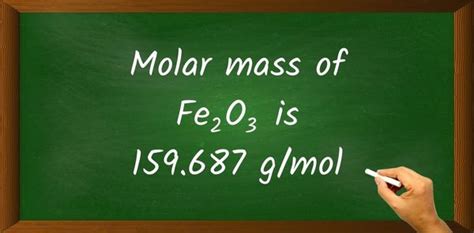The molar mass of Fe2O3, also known as iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that has numerous applications in various fields, including materials science, catalysis, and environmental remediation. To calculate the molar mass of Fe2O3, we need to consider the atomic masses of its constituent elements, namely iron (Fe) and oxygen (O). The atomic mass of iron is approximately 55.847 g/mol, while the atomic mass of oxygen is approximately 15.999 g/mol.
Key Points
- The molar mass of Fe2O3 can be calculated using the atomic masses of iron and oxygen.
- The formula for calculating the molar mass of Fe2O3 is 2(55.847) + 3(15.999) = 111.694 + 47.997 = 159.691 g/mol.
- Understanding the molar mass of Fe2O3 is crucial for various applications, including materials synthesis and catalysis.
- Fe2O3 has a range of applications, including pigments, catalysts, and magnetic materials.
- The molar mass of Fe2O3 is an essential parameter in determining its physical and chemical properties.
Calculating the Molar Mass of Fe2O3
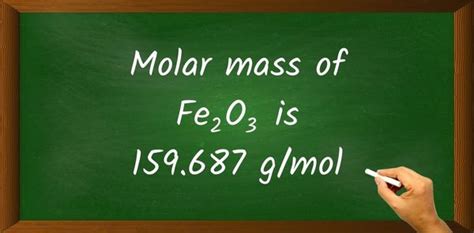
To calculate the molar mass of Fe2O3, we need to multiply the atomic mass of iron by 2 and the atomic mass of oxygen by 3, and then add the results together. Using the atomic masses mentioned earlier, the calculation is as follows: 2(55.847) + 3(15.999) = 111.694 + 47.997 = 159.691 g/mol. This value represents the molar mass of Fe2O3, which is essential for various chemical calculations and applications.
Applications of Fe2O3 Molar Mass
The molar mass of Fe2O3 has numerous applications in various fields. For example, in materials science, the molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to determine the stoichiometry of iron oxide-based materials, which is crucial for their synthesis and characterization. In catalysis, the molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to calculate the amount of catalyst required for a specific reaction, which is essential for optimizing reaction conditions and yields.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms | Total Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | 55.847 | 2 | 111.694 |
| Oxygen (O) | 15.999 | 3 | 47.997 |
| Total | 159.691 |
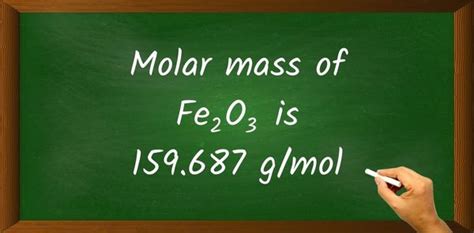
5 Ways to Apply the Molar Mass of Fe2O3

The molar mass of Fe2O3 has numerous applications in various fields, including materials science, catalysis, and environmental remediation. Here are 5 ways to apply the molar mass of Fe2O3:
1. Materials Synthesis: The molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to determine the stoichiometry of iron oxide-based materials, which is crucial for their synthesis and characterization. By controlling the stoichiometry of Fe2O3, researchers can create materials with specific properties, such as magnetic, optical, or catalytic properties.
2. Catalysis: The molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to calculate the amount of catalyst required for a specific reaction, which is essential for optimizing reaction conditions and yields. Fe2O3 is a common catalyst for various reactions, including the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and the oxidation of carbon monoxide.
3. Environmental Remediation: The molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to calculate the amount of iron oxide required for environmental remediation applications, such as the removal of heavy metals from contaminated soil or water. Fe2O3 has been shown to be effective in removing various heavy metals, including lead, mercury, and arsenic.
4. Pharmaceutical Applications: The molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to calculate the amount of iron oxide required for pharmaceutical applications, such as the synthesis of iron-based drugs or the development of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents. Fe2O3 has been shown to be biocompatible and non-toxic, making it a promising material for biomedical applications.
5. Magnetic Materials: The molar mass of Fe2O3 is used to calculate the amount of iron oxide required for the synthesis of magnetic materials, such as ferrofluids or magnetic nanoparticles. Fe2O3 has been shown to exhibit unique magnetic properties, making it a promising material for various applications, including magnetic storage devices and magnetic sensors.
What is the molar mass of Fe2O3?
+The molar mass of Fe2O3 is approximately 159.691 g/mol.
What are the applications of Fe2O3 molar mass?
+The molar mass of Fe2O3 has numerous applications in various fields, including materials science, catalysis, environmental remediation, pharmaceutical applications, and magnetic materials.
How is the molar mass of Fe2O3 calculated?
+The molar mass of Fe2O3 is calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of iron by 2 and the atomic mass of oxygen by 3, and then adding the results together.