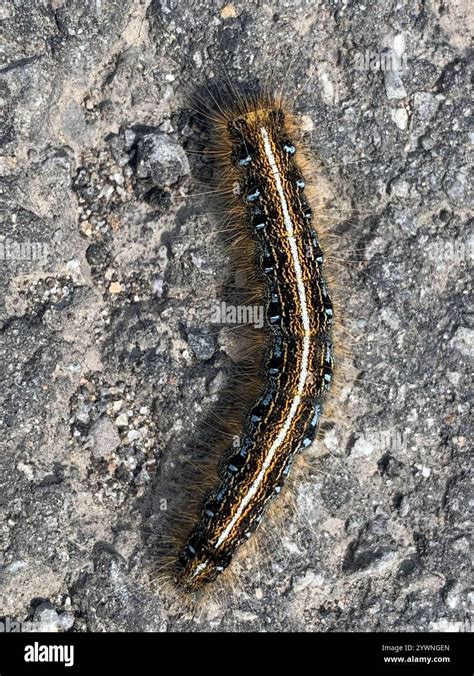
The Eastern Tent Caterpillar, also known as Malacosoma americanum, is a species of caterpillar that is native to North America, specifically the eastern and central regions of the United States. These caterpillars are known for their distinctive tents, which they construct in trees, and their ability to defoliate entire branches. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Eastern Tent Caterpillars, exploring their life cycle, habits, and the impact they have on their ecosystems.
Life Cycle and Development

The life cycle of the Eastern Tent Caterpillar consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The female moths lay their eggs in the summer, typically on the branches of trees, and the eggs hatch in the spring. The newly hatched larvae are about 1⁄4 inch long and are covered in fine, downy hair. As they grow, they molt several times, increasing in size and developing their distinctive tent-like structures. The caterpillars go through five instars, or stages of growth, before pupating and emerging as adult moths.
Habitat and Diet
Eastern Tent Caterpillars are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, woodlands, and even urban areas. They are particularly fond of trees in the Rosaceae family, such as apple, cherry, and plum trees. The caterpillars are herbivores and feed on the leaves of their host trees, using their powerful jaws to consume large quantities of foliage. In fact, a single caterpillar can eat up to 2.5 times its body weight in leaves per day.
| Tree Species | Prevalence of Infestation |
|---|---|
| Apple | High |
| Cherry | Medium |
| Plum | Low |

Key Points
- The Eastern Tent Caterpillar is native to the eastern and central United States.
- They are known for their distinctive tents, which they construct in trees.
- The caterpillars go through five instars, or stages of growth, before pupating and emerging as adult moths.
- They are herbivores and feed on the leaves of their host trees, particularly those in the Rosaceae family.
- A single caterpillar can eat up to 2.5 times its body weight in leaves per day.
Behavior and Social Structure

Eastern Tent Caterpillars are social creatures and live in large colonies. They are known for their distinctive tents, which they construct using silk threads and leaves. The tents serve as a protective shelter for the caterpillars, providing them with a safe place to feed, rest, and molt. The caterpillars are also able to communicate with each other through chemical signals, known as pheromones, which help them coordinate their behavior and maintain their social structure.
Impact on Ecosystems
The Eastern Tent Caterpillar can have significant impacts on their ecosystems. Their feeding habits can cause significant defoliation, which can weaken the host tree and make it more susceptible to disease and pests. In addition, the caterpillars’ tents can provide a habitat for other insects, such as wasps and flies, which can further exacerbate the problem. However, it’s worth noting that the Eastern Tent Caterpillar is also an important food source for many animals, including birds, bats, and spiders.
In terms of conservation efforts, it's essential to adopt a balanced approach that takes into account the complex relationships between the Eastern Tent Caterpillar and its ecosystem. This can include practices such as integrated pest management, which involves using a combination of techniques, such as biological control, cultural control, and chemical control, to manage pest populations. Additionally, habitat preservation and restoration efforts can help to maintain the health and diversity of ecosystems, reducing the risk of infestations and promoting the long-term sustainability of ecosystems.
| Conservation Effort | Description |
|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management | A holistic approach to managing pest populations using a combination of techniques. |
| Habitat Preservation | Efforts to protect and conserve natural habitats, reducing the risk of infestations and promoting ecosystem health. |
| Habitat Restoration | Practices aimed at restoring degraded or damaged ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. |
What is the typical lifespan of an Eastern Tent Caterpillar?
+The typical lifespan of an Eastern Tent Caterpillar is around 6-8 weeks, although this can vary depending on factors such as food availability and environmental conditions.
How can I control an infestation of Eastern Tent Caterpillars?
+Control methods can include hand-picking the caterpillars, using insecticidal soap or Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis), and pruning infested branches. It's also essential to adopt a long-term approach, focusing on integrated pest management and habitat preservation to reduce the risk of future infestations.
What are some common predators of the Eastern Tent Caterpillar?
+Common predators of the Eastern Tent Caterpillar include birds, such as robins and blue jays, as well as bats, spiders, and other insects. These predators play a crucial role in regulating the caterpillar population and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Meta Description: Discover the fascinating world of Eastern Tent Caterpillars, including their life cycle, habits, and impact on ecosystems, and learn how to control infestations and promote ecosystem health. (149 characters)