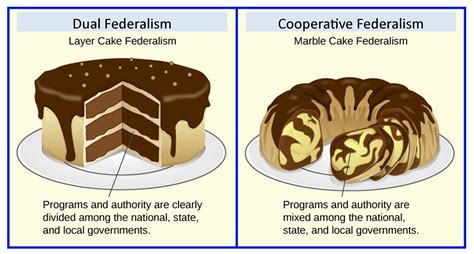
The concept of dual federalism, also known as "layer cake federalism," has been a cornerstone of the United States' system of government since its inception. At its core, dual federalism refers to the division of power between the federal government and the individual states, with each level of government having distinct and separate areas of authority. This concept is rooted in the Constitution, which outlines the powers granted to the federal government and those reserved to the states. In this framework, the federal government is responsible for matters of national importance, such as foreign policy, national defense, and interstate commerce, while the states retain control over issues more closely related to the daily lives of their citizens, including education, law enforcement, and local infrastructure.
Historically, the principle of dual federalism was established to ensure a balance of power and to prevent any one level of government from becoming too dominant. The idea was to create a system where both the federal government and the states had significant autonomy in their respective domains, thereby fostering a more federalized system. This approach also aimed to address the concerns of smaller states, which feared being overshadowed by larger, more populous states, by giving them equal representation in the Senate. Over time, however, the boundaries between federal and state powers have evolved, with the federal government increasingly playing a more significant role in areas traditionally reserved for the states.
Key Points
- Dual federalism is based on the division of power between the federal government and individual states.
- The federal government is responsible for national matters like foreign policy and defense.
- States have authority over local issues such as education and law enforcement.
- The principle aims to balance power and prevent any level of government from becoming too dominant.
- Historical context shows an evolution in the balance of power, with the federal government's role expanding.
Evolution of Dual Federalism

The evolution of dual federalism has been marked by significant shifts in the balance of power between the federal government and the states. Initially, the system was designed to be more state-centric, with the federal government playing a limited role. However, with the passage of time and the growth of the nation, the federal government's responsibilities and powers have expanded. The Great Depression and World War II, for instance, necessitated a more active federal role in economic regulation and national security, respectively. The Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s also led to federal intervention in areas such as voting rights and public accommodations, traditionally under state jurisdiction. These developments have resulted in a more intertwined relationship between federal and state powers, often referred to as "marble cake federalism," where the layers of authority are not as distinct as they once were.
Impact on State and Federal Relations
The evolution of dual federalism has had a profound impact on the relationship between the states and the federal government. While the system was initially designed to promote state autonomy and limit federal interference, the expansion of federal powers has led to increased tension. Many states have expressed concerns over what they perceive as federal overreach, citing issues such as healthcare reform, environmental regulation, and education standards as examples of the federal government encroaching on state sovereignty. On the other hand, the federal government has often justified its expanded role as necessary to address national problems that transcend state boundaries, such as economic crises, national security threats, and civil rights violations.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Historical Context | The concept of dual federalism has its roots in the U.S. Constitution and the system of government designed by the Founding Fathers. |
| Evolution | Over time, the balance of power has shifted, with the federal government taking on more responsibilities, especially in times of national crisis. |
| Current State | The relationship between the federal government and the states is complex, with ongoing debates over issues like healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. |

Challenges and Future Directions

Despite its importance, dual federalism faces several challenges in the contemporary political landscape. One of the significant issues is the debate over states' rights versus federal authority, which has become more pronounced in recent years. The Supreme Court has played a crucial role in defining the boundaries of federal and state powers, with landmark decisions such as United States v. Lopez and United States v. Morrison limiting federal authority in certain areas. Furthermore, the increasing polarization of American politics has led to tensions between states with differing political leanings and the federal government, complicating the already complex relationship between the two levels of government.
Looking forward, the future of dual federalism will likely be shaped by how these challenges are addressed. There is a growing need for a more cooperative federalism, where the federal government and the states work together to solve national problems while respecting the principles of state sovereignty. This could involve greater collaboration in policy areas such as healthcare, education, and environmental protection, where federal standards can provide a framework for state action. Additionally, technological advancements and demographic changes will continue to test the traditional boundaries of dual federalism, requiring innovative solutions that balance national unity with regional diversity.
What is the primary purpose of dual federalism?
+The primary purpose of dual federalism is to divide power between the federal government and the states, ensuring a balance that prevents any one level of government from becoming too powerful.
How has dual federalism evolved over time?
+Dual federalism has evolved significantly, with the federal government taking on more responsibilities, especially in times of national crisis, leading to a more intertwined relationship between federal and state powers.
What are some of the challenges facing dual federalism today?
+Dual federalism faces challenges such as the debate over states' rights versus federal authority, political polarization, and the need for cooperation in solving national problems while respecting state sovereignty.
In conclusion, dual federalism is a foundational concept in the United States’ system of government, designed to ensure a balance of power between the federal government and the states. While it has faced numerous challenges and has evolved significantly over time, its importance in maintaining the federal character of the United States cannot be overstated. As the nation continues to grow and face new challenges, the principle of dual federalism will remain a critical framework for understanding and navigating the complex relationship between the federal government and the states.