Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) is a powerful analytical technique used to study the electrochemical properties of materials and systems. By applying a small amplitude alternating current (AC) signal to an electrochemical cell, EIS can provide valuable information about the cell's impedance, which is a measure of its resistance to the flow of electric current. This guide will provide an in-depth overview of the principles, instrumentation, and applications of EIS, as well as its advantages and limitations.
Key Points
- EIS is a non-destructive technique that can be used to study a wide range of electrochemical systems, including batteries, fuel cells, and corrosion.
- The technique involves applying a small amplitude AC signal to an electrochemical cell and measuring the resulting current and voltage.
- EIS can provide information about the electrochemical properties of materials, including their impedance, capacitance, and resistance.
- The technique has a wide range of applications, including the study of battery performance, fuel cell efficiency, and corrosion mechanisms.
- EIS can be used in conjunction with other techniques, such as cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry, to provide a more complete understanding of electrochemical systems.
Principles of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
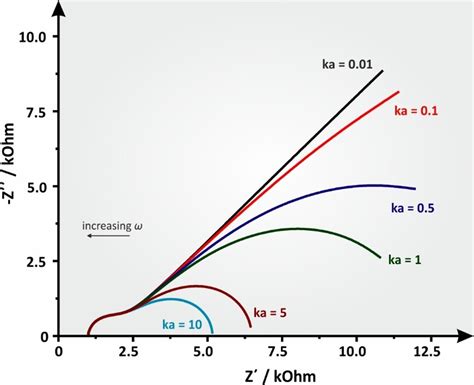
EIS is based on the principle of impedance, which is a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current in an electrochemical cell. The impedance of a cell is composed of two components: the real component, which represents the resistance of the cell, and the imaginary component, which represents the reactance of the cell. The reactance of a cell is related to its capacitance and inductance, and can provide valuable information about the electrochemical properties of the cell.
Instrumentation for Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
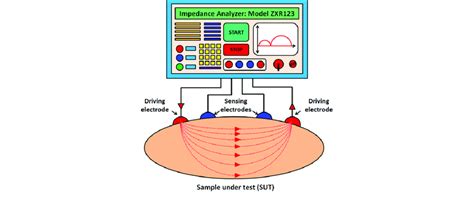
The instrumentation for EIS typically consists of a potentiostat, a frequency response analyzer, and a computer. The potentiostat is used to apply a small amplitude AC signal to the electrochemical cell, while the frequency response analyzer is used to measure the resulting current and voltage. The computer is used to control the instrumentation and to analyze the data.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Potentiostat | Applies a small amplitude AC signal to the electrochemical cell |
| Frequency Response Analyzer | Measures the resulting current and voltage |
| Computer | Controls the instrumentation and analyzes the data |
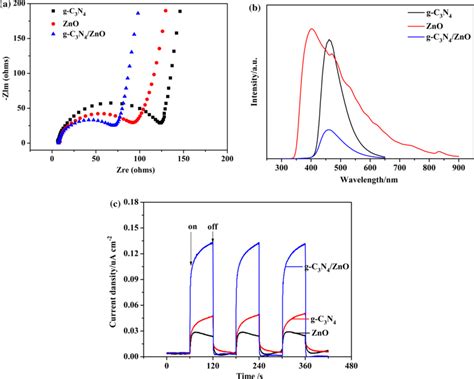
Applications of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
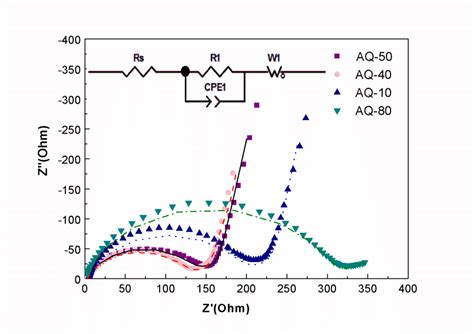
EIS has a wide range of applications in the field of electrochemistry, including the study of battery performance, fuel cell efficiency, and corrosion mechanisms. The technique can be used to study the electrochemical properties of materials, including their impedance, capacitance, and resistance. EIS can also be used to study the effects of different variables, such as temperature and electrolyte concentration, on the electrochemical properties of materials.
Advantages and Limitations of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
EIS has several advantages, including its non-destructive nature and its ability to provide detailed information about the electrochemical properties of materials. However, the technique also has some limitations, including its complexity and the need for specialized instrumentation. Additionally, EIS can be sensitive to experimental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, which can affect the accuracy of the results.
What is Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy?
+Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) is a technique used to study the electrochemical properties of materials and systems by applying a small amplitude alternating current (AC) signal to an electrochemical cell and measuring the resulting current and voltage.
What are the advantages of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy?
+The advantages of EIS include its non-destructive nature, its ability to provide detailed information about the electrochemical properties of materials, and its wide range of applications.
What are the limitations of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy?
+The limitations of EIS include its complexity, the need for specialized instrumentation, and its sensitivity to experimental conditions, such as temperature and humidity.
In conclusion, Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy is a powerful technique for studying the electrochemical properties of materials and systems. By analyzing the impedance of a cell, researchers can gain valuable insights into the electrochemical mechanisms that occur at the electrode-solution interface. While the technique has several advantages, including its non-destructive nature and its ability to provide detailed information about the electrochemical properties of materials, it also has some limitations, including its complexity and the need for specialized instrumentation. Despite these limitations, EIS remains a widely used and powerful tool in the field of electrochemistry.