Ethylene, a simple hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C2H4, is a highly versatile and widely used compound in various industries. Its unique properties make it an essential component in the production of numerous consumer goods, from plastics and fibers to fuels and chemicals. In this article, we will explore five significant ways ethylene is utilized, highlighting its importance and impact on modern society.
Key Points
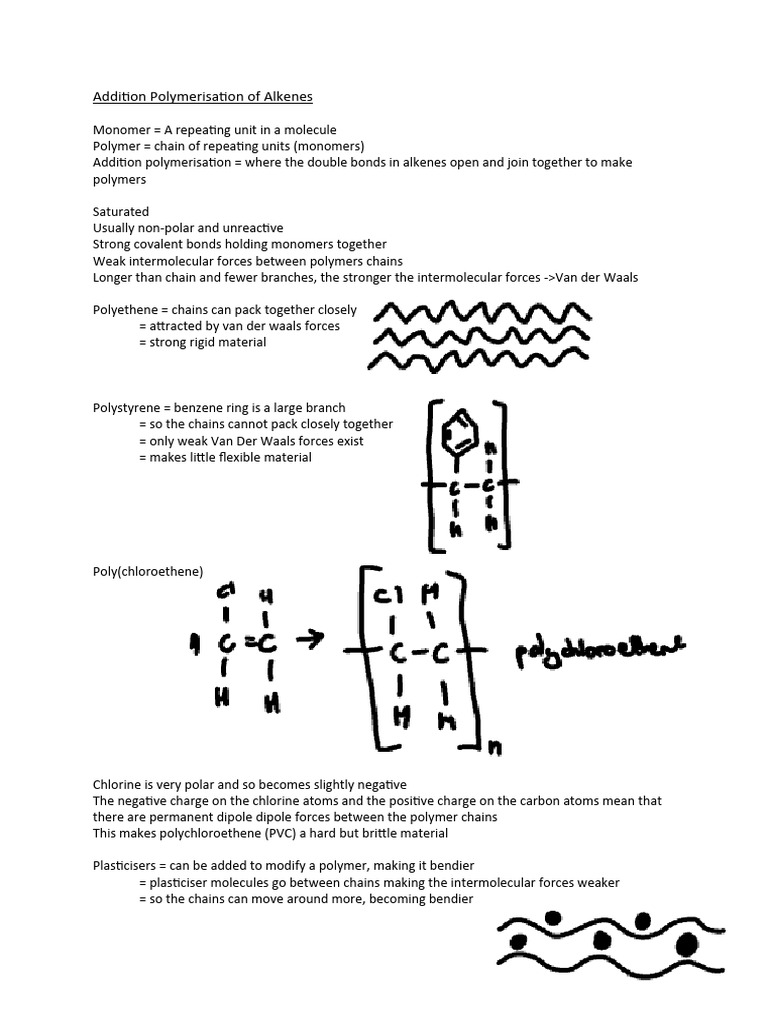
- Ethylene is a fundamental building block in the production of polyethylene, one of the most commonly used plastics worldwide.
- It serves as a critical raw material in the manufacture of ethylene glycol, a key component in antifreeze and polyester fibers.
- Ethylene is used in the creation of ethylene oxide, which is then converted into ethylene glycol and other important chemicals.
- The compound plays a crucial role in the production of vinyl chloride, the primary material used to manufacture PVC (polyvinyl chloride), a widely used plastic in construction and other industries.
- Ethylene is also utilized in the agricultural sector as a plant growth regulator, influencing fruit ripening and flowering in various crops.
Production of Polyethylene
Polyethylene, one of the most widely used plastics globally, is primarily produced from ethylene through a process known as polymerization. This process involves the combination of ethylene molecules to form long chains, resulting in a versatile material with a range of properties that can be tailored for specific applications. Polyethylene is used in packaging materials, such as plastic bags and containers, as well as in more durable products like piping systems and storage tanks. The versatility and widespread use of polyethylene underscore the significance of ethylene as a foundational chemical in the plastics industry.
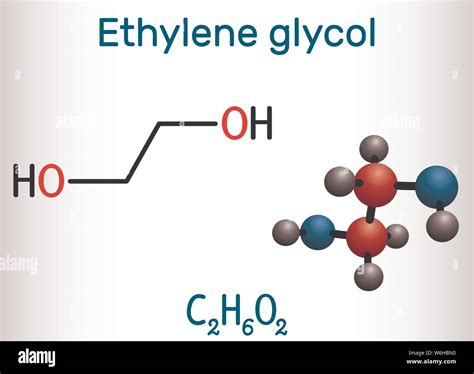
Ethylene Glycol Production
Ethylene glycol, another crucial derivative of ethylene, is produced through the oxidation of ethylene to form ethylene oxide, which is then reacted with water to produce ethylene glycol. This compound is critical in the manufacture of antifreeze, which is used in vehicle cooling systems to prevent the freezing of water in cold temperatures. Additionally, ethylene glycol is a key raw material in the production of polyester fibers, widely used in clothing and textiles. The demand for ethylene glycol is substantial, reflecting the essential role ethylene plays in meeting the needs of both the automotive and textile industries.
| Derivative | Primary Use |
|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Packaging, piping, storage tanks |
| Ethylene Glycol | Antifreeze, polyester fibers |
| Ethylene Oxide | Production of ethylene glycol and other chemicals |
| Vinyl Chloride | Manufacture of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) |
Vinyl Chloride and PVC Production
Vinyl chloride, produced from ethylene through a reaction with chlorine, is the primary precursor to PVC (polyvinyl chloride), one of the world’s most widely used plastics. PVC is renowned for its durability, resistance to corrosion, and versatility, making it an ideal material for a broad range of applications, including construction (e.g., piping, vinyl siding), electronics (e.g., wire insulation), and consumer products (e.g., vinyl records, credit cards). The reliance on vinyl chloride for PVC production underscores ethylene’s indirect yet crucial role in these industries.
Agricultural Applications
Beyond its industrial applications, ethylene also plays a significant role in agriculture as a plant growth regulator. It is used to stimulate fruit ripening and to induce flowering in certain crops, thereby enhancing yield and improving the quality of the produce. This biological activity of ethylene is harnessed through the use of ethylene-releasing compounds or by controlling the atmosphere around the crops to optimize ethylene levels. The use of ethylene in agriculture reflects its multifaceted nature, extending its influence from manufacturing to biological processes.
What is the primary method of ethylene production?
+Ethylene is primarily produced through the steam cracking of hydrocarbons, such as ethane or naphtha, in the presence of high temperatures and pressures.
How is ethylene used in the production of antifreeze?
+Ethylene is converted into ethylene oxide and then reacted with water to form ethylene glycol, which is the primary component of antifreeze, used to prevent the freezing of water in vehicle cooling systems.
What are some common applications of PVC?
+PVC is widely used in construction for piping and vinyl siding, in electronics for wire insulation, and in consumer products such as credit cards and vinyl records, due to its durability, resistance to corrosion, and versatility.
In conclusion, ethylene’s impact on modern society is profound, with its derivatives influencing numerous aspects of daily life, from the plastics and textiles used in consumer goods to the antifreeze in vehicle cooling systems and the PVC in construction materials. The agricultural applications of ethylene further underscore its multifaceted nature, demonstrating its role in enhancing crop yields and quality. As the demand for these products continues to grow, the importance of ethylene as a foundational chemical in various industries will only continue to increase, highlighting the need for efficient, sustainable, and safe production methods to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.