note that hormonal imbalances can have complex underlying causes, and comprehensive diagnostic approaches often involve a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
What is the purpose of female hormone tests?
+Female hormone tests are used to measure the levels of different hormones in the body, helping to diagnose and manage hormonal imbalances that can lead to various health issues, including irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and mood changes.
How are female hormone tests performed?
+These tests can be performed through blood samples, urine samples, or saliva samples, depending on the hormone being tested and the specific requirements of the test.
What factors can affect the results of female hormone tests?
+Several factors can influence hormone levels, including the phase of the menstrual cycle, age, certain medications, and overall health status. It's essential to consider these factors when interpreting test results.
In conclusion, female hormone tests are indispensable tools for diagnosing and managing conditions related to hormonal imbalances in women. Understanding the different types of tests, their applications, and the factors that can influence their results is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. By leveraging this knowledge, individuals can better navigate the complex landscape of female hormone health, leading to more informed decisions and improved outcomes.