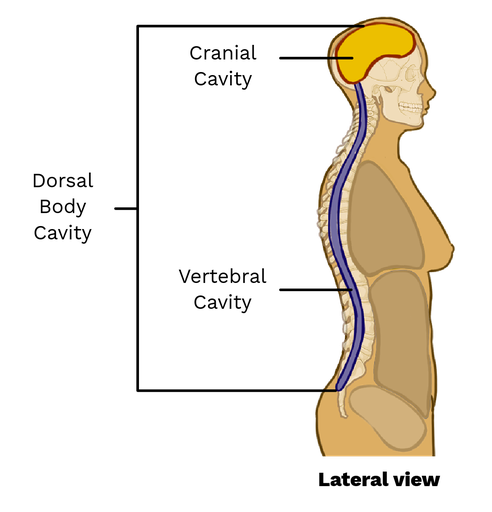
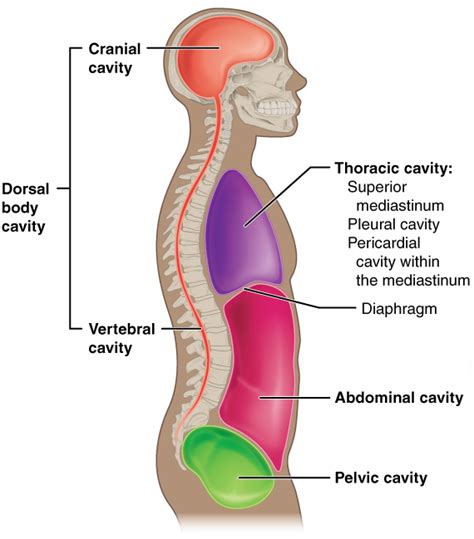
The dorsal body cavity, also known as the posterior body cavity, is a vital anatomical compartment that houses and protects several essential organs and structures within the human body. It is divided into two main sections: the cranial cavity, which encloses the brain, and the spinal cavity, also known as the vertebral canal, which contains the spinal cord. Understanding the dorsal body cavity is crucial for comprehending the complex interplay of bodily functions, from the transmission of nerve impulses to the protection of vital organs. In this article, we will delve into five key aspects of the dorsal body cavity, exploring its structure, function, and significance in human anatomy.
Key Points
- The dorsal body cavity is a protective space that encloses the brain and spinal cord.
- It is divided into the cranial cavity and the spinal cavity.
- The meninges, a protective membrane, surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
- Cerebrospinal fluid cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord.
- Understanding the dorsal body cavity is essential for diagnosing and treating neurological conditions.
Structure of the Dorsal Body Cavity
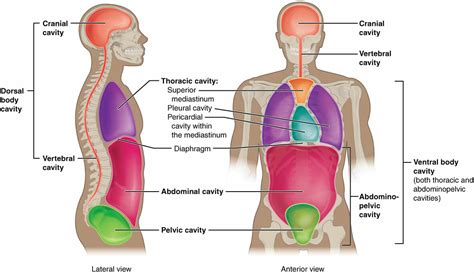
The dorsal body cavity is a complex anatomical structure that provides a safe environment for the brain and spinal cord. The cranial cavity, located within the skull, is a rigid compartment that encloses the brain, while the spinal cavity, extending from the base of the brain down to the lower back, contains the spinal cord. Both of these cavities are lined with a protective membrane known as the meninges, which consists of three layers: the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. The meninges play a crucial role in cushioning the brain and spinal cord, protecting them from mechanical injury and infection.
The Role of Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless fluid that circulates within the dorsal body cavity, surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Produced by the choroid plexus in the ventricles of the brain, CSF serves multiple functions, including cushioning the brain and spinal cord, supplying them with nutrients, and removing waste products. The circulation of CSF is vital for maintaining the health and function of the central nervous system. Any disruption in CSF circulation or composition can lead to serious neurological conditions, such as hydrocephalus or meningitis.
| Component of Dorsal Body Cavity | Function |
|---|---|
| Cranial Cavity | Encloses and protects the brain |
| Spinal Cavity | Contains and protects the spinal cord |
| Meninges | Protective membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | Cushions, nourishes, and removes waste from the brain and spinal cord |
Functions of the Dorsal Body Cavity
Beyond its protective role, the dorsal body cavity plays a critical part in facilitating the functions of the brain and spinal cord. The cranial cavity allows for the expansion and contraction of the brain during different states of activity and rest, while the spinal cavity provides a conduit for the spinal cord to transmit nerve impulses between the brain and the rest of the body. The dorsal body cavity also houses the cerebrospinal fluid, which, as mentioned, has multiple roles in maintaining the health of the central nervous system.
Clinical Significance of the Dorsal Body Cavity
The clinical significance of the dorsal body cavity cannot be overstated. Conditions affecting the dorsal body cavity, such as spinal cord injuries, meningitis, or hydrocephalus, can have profound impacts on an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the dorsal body cavity is essential for healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat these conditions effectively. Furthermore, advances in medical imaging and surgical techniques have improved outcomes for patients with conditions affecting the dorsal body cavity, highlighting the importance of continued research and innovation in this area.
What is the primary function of the meninges in the dorsal body cavity?
+The primary function of the meninges is to protect the brain and spinal cord from mechanical injury and infection, providing a cushioning effect and facilitating the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
How does cerebrospinal fluid contribute to the health of the central nervous system?
+Cerebrospinal fluid cushions and protects the brain and spinal cord, supplies them with nutrients, and removes waste products, playing a vital role in maintaining the health and function of the central nervous system.
What are some common conditions that affect the dorsal body cavity?
+Common conditions include spinal cord injuries, meningitis, hydrocephalus, and spinal tumors, each requiring prompt and appropriate medical intervention to prevent long-term neurological damage.
In conclusion, the dorsal body cavity is a complex and vital anatomical structure that plays a critical role in protecting and facilitating the functions of the brain and spinal cord. Its components, including the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid, work in harmony to maintain the health of the central nervous system. Understanding the dorsal body cavity is essential not only for healthcare professionals but also for anyone interested in human anatomy and the intricate mechanisms that underpin our bodily functions. By appreciating the importance of the dorsal body cavity, we can better understand the delicate balance of the human body and the need for careful preservation of its integrity.