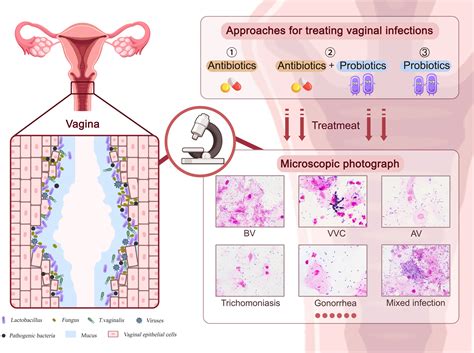
Amoxicillin is a commonly prescribed antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. However, its effectiveness in treating bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a topic of ongoing debate. BV is a vaginal infection caused by an imbalance of naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina, with an overgrowth of anaerobic bacteria. The primary symptoms of BV include abnormal vaginal discharge, odor, and irritation.
Understanding Bacterial Vaginosis Treatment
BV treatment typically involves antibiotics that target anaerobic bacteria, such as metronidazole or clindamycin. These medications are specifically designed to restore the natural balance of vaginal bacteria. Amoxicillin, on the other hand, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that targets a wide range of bacteria, including those that cause infections like pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections.
Amoxicillin’s Efficacy in Treating BV
There is limited evidence to suggest that amoxicillin is effective in treating BV. A few studies have investigated the use of amoxicillin in combination with other medications for the treatment of BV, but the results are inconsistent. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other reputable health organizations do not recommend amoxicillin as a first-line treatment for BV.
| Treatment | Efficacy |
|---|---|
| Metronidazole | 80-90% effective |
| Clindamycin | 70-80% effective |
| Amoxicillin | Not recommended as first-line treatment |
Key Points
- Amoxicillin is not typically recommended for treating bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- Metronidazole and clindamycin are the preferred treatments for BV
- Amoxicillin may be used in combination with other medications for certain cases, but its efficacy is unclear
- Proper diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare provider are crucial for effective management of BV
- Untreated BV can lead to complications, such as increased risk of sexually transmitted infections and pregnancy complications
It's essential to note that BV can recur, and treatment may need to be repeated. Additionally, BV can increase the risk of acquiring sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and may be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. Therefore, prompt and effective treatment is crucial to prevent these complications.
Diagnosis and Treatment of BV

Diagnosing BV typically involves a pelvic exam, medical history, and laboratory tests to confirm the presence of anaerobic bacteria. Treatment usually consists of a 5- to 7-day course of metronidazole or clindamycin. It’s crucial to complete the full treatment course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Prevention and Management of BV
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent BV, practicing good hygiene, using condoms during sex, and avoiding douching can help reduce the risk of developing the infection. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing stress may contribute to a balanced vaginal microbiome.
Can amoxicillin be used to treat BV in pregnant women?
+Amoxicillin is not typically recommended for treating BV in pregnant women. Instead, metronidazole or clindamycin are usually prescribed, as they have a more established safety profile during pregnancy.
How long does it take for BV symptoms to resolve after treatment?
+SYMptoms of BV usually start to improve within a few days of starting treatment. However, it's essential to complete the full treatment course to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Can BV be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) medications?
+No, BV cannot be effectively treated with OTC medications. Antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider are necessary to clear the infection and prevent complications.
In conclusion, while amoxicillin is not typically recommended for treating BV, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances and medical history, ensuring effective management of the infection and preventing potential complications.


