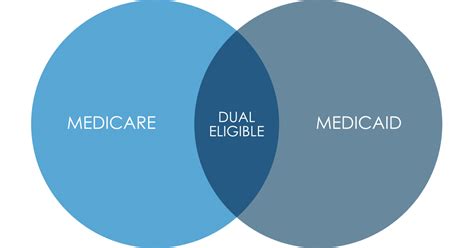
Dual Eligible Medicare Medicaid refers to individuals who are enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid, two of the largest government-funded health insurance programs in the United States. This dual eligibility is a critical aspect of healthcare coverage, as it provides comprehensive benefits to those who need it most. According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), as of 2022, approximately 12.2 million individuals are dually eligible for Medicare and Medicaid, accounting for about 20% of all Medicare beneficiaries.
These individuals often face significant health challenges, including higher rates of chronic conditions, disabilities, and mental health issues. The dual eligibility program is designed to provide them with access to a broader range of healthcare services, including hospital care, physician services, prescription drugs, and long-term care. The Medicare program, which is primarily designed for individuals 65 and older, as well as certain younger people with disabilities, provides a foundation of coverage for these services. Meanwhile, Medicaid, which is designed for low-income individuals and families, provides additional coverage for services such as dental care, vision care, and home health care.
Key Points
- Dual Eligible Medicare Medicaid beneficiaries account for approximately 20% of all Medicare beneficiaries
- These individuals often face significant health challenges, including higher rates of chronic conditions and disabilities
- The dual eligibility program provides comprehensive benefits, including hospital care, physician services, and long-term care
- Medicaid provides additional coverage for services such as dental care, vision care, and home health care
- Dual eligible individuals are more likely to experience gaps in care and unmet healthcare needs due to lack of coordination between Medicare and Medicaid
MEDICARE AND MEDICAID COVERAGE FOR DUAL ELIGIBLES

MEDICARE AND MEDICAID provide different types of coverage for dual eligible individuals. Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance) provide coverage for inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, and physician services. Medicare Part D (prescription drug coverage) provides coverage for prescription medications. Meanwhile, Medicaid provides coverage for additional services such as dental care, vision care, and home health care. Dual eligible individuals are also eligible for special programs, such as the Program of All-Inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE), which provides comprehensive care for frail, elderly individuals.
Medicare Advantage Plans for Dual Eligibles
Medicare Advantage plans are an alternative to traditional Medicare for dual eligible individuals. These plans are offered by private insurance companies and provide all Medicare Part A and Part B benefits, as well as additional benefits such as dental, vision, and hearing care. Some Medicare Advantage plans also provide special services, such as transportation to medical appointments and home meal delivery. According to a report by the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC), in 2022, approximately 42% of dual eligible beneficiaries were enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans.
| Category | Percentage of Dual Eligibles |
|---|---|
| Medicare Advantage Plans | 42% |
| Traditional Medicare | 58% |

CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES IN DUAL ELIGIBLE CARE

Despite the importance of the dual eligibility program, there are several challenges and opportunities for improvement. One major challenge is the lack of coordination between Medicare and Medicaid, which can lead to gaps in care and unmet healthcare needs. Another challenge is the complexity of the dual eligibility program, which can make it difficult for individuals to navigate and access the care they need. Additionally, dual eligible individuals often face significant health disparities and social determinants of health, such as poverty, housing instability, and food insecurity.
However, there are also opportunities for improvement. One opportunity is the use of data analytics and care coordination to improve the quality and efficiency of care for dual eligible individuals. Another opportunity is the development of specialized care models, such as the PACE program, which can provide comprehensive and coordinated care for frail, elderly individuals. Additionally, policymakers and healthcare providers can work together to address the social determinants of health and health disparities faced by dual eligible individuals, such as by providing access to housing support, food assistance, and transportation services.
Policymaker and Healthcare Provider Perspectives
Policymakers and healthcare providers have different perspectives on the dual eligibility program. Policymakers often focus on the financial and administrative aspects of the program, such as the cost of care and the complexity of the payment system. Healthcare providers, on the other hand, often focus on the clinical and quality aspects of care, such as the development of care plans and the coordination of services. However, both policymakers and healthcare providers agree on the importance of improving the dual eligibility program to better meet the needs of dual eligible individuals.
What is the dual eligibility program, and who is eligible?
+The dual eligibility program is a healthcare program that provides comprehensive benefits to individuals who are enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid. To be eligible, individuals must meet the eligibility requirements for both Medicare and Medicaid, which typically include being 65 or older, or having a disability, and having a low income.
What services are covered under the dual eligibility program?
+The dual eligibility program provides comprehensive benefits, including hospital care, physician services, prescription drugs, and long-term care. Medicaid also provides additional coverage for services such as dental care, vision care, and home health care.
What are some challenges and opportunities in dual eligible care?
+Some challenges in dual eligible care include the lack of coordination between Medicare and Medicaid, the complexity of the dual eligibility program, and the significant health disparities and social determinants of health faced by dual eligible individuals. Opportunities for improvement include the use of data analytics and care coordination, the development of specialized care models, and addressing the social determinants of health and health disparities faced by dual eligible individuals.
In conclusion, the dual eligibility program is a critical aspect of healthcare coverage for individuals who are enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid. Despite the challenges and complexities of the program, there are opportunities for improvement, such as the use of data analytics and care coordination, the development of specialized care models, and addressing the social determinants of health and health disparities faced by dual eligible individuals. By working together, policymakers, healthcare providers, and individuals can improve the dual eligibility program to better meet the needs of dual eligible individuals and provide them with high-quality, comprehensive care.