The concept of even numbers is a fundamental aspect of mathematics, playing a crucial role in various mathematical operations, patterns, and applications. At its core, an even number is defined as any integer that can be exactly divided by 2, leaving no remainder. This simple yet profound property makes even numbers integral to understanding arithmetic, algebra, and beyond. In this guide, we will delve into the world of even numbers, exploring their definition, properties, applications, and the significant role they play in mathematics and real-world scenarios.
Definition and Properties of Even Numbers
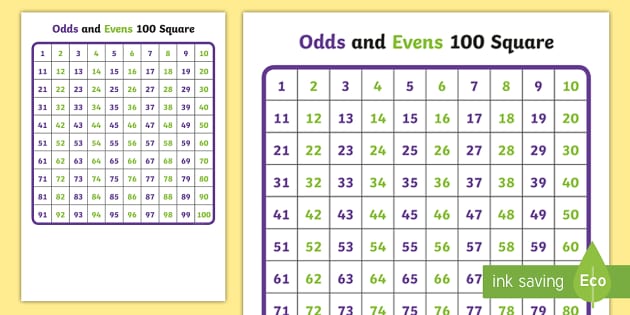
To comprehend even numbers fully, it’s essential to grasp their definition and inherent properties. An even number, as mentioned, is any number that is divisible by 2 without leaving a remainder. This means that when an even number is divided by 2, the result is always another whole number. For example, 4, 6, and 8 are even numbers because they can be divided by 2 (4 ÷ 2 = 2, 6 ÷ 2 = 3, 8 ÷ 2 = 4). On the other hand, numbers like 3, 5, and 7 are odd because they cannot be divided by 2 without leaving a remainder.
Mathematical Operations with Even Numbers
Even numbers exhibit unique behaviors under different mathematical operations. For instance, when you add two even numbers, the result is always even (e.g., 2 + 4 = 6). Similarly, when you multiply two even numbers, the product is also even (e.g., 4 * 6 = 24). However, the sum or product of an even and an odd number, or two odd numbers, can yield different results. Understanding these patterns is crucial for solving arithmetic problems and recognizing numerical sequences.
| Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Adding two even numbers | 4 + 6 | 10 (even) |
| Multiplying two even numbers | 4 * 6 | 24 (even) |
| Adding an even and an odd number | 4 + 5 | 9 (odd) |
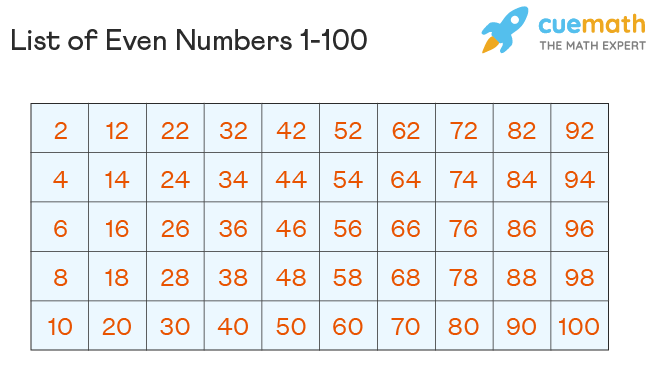
Applications of Even Numbers

Even numbers have numerous applications across various fields, from mathematics and computer science to engineering and economics. In programming, for example, even numbers can be used to represent the number of bytes in a data structure or the size of an array. In architecture, even dimensions are often preferred for buildings and rooms to facilitate division and use of space. Moreover, economic and financial models frequently rely on even numbers to simplify calculations and predict trends.
Real-World Examples and Implications
The presence and application of even numbers can be observed in many real-world scenarios. For instance, the number of wheels on most vehicles is even, which provides stability and balance. The structure of molecules, where the number of electrons in an atom’s outer shell often follows even patterns, is another example. Even numbers are also essential in music, where rhythms and beats often follow even patterns to create harmony and melody.
Key Points
- Even numbers are integers that can be divided by 2 without a remainder.
- The sum and product of two even numbers are always even.
- Even numbers have widespread applications in mathematics, computer science, engineering, and economics.
- Recognizing patterns and properties of even numbers is crucial for solving arithmetic problems and understanding numerical sequences.
- Even numbers play a significant role in real-world applications, including architecture, finance, and molecular structure.
In conclusion, even numbers form a fundamental part of the numerical system, with their properties and applications extending far beyond basic arithmetic. Understanding even numbers is not only essential for mathematical literacy but also for grasping more complex concepts and appreciating the intricate patterns that govern our world. As we continue to explore and apply mathematical principles, the significance of even numbers will remain a cornerstone of both theoretical knowledge and practical application.
What is the definition of an even number?
+An even number is any integer that can be exactly divided by 2, leaving no remainder.
Can you provide examples of even numbers?
+Yes, examples of even numbers include 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10, as these numbers can all be divided by 2 without leaving a remainder.
What are some real-world applications of even numbers?
+Even numbers have applications in architecture, where even dimensions are preferred for buildings and rooms, in finance for simplifying calculations, and in molecular structure, where the number of electrons in an atom’s outer shell often follows even patterns.