The Spanish language is renowned for its complex verb conjugations, and the preterite tense is no exception. One of the most fundamental verbs in Spanish is "estar," which means "to be" and is used to describe temporary or changing conditions. Mastering the preterite conjugation of "estar" is essential for effective communication in Spanish. In this article, we will delve into the world of "estar" preterite conjugation, exploring its various forms, usage, and providing examples to facilitate a deeper understanding of this crucial verb.
Key Points
- The verb "estar" is used to describe temporary or changing conditions in Spanish.
- The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past.
- Mastering the preterite conjugation of "estar" is essential for effective communication in Spanish.
- The conjugation of "estar" in the preterite tense varies depending on the subject pronoun.
- Understanding the nuances of "estar" preterite conjugation can help learners improve their Spanish language skills.
Understanding the Preterite Tense

The preterite tense, also known as the simple past, is used to describe completed actions in the past. It is essential to understand the preterite tense to communicate effectively in Spanish, as it is used to describe events that occurred at a specific point in the past. The preterite tense is often used in conjunction with other tenses, such as the imperfect, to provide a more detailed description of past events.
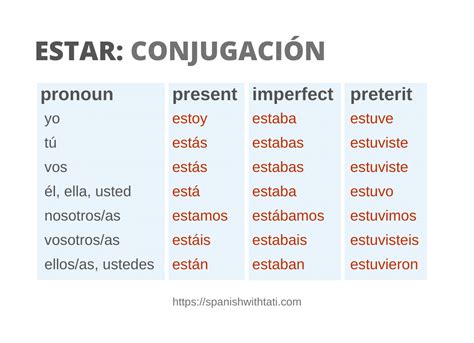
Conjugation of Estar in the Preterite Tense
The conjugation of “estar” in the preterite tense is as follows:
| Subject Pronoun | Preterite Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | estuve |
| Tú | estuviste |
| Él/ella/usted | estuvo |
| Nosotros/as | estuvimos |
| Vosotros/as | estuvisteis |
| Ellos/as | estuvieron |
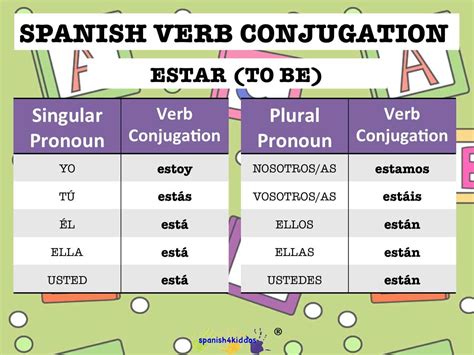
As can be seen from the table, the conjugation of "estar" in the preterite tense varies depending on the subject pronoun. It is essential to memorize these conjugations to use the verb correctly in context.
Usage of Estar in the Preterite Tense
The preterite tense of “estar” is used to describe temporary or changing conditions in the past. For example:
Yo estuve cansado ayer. (I was tired yesterday.)
Él estuvo enfermo la semana pasada. (He was sick last week.)
Nosotros estuvimos de vacaciones en verano. (We were on vacation in the summer.)
As can be seen from these examples, the preterite tense of "estar" is used to describe conditions that were true at a specific point in the past but are no longer true.
Common Mistakes and Nuances
One of the most common mistakes made by learners of Spanish is confusing the preterite tense with the imperfect tense. While the preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, the imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past. For example:
Yo estaba estudiando cuando sonó el teléfono. (I was studying when the phone rang.)
Yo estuve estudiando durante tres horas. (I studied for three hours.)
In the first example, the imperfect tense is used to describe an ongoing action in the past, while in the second example, the preterite tense is used to describe a completed action in the past.
Practical Applications
The preterite conjugation of “estar” has numerous practical applications in Spanish. For example, it can be used to describe:
- Temporary physical or emotional states: Yo estuve enfermo la semana pasada. (I was sick last week.)
- Locations or positions: Ella estuvo en la biblioteca ayer. (She was at the library yesterday.)
- Conditions or situations: Nosotros estuvimos en una situación difícil. (We were in a difficult situation.)
As can be seen from these examples, the preterite conjugation of "estar" is essential for describing a wide range of situations and conditions in Spanish.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, mastering the preterite conjugation of “estar” is essential for effective communication in Spanish. By understanding the nuances of the preterite tense and the imperfect tense, learners can improve their Spanish language skills and communicate more effectively. The preterite conjugation of “estar” has numerous practical applications, and its correct usage can help learners describe temporary or changing conditions in the past with precision and accuracy.
What is the difference between the preterite tense and the imperfect tense in Spanish?
+The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, while the imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past.
How do I conjugate “estar” in the preterite tense?
+The conjugation of “estar” in the preterite tense varies depending on the subject pronoun. The conjugations are as follows: yo estuve, tú estuviste, él/ella/usted estuvo, nosotros/as estuvimos, vosotros/as estuvisteis, ellos/as estuvieron.
What are some common mistakes made by learners of Spanish when using the preterite tense?
+One of the most common mistakes made by learners of Spanish is confusing the preterite tense with the imperfect tense. It is essential to understand the nuances of both tenses to communicate effectively in Spanish.



