The concept of arithmetic sequences is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, particularly in the realm of number patterns and algebra. An arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers where the difference between any two successive members is constant. This constant difference is called the common difference. Understanding arithmetic sequences is crucial for solving various mathematical problems and for applying mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios. In this article, we will explore five key aspects of arithmetic sequences to deepen our understanding of this important mathematical concept.
Definition and Basic Properties
An arithmetic sequence is defined by the formula a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d, where a_n is the nth term of the sequence, a_1 is the first term, n is the term number, and d is the common difference. For example, the sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, 14 is an arithmetic sequence with a first term a_1 = 2 and a common difference d = 3. The basic properties of arithmetic sequences include the fact that the difference between consecutive terms is constant, and the sequence can be finite or infinite.
Calculating the nth Term
One of the critical applications of arithmetic sequences is calculating the nth term. This can be done using the formula a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d. For instance, to find the 10th term of the sequence 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, we use a_{10} = 2 + (10-1)3 = 2 + 9*3 = 2 + 27 = 29. Understanding how to calculate the nth term is essential for predicting future terms in a sequence and for solving problems that involve sequences.
| Term Number | Term Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 8 |
| 4 | 11 |
| 5 | 14 |

Applications of Arithmetic Sequences
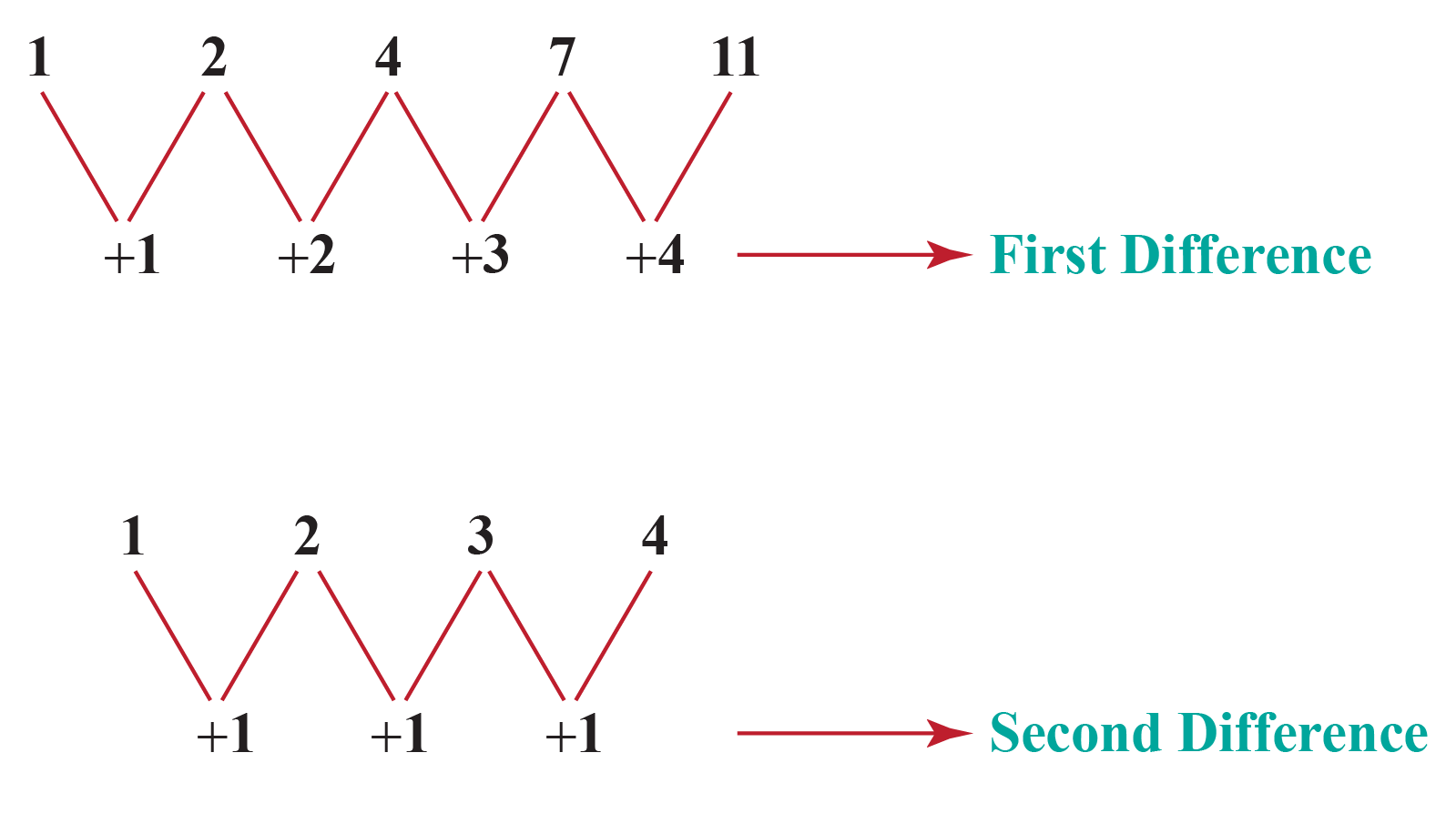
Arithmetic sequences have numerous applications in real-world scenarios. They can be used to model population growth, financial transactions, and other phenomena where a constant change occurs over a period. For example, if a company’s profit increases by 10,000 every year, starting from an initial profit of 50,000, the sequence of profits over the years would form an arithmetic sequence with a first term of 50,000 and a common difference of 10,000.
Solving Problems Involving Arithmetic Sequences
Solving problems involving arithmetic sequences often requires identifying the first term and the common difference. Once these are known, the nth term formula can be applied to find any term in the sequence. Problems may also involve finding the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence, which can be calculated using the formula S_n = \frac{n}{2}(a_1 + a_n), where S_n is the sum of the first n terms, a_1 is the first term, and a_n is the nth term.
Key Points
- Arithmetic sequences are characterized by a constant difference between consecutive terms.
- The nth term of an arithmetic sequence can be found using the formula $a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d$.
- Arithmetic sequences have practical applications in modeling growth or decline in various fields.
- Solving problems involving arithmetic sequences requires identifying the first term and the common difference.
- The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence can be calculated using the formula $S_n = \frac{n}{2}(a_1 + a_n)$.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, arithmetic sequences are a fundamental concept in mathematics with a wide range of applications. Understanding how to identify, calculate, and apply arithmetic sequences is essential for advancing in mathematical studies and for solving real-world problems. As mathematics continues to evolve, the study of arithmetic sequences remains a crucial foundation upon which more complex mathematical concepts are built. Future directions in the study of arithmetic sequences may involve exploring their applications in emerging fields such as data science and artificial intelligence.
What is the formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence?
+The formula for the nth term of an arithmetic sequence is a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d, where a_n is the nth term, a_1 is the first term, n is the term number, and d is the common difference.
How do you calculate the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence?
+The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic sequence can be calculated using the formula S_n = \frac{n}{2}(a_1 + a_n), where S_n is the sum of the first n terms, a_1 is the first term, and a_n is the nth term.
What are some real-world applications of arithmetic sequences?
+Arithmetic sequences have numerous real-world applications, including modeling population growth, financial transactions, and other phenomena where a constant change occurs over a period.



