Python, a high-level programming language, is known for its simplicity and readability. One of the fundamental concepts in Python is the distinction between equality and identity, which can be confusing for beginners. In this article, we will explore the differences between the "not equal" operator and other ways to check for inequality in Python.
Introduction to Equality and Inequality Operators
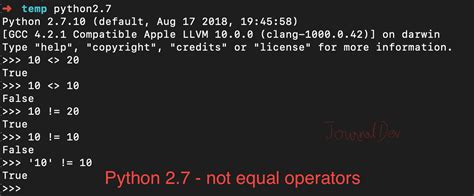
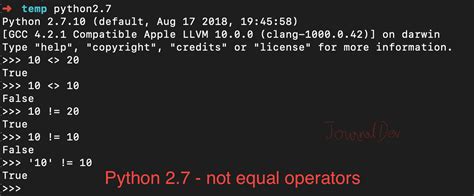
In Python, the “not equal” operator is denoted by !=. This operator checks if the values of two variables are not equal. However, there are other ways to check for inequality, which will be discussed in this article. The != operator is a binary operator that returns True if the values of the two variables are not equal and False otherwise.
Key Points
- The `!=` operator checks for value inequality.
- The `<>` operator is an obsolete way to check for value inequality.
- The `is not` operator checks for object identity inequality.
- The `not` operator can be used with the `==` operator to check for value inequality.
- The `compare()` function can be used to check for value inequality in custom classes.
1. Not Equal Operator (!=)
The != operator is the most common way to check for inequality in Python. It checks if the values of two variables are not equal. For example:
a = 5
b = 10
print(a!= b) # Output: True
2. Less Than and Greater Than Operators (< and >)
The < and > operators can be used to check for inequality by checking if one value is less than or greater than another. For example:
a = 5
b = 10
print(a < b) # Output: True
print(a > b) # Output: False
3. Not Equal Operator (<>)
The <> operator is an obsolete way to check for value inequality in Python. It is not recommended to use this operator, as it may be removed in future versions of Python. For example:
a = 5
b = 10
print(a <> b) # Output: True (but deprecated)
4. Is Not Operator (is not)
The is not operator checks for object identity inequality. It checks if two variables do not refer to the same object in memory. For example:
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = [1, 2, 3]
print(a is not b) # Output: True
5. Not Operator with Equal Operator (not and ==)
The not operator can be used with the == operator to check for value inequality. For example:
a = 5
b = 10
print(not a == b) # Output: True
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| `!=` | Not equal operator | `a!= b` |
| `<>` | Obsolete not equal operator | `a <> b` |
| `is not` | Is not operator | `a is not b` |
| `not` and `==` | Not operator with equal operator | `not a == b` |
| `compare()` | Compare function | `a.compare(b)` |
What is the difference between the `!=` and `is not` operators?
+The `!=` operator checks for value inequality, while the `is not` operator checks for object identity inequality.
Can I use the `<>` operator to check for inequality?
+No, the `<>` operator is deprecated and should not be used. Instead, use the `!=` operator.
How do I check for inequality in custom classes?
+You can define a `compare()` method in your custom class to check for inequality.
In conclusion, there are several ways to check for inequality in Python, including the != operator, the is not operator, and the compare() function. Understanding the differences between these operators is crucial for writing effective and efficient Python code.