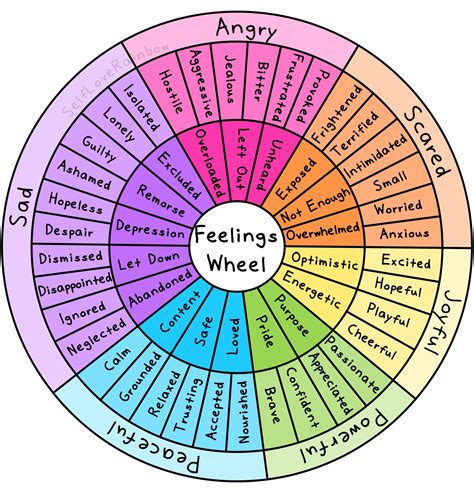
The emotional wheel, a concept rooted in psychology and emotional intelligence, serves as a visual representation of the complex array of emotions that humans experience. Developed by Robert Plutchik, a renowned psychologist, the emotional wheel is a fundamental tool in understanding the primary emotions that drive human behavior and decision-making. The wheel itself is divided into eight primary emotions: joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, anticipation, anger, and disgust. These emotions are not mutually exclusive but rather interconnected, influencing one another in complex ways.
Understanding the Emotional Wheel
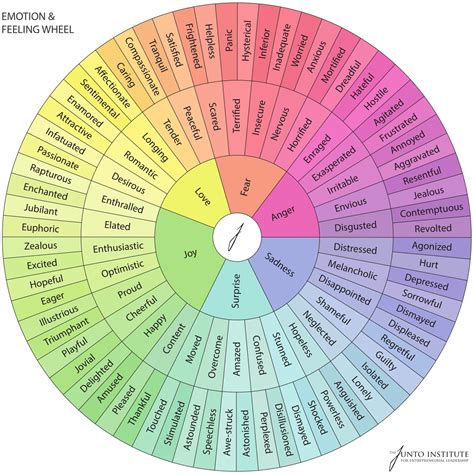
At the core of the emotional wheel are the primary emotions, which are further divided into secondary emotions through various combinations. For instance, the combination of joy and trust gives rise to love, while the blend of fear and surprise results in alarm. This nuanced understanding of emotions highlights the dynamic nature of human emotional experiences, where emotions can shift rapidly depending on the situation and personal interactions. The emotional wheel is not just a theoretical construct but a practical tool that helps individuals, therapists, and educators navigate the intricate landscape of human emotions.
Primary Emotions and Their Significance
Each primary emotion on the wheel has a unique significance and role in human emotional experiences. Joy, for example, is associated with feelings of happiness and contentment, often stemming from positive experiences or achievements. Trust, on the other hand, is foundational for building strong relationships and is closely linked with feelings of security and reliability. Fear, a protective emotion, alerts individuals to potential dangers and motivates them to take action to ensure their safety. Understanding these primary emotions and their interactions is crucial for developing emotional intelligence and fostering healthier emotional responses to life’s challenges.
| Primary Emotion | Description |
|---|---|
| Joy | Feeling of happiness and contentment |
| Trust | Foundation for relationships, associated with security and reliability |
| Fear | Protective emotion, alerts to potential dangers |
| Surprise | Reaction to unexpected events or information |
| Sadness | Emotional response to loss or separation |
| Anticipation | Expectation of a future event, can be positive or negative |
| Anger | Emotional response to perceived injustice or threat |
| Disgust | Reaction to something considered distasteful or morally wrong |

Applications of the Emotional Wheel
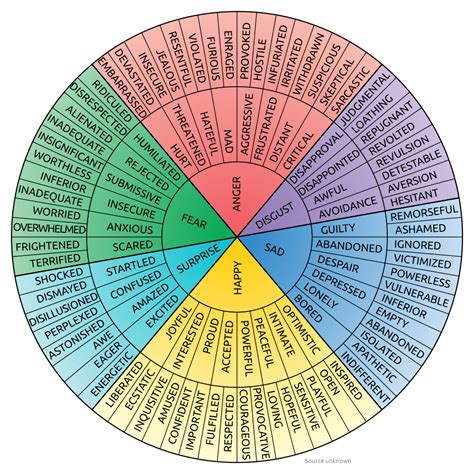
The emotional wheel has numerous applications across various fields, including psychology, education, and business. In therapy, understanding the emotional wheel can help individuals identify and manage their emotions more effectively, leading to better mental health outcomes. Educators can use the emotional wheel to create more emotionally supportive learning environments, recognizing the emotional needs of their students and fostering a culture of empathy and understanding. In the workplace, acknowledging and addressing emotions through the lens of the emotional wheel can improve communication, reduce conflict, and enhance teamwork and productivity.
Emotional Intelligence and the Emotional Wheel
Emotional intelligence (EI) is closely linked with the emotional wheel, as it involves the ability to recognize and understand emotions in oneself and others, and to use this awareness to guide thought and behavior. Developing emotional intelligence requires a deep understanding of the emotional wheel and its implications for personal and interpersonal dynamics. By cultivating emotional intelligence, individuals can better navigate the complexities of the emotional wheel, leading to more harmonious relationships, improved decision-making, and enhanced personal growth.
Key Points
- The emotional wheel is a visual representation of the complex array of human emotions, divided into eight primary emotions.
- Understanding the emotional wheel is crucial for developing emotional intelligence and navigating personal and interpersonal emotional dynamics.
- The emotional wheel has practical applications in psychology, education, and business, contributing to improved mental health, learning environments, and workplace communication.
- Emotional intelligence is closely linked with the emotional wheel, involving the recognition and management of emotions to guide thought and behavior.
- Cultivating emotional intelligence through the understanding of the emotional wheel can lead to better relationships, decision-making, and personal growth.
In conclusion, the emotional wheel offers a profound insight into the human emotional experience, highlighting the interconnectedness and complexity of emotions. By embracing this understanding and applying it in various aspects of life, individuals can foster a deeper connection with themselves and others, ultimately leading to a more emotionally intelligent and compassionate world.
What are the primary emotions on the emotional wheel?
+The primary emotions on the emotional wheel are joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, anticipation, anger, and disgust. These emotions are foundational and give rise to secondary emotions through various combinations.
How does the emotional wheel relate to emotional intelligence?
+The emotional wheel is closely linked with emotional intelligence, as understanding and recognizing emotions (both in oneself and others) is a key component of emotional intelligence. Developing emotional intelligence involves a deep understanding of the emotional wheel and its implications for personal and interpersonal dynamics.
What are some practical applications of the emotional wheel?
+The emotional wheel has practical applications in therapy, education, and the workplace. It can be used to identify and manage emotions, create supportive learning environments, improve communication, and enhance teamwork and productivity.