The concept of equilateral triangle angles is a fundamental aspect of geometry, with far-reaching implications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. An equilateral triangle, by definition, is a triangle with all sides of equal length. This unique property gives rise to a distinct set of characteristics, particularly with regard to its angles. In this article, we will delve into the properties of equilateral triangle angles, exploring their measurements, implications, and applications.
Key Points
- An equilateral triangle has all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure.
- Each angle of an equilateral triangle measures 60 degrees.
- The sum of the angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Equilateral triangles have unique properties, including symmetry and equal area distribution.
- Understanding equilateral triangle angles is crucial in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, and design.
Properties of Equilateral Triangle Angles
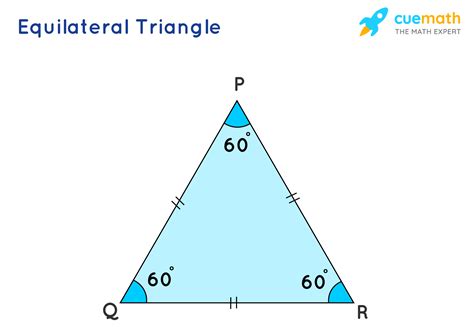
An equilateral triangle, due to its symmetrical nature, exhibits a unique set of properties. One of the most notable properties is that all three angles of an equilateral triangle are equal. Since the sum of the angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees, we can deduce that each angle of an equilateral triangle measures exactly 60 degrees. This property is a direct consequence of the triangle’s equilateral nature and is a fundamental concept in geometry.
Geometric Implications
The fact that each angle of an equilateral triangle is 60 degrees has significant implications for the triangle’s overall geometry. For instance, this property implies that an equilateral triangle is also an equiangular triangle, meaning all its angles are equal. This unique combination of properties gives rise to a high degree of symmetry, making equilateral triangles particularly useful in design and architecture. Furthermore, the 60-degree angle measurement is a key factor in the construction of various geometric shapes, including hexagons and other polygons.
| Triangle Type | Angle Measurement |
|---|---|
| Equilateral Triangle | 60 degrees (each angle) |
| Isosceles Triangle | Varies (dependent on side lengths) |
| Right Triangle | 90 degrees (right angle), with other angles varying |
Applications and Real-World Examples
The unique properties of equilateral triangle angles make them a staple in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. For instance, the symmetry and balance provided by equilateral triangles are often utilized in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures. Additionally, the 60-degree angle is a key component in the construction of regular hexagons, which are found in nature (e.g., in the structure of honeycombs) and are used in numerous applications, from packaging to engineering.
Practical Considerations
When working with equilateral triangles in practical applications, it is essential to consider the implications of their angles. For example, the use of equilateral triangles in the design of load-bearing structures can provide excellent stability due to their symmetrical distribution of weight. However, it is also crucial to consider the limitations and potential drawbacks of relying solely on equilateral triangles, such as the potential for decreased flexibility in design.
What is the sum of the angles in an equilateral triangle?
+The sum of the angles in any triangle, including an equilateral triangle, is always 180 degrees. Since an equilateral triangle has three equal angles, each angle measures 60 degrees, resulting in a total sum of 180 degrees.
Are equilateral triangles always equiangular?
+Yes, equilateral triangles are always equiangular. This means that all three angles of an equilateral triangle are equal, each measuring 60 degrees.
What are some real-world applications of equilateral triangles?
+Equilateral triangles are used in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. They are found in the structure of buildings, bridges, and other load-bearing structures, as well as in the design of regular hexagons, which have numerous applications in packaging, engineering, and nature.
In conclusion, the concept of equilateral triangle angles is a fundamental aspect of geometry, with significant implications for various fields. Understanding the properties and applications of equilateral triangles is essential for architects, engineers, designers, and anyone seeking to create symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing structures. By recognizing the unique characteristics of equilateral triangles, individuals can harness their potential to create innovative and efficient designs that leverage the power of geometry.


