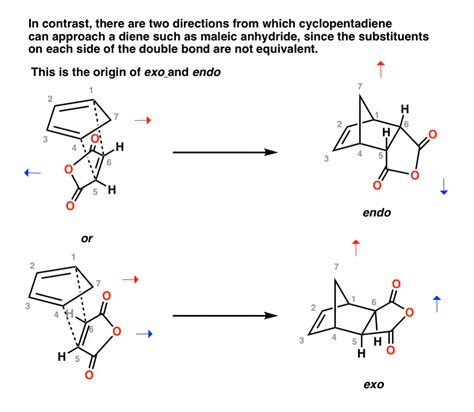
The terms "endo" and "exo" are prefixes that originate from Greek, with "endo" meaning "within" or "inside" and "exo" meaning "outside" or "external." These prefixes are widely used in various scientific fields, including biology, chemistry, and physics, to describe the location or origin of a process, structure, or reaction. Understanding the difference between endo and exo is crucial for comprehending complex concepts in these fields.
Biological Context: Endo vs Exo

In biology, the terms endo and exo are used to describe the location of processes or structures within an organism. For example, endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside the cell by engulfing them with their cell membrane, while exocytosis is the process of releasing substances contained in vesicles to the outside of the cell. Similarly, endogenous refers to substances or processes that originate from within an organism, such as endogenous hormones, whereas exogenous refers to substances or influences that come from outside the organism, such as exogenous hormones or environmental factors.
Chemical Reactions: Endo vs Exo
In chemistry, the terms endo and exo are used to describe the stereochemistry of molecules, particularly in the context of ring structures. An endo reaction or process occurs when a substituent or a reaction site is located inside a ring or a cyclic structure, whereas an exo reaction occurs when the substituent or reaction site is located outside the ring. This distinction is important in understanding the reactivity and properties of molecules, as the stereochemistry can significantly influence the outcome of chemical reactions.
| Term | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Endo | Within or inside | Endocytosis, endogenous |
| Exo | Outside or external | Exocytosis, exogenous |

Physical and Environmental Context
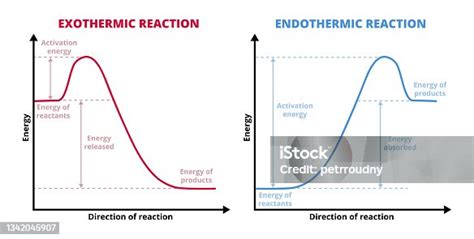
Beyond biological and chemical contexts, the terms endo and exo are also used in physics and environmental science. For instance, endothermic reactions absorb heat from the surroundings to proceed, whereas exothermic reactions release heat to the environment. In environmental science, endogenous processes refer to those that occur within an ecosystem, such as nutrient cycling, while exogenous factors are external influences, such as climate change or pollution, that can impact the ecosystem.
Application and Implications
The distinction between endo and exo has significant implications for various applications, including medicine, agriculture, and materials science. For example, understanding the endocytosis pathway is crucial for the development of targeted drug delivery systems, while knowledge of exogenous factors influencing plant growth can inform agricultural practices. In materials science, the stereochemistry of molecules, including endo and exo configurations, can influence the properties and potential applications of materials.
Key Points
- The prefixes "endo" and "exo" refer to "within" or "inside" and "outside" or "external," respectively.
- These terms are used across various scientific disciplines to describe location, origin, or stereochemistry.
- Understanding the difference between endo and exo is crucial for comprehending biological processes, chemical reactions, and environmental phenomena.
- The distinction has significant implications for applications in medicine, agriculture, materials science, and more.
- The correct usage of these terms can provide insights into the mechanisms and outcomes of various scientific processes.
In conclusion, the difference between endo and exo is fundamental to understanding a wide range of scientific concepts and processes. By recognizing and applying these terms correctly, scientists and researchers can deepen their understanding of complex phenomena and develop innovative solutions to real-world problems.
What does the term "endo" mean in scientific contexts?
+The term "endo" means "within" or "inside," and it is used to describe processes, structures, or reactions that occur within an organism, cell, or molecule.
How does the term "exo" differ from "endo"?
+The term "exo" means "outside" or "external," and it refers to processes, influences, or structures that originate from or are located outside an organism, cell, or molecule.
What are some examples of endo and exo processes in biology?
+Examples of endo processes include endocytosis (the uptake of substances into a cell) and endogenous hormone production (hormones produced within an organism). Examples of exo processes include exocytosis (the release of substances from a cell) and exogenous hormone administration (hormones introduced from outside the organism).
Meta Description: Understand the difference between endo and exo, prefixes used in science to describe location and origin, and explore their implications in biology, chemistry, and beyond.